Abstract
A salicylic acid (SA)-inducible uridine 5′-diphosphate (UDP)-glucose:SA 3-O-glucosyltransferase was extracted from oat (Avena sativa L. cv Dal) roots. Reverse phase high-performance liquid chromatography or anion exchange chromatography was used to separate SA from the product, β-O-d-glucosylsalicylic acid. The soluble enzyme was purified 176-fold with 5% recovery using a combination of pH fractionation, anion exchange, gel filtration, and chromatofocusing chromatography. The partially purified protein had a native molecular weight of about 50,000, an apparent isoelectric point at pH 5.0, and maximum activity at pH 5.5. The enzyme had a Km of 0.28 mm for UDP-glucose and was highly specific for this sugar donor. More than 20 hydroxybenzoic and hydroxycinnamic acid derivatives were assayed as potential glucose acceptors. UDP-glucose:SA 3-O-glucosyltransferase activity was highly specific toward SA (Km = 0.16 mm). The enzyme was inhibited by UDP and uridine 5′-triphosphate but not by up to 7.5 mm uridine 5′-monophosphate.
Full text
PDF

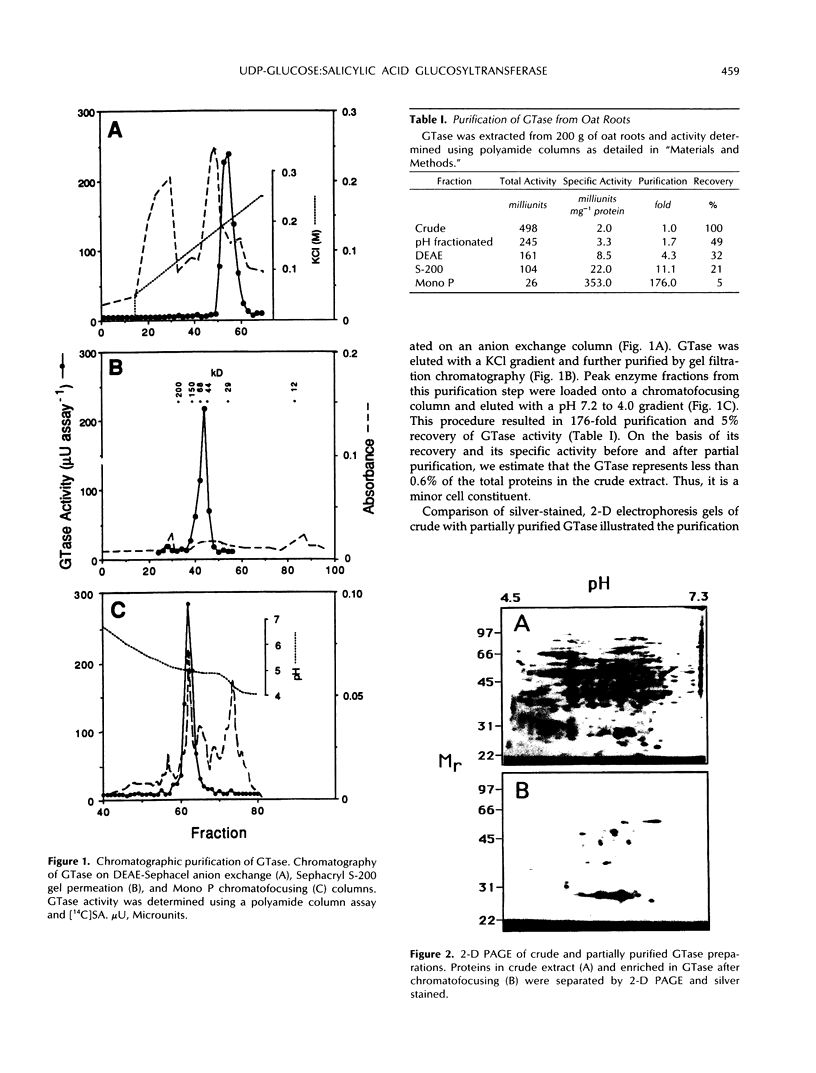

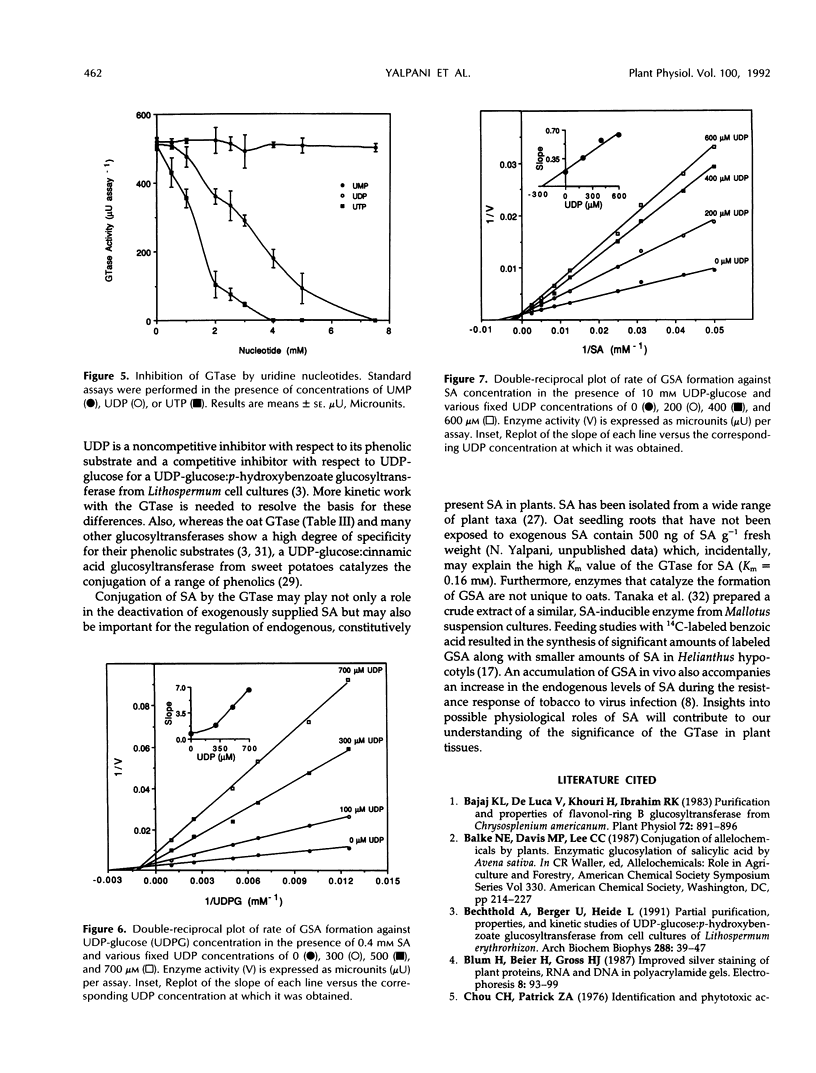

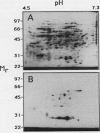
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bajaj K. L., de Luca V., Khouri H., Ibrahim R. K. Purification and Properties of Flavonol-Ring B Glucosyltransferase from Chrysosplenium americanum. Plant Physiol. 1983 Jul;72(3):891–896. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.3.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bechthold A., Berger U., Heide L. Partial purification, properties, and kinetic studies of UDP-glucose:p-hydroxybenzoate glucosyltransferase from cell cultures of Lithospermum erythrorhizon. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991 Jul;288(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(91)90162-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enyedi A. J., Yalpani N., Silverman P., Raskin I. Localization, conjugation, and function of salicylic acid in tobacco during the hypersensitive reaction to tobacco mosaic virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2480–2484. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass A. D. Influence of phenolic acids on ion uptake: I. Inhibition of phosphate uptake. Plant Physiol. 1973 Jun;51(6):1037–1041. doi: 10.1104/pp.51.6.1037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. R., Balke N. E. Characterization of the inhibition of k absorption in oat roots by salicylic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1981 Dec;68(6):1349–1353. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.6.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurkman W. J., Tanaka C. K. Solubilization of plant membrane proteins for analysis by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Plant Physiol. 1986 Jul;81(3):802–806. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.3.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie C. A., Romani R. J. Inhibition of ethylene biosynthesis by salicylic Acid. Plant Physiol. 1988 Nov;88(3):833–837. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.3.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malamy J., Carr J. P., Klessig D. F., Raskin I. Salicylic Acid: a likely endogenous signal in the resistance response of tobacco to viral infection. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):1002–1004. doi: 10.1126/science.250.4983.1002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Métraux J. P., Signer H., Ryals J., Ward E., Wyss-Benz M., Gaudin J., Raschdorf K., Schmid E., Blum W., Inverardi B. Increase in salicylic Acid at the onset of systemic acquired resistance in cucumber. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):1004–1006. doi: 10.1126/science.250.4983.1004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raskin I., Ehmann A., Melander W. R., Meeuse B. J. Salicylic Acid: a natural inducer of heat production in arum lilies. Science. 1987 Sep 25;237(4822):1601–1602. doi: 10.1126/science.237.4822.1601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu T., Kojima M. Partial purification and characterization of UDPG:t-cinnamate glucosyltransferase in the root of sweet potato, Ipomoea batatas Lam. J Biochem. 1984 Jan;95(1):205–212. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stitt M., Wirtz W., Heldt H. W. Metabolite levels during induction in the chloroplast and extrachloroplast compartments of spinach protoplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Nov 5;593(1):85–102. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(80)90010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun Y., Hrazdina G. Isolation and Characterization of a UDPGlucose: Flavonol O-Glucosyltransferase from Illuminated Red Cabbage (Brassica oleracea cv Red Danish) Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1991 Feb;95(2):570–576. doi: 10.1104/pp.95.2.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalpani N., Silverman P., Wilson T. M., Kleier D. A., Raskin I. Salicylic acid is a systemic signal and an inducer of pathogenesis-related proteins in virus-infected tobacco. Plant Cell. 1991 Aug;3(8):809–818. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.8.809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]