Abstract
The proton-translocating, plasma membrane ATPase was purified from tomato roots. At the final stage of purification approximately 80% of the protein was found in a single band with an apparent molecular weight of 90 kilodaltons. Cross-linking studies indicated that the ATPase normally exists as a trimer of catalytic subunits. No evidence was found for any additional subunits. The pH optimum for ATP hydrolysis by the purified protein was 6.5. Activity was stimulated by K+, especially at low pH, and inhibited by vanadate, N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, and diethylstilbestrol; nitrate was weakly inhibitory. Activity was stimulated by lysolecithin but inhibited by sonicated phospholipids. The inhibition by lipids could be prevented if octylglucoside was added with the lipids; the combination of octylglucoside and lipids actually stimulated activity. The purified protein could be reconstituted into liposomes and catalyzed ATP-dependent, vanadate-sensitive proton translocation.
Full text
PDF

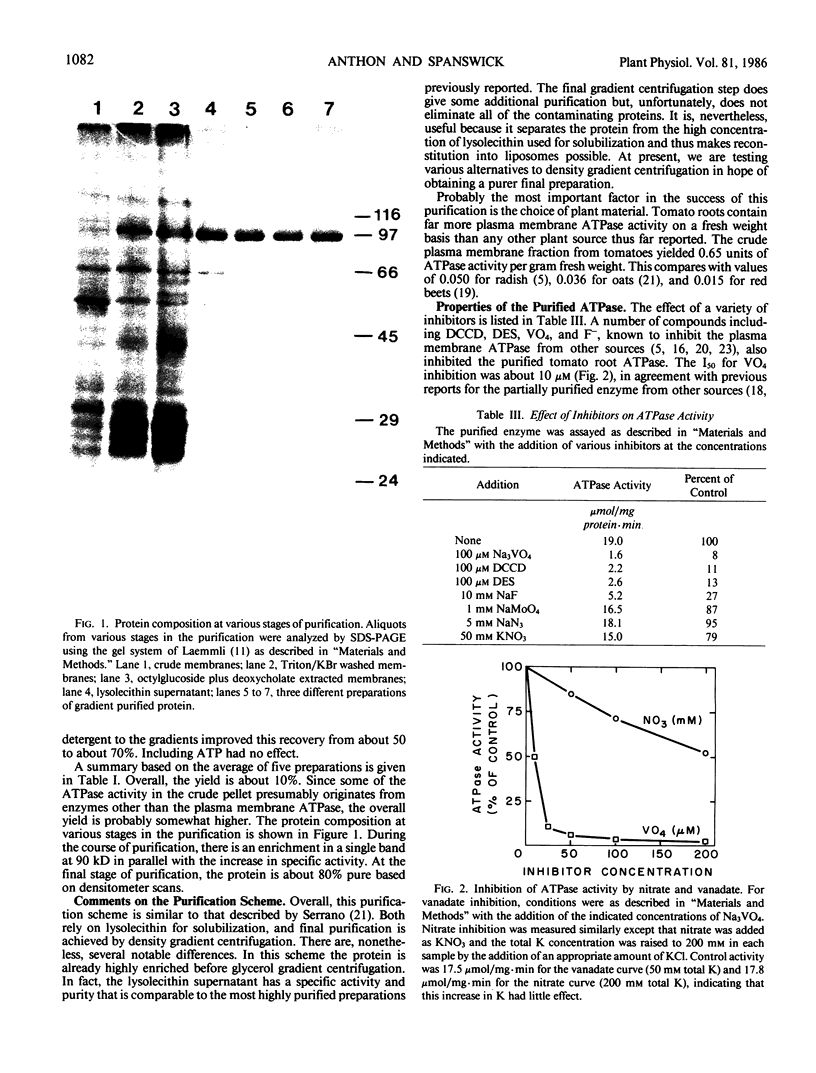
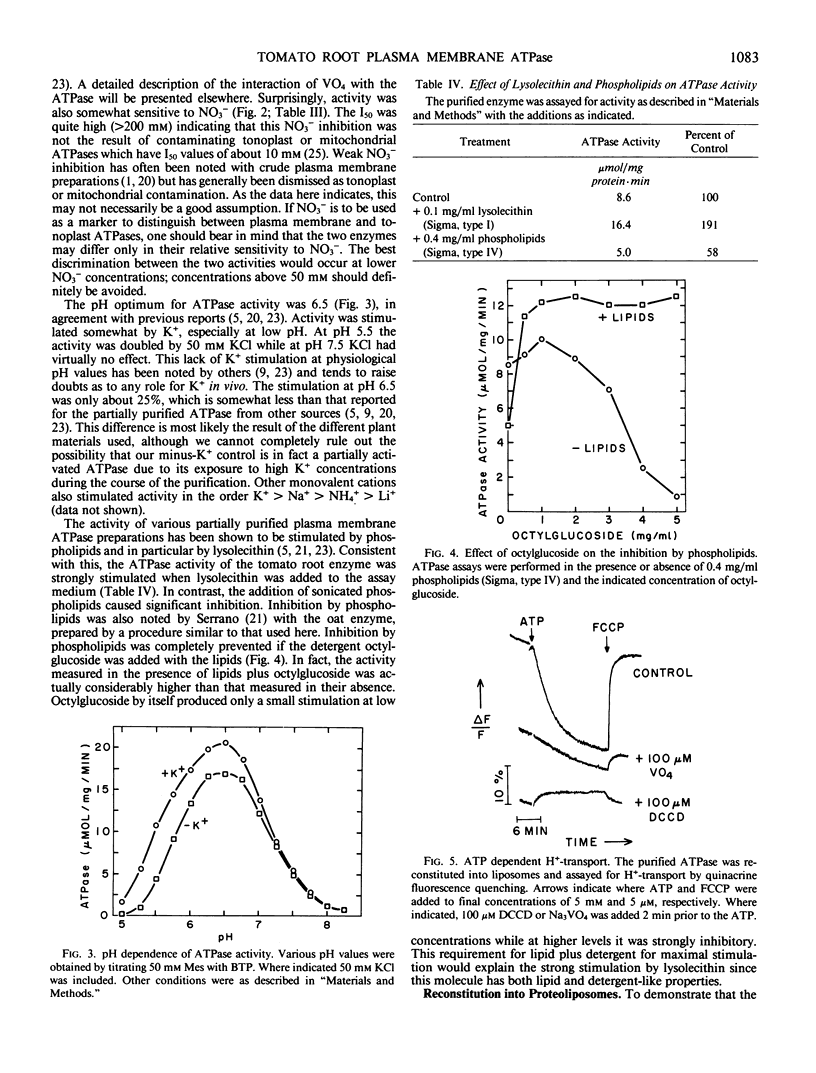

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett A. B., O'neill S. D., Spanswick R. M. H-ATPase Activity from Storage Tissue of Beta vulgaris: I. Identification and Characterization of an Anion-Sensitive H-ATPase. Plant Physiol. 1984 Mar;74(3):538–544. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.3.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briskin D. P., Thornley W. R., Roti-Roti J. L. Target molecular size of the red beet plasma membrane ATPase. Plant Physiol. 1985 Jul;78(3):642–644. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.3.642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig W. S. Determination of the distribution of sodium and potassium ion activated adenosinetriphosphatase among the various oligomers formed in solutions of nonionic detergents. Biochemistry. 1982 May 25;21(11):2667–2674. doi: 10.1021/bi00540a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies G. E., Stark G. R. Use of dimethyl suberimidate, a cross-linking reagent, in studying the subunit structure of oligomeric proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jul;66(3):651–656. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.3.651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Burke L. L., Spanswick R. M. Characterization of a partially purified adenosine triphosphatase from a corn root plasma membrane fraction. Plant Physiol. 1981 Jan;67(1):59–63. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann R., Jaenicke R., Rudolph R. Analysis of the reconstitution of oligomeric enzymes by cross-linking with glutaraldehyde: kinetics of reassociation of lactic dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1981 Sep 1;20(18):5195–5201. doi: 10.1021/bi00521a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbrie C. W., Murphy T. M. Solubilization and partial purification of ATPase from a rose cell plasma membrane fraction. Plant Physiol. 1984 Mar;74(3):611–616. doi: 10.1104/pp.74.3.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanzetta P. A., Alvarez L. J., Reinach P. S., Candia O. A. An improved assay for nanomole amounts of inorganic phosphate. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 15;100(1):95–97. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90115-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBel D., Poirier G. G., Beaudoin A. R. A convenient method for the ATPase assay. Anal Biochem. 1978 Mar;85(1):86–89. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90277-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew R. R., Spanswick R. M. Characterization of the Electrogenicity of Soybean (Glycine max L.) Roots : ATP Dependence and Effect of ATPase Inhibitors. Plant Physiol. 1984 May;75(1):1–6. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrè E., Ballarin-Denti A. The proton pumps of the plasmalemma and the tonoplast of higher plants. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1985 Feb;17(1):1–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00744985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'neill S. D., Spanswick R. M. Effects of vanadate on the plasma membrane ATPase of red beet and corn. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):586–591. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serrano R. Purification of the proton pumping ATPase from plant plasma membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jun 15;121(2):735–740. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90243-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vara F., Serrano R. Partial purification and properties of the proton-translocating ATPase of plant plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12826–12830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vara F., Serrano R. Phosphorylated intermediate of the ATPase of plant plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5334–5336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y., Sze H. Similarities and differences between the tonoplast-type and the mitochondrial H+-ATPases of oat roots. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10434–10443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]