Abstract
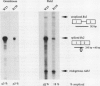
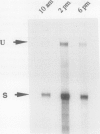
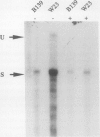
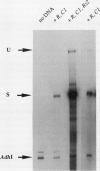
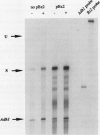
A large fraction of the transcripts of the Bronze-2 (Bz2) gene of maize (Zea mays L.) are unspliced in purple husk tissues. The accumulation of unspliced messages could have destructive potential if the intron-bearing mRNAs are translated into aberrant proteins. Our initial studies suggested that both genetic and physiological factors may influence the degree of splicing failure. Nuclear background rather than cis-sequence effects is shown to contribute to the genetic component. The accumulation of unspliced message does not appear to be directly influenced by diurnal effects on transcript abundance, by the expression level of the Bz2 gene, or by thermal stress. We also show that maize cell cultures (Black Mexican Sweet, BMS) can be used to examine the molecular details involved in splicing failure. Much like whole maize plants, the BMS cells excise the Bz2 intron with varying degrees of efficiency. In contrast with heterologous constructs containing plant introns, splicing of the native Bz2 intron can appproach 100% in BMS cells. Splicing of transcripts from a marked, introduced gene can be compared to the endogeneous Bz2 gene facilitating analysis of the impact of sequence changes.
Full text
PDF
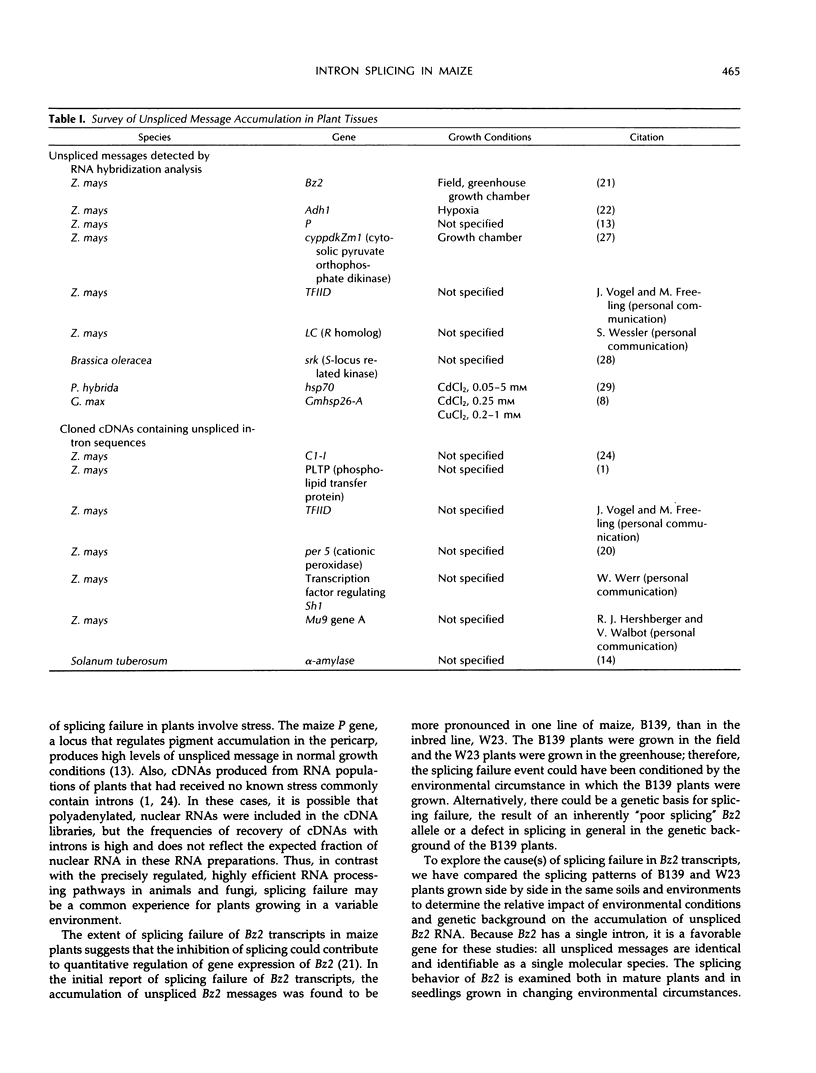


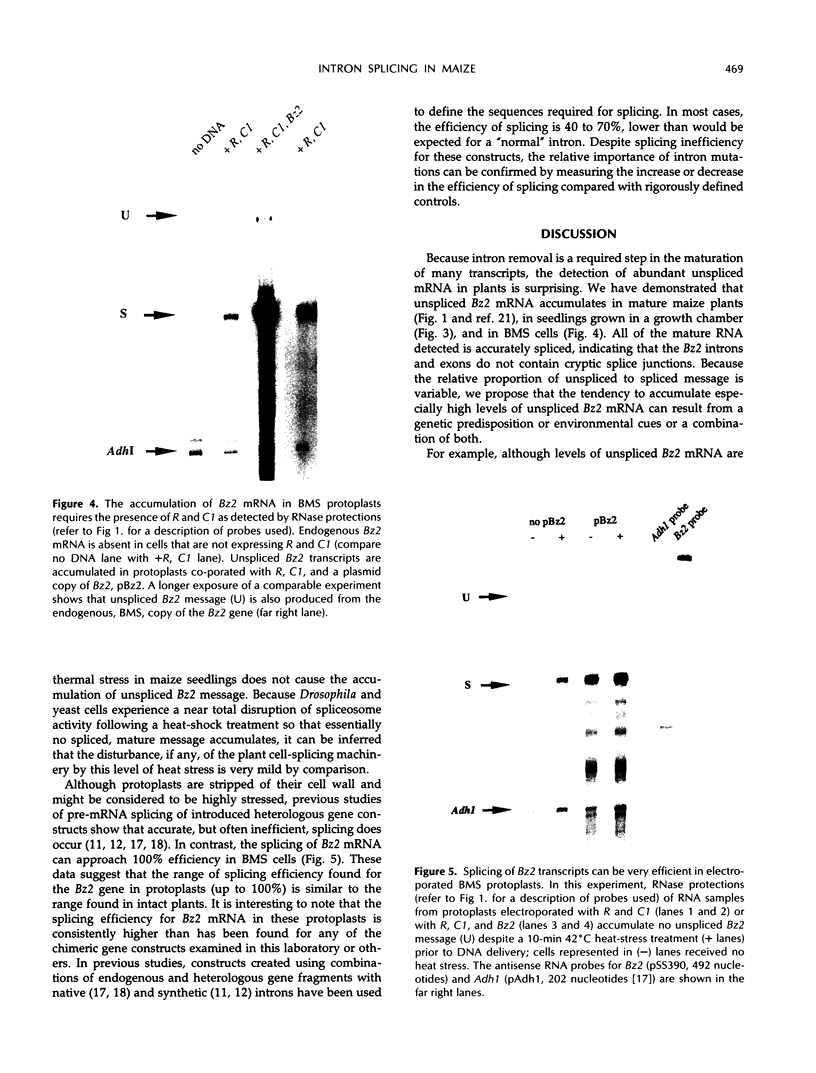

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arondel V., Tchang F., Baillet B., Vignols F., Grellet F., Delseny M., Kader J. C., Puigdomènech P. Multiple mRNA coding for phospholipid-transfer protein from Zea mays arise from alternative splicing. Gene. 1991 Mar 1;99(1):133–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90045-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodeau J. P., Walbot V. Regulated transcription of the maize Bronze-2 promoter in electroporated protoplasts requires the C1 and R gene products. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jun;233(3):379–387. doi: 10.1007/BF00265434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W. A catalogue of splice junction and putative branch point sequences from plant introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 22;14(24):9549–9559. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.24.9549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burtis K. C., Baker B. S. Drosophila doublesex gene controls somatic sexual differentiation by producing alternatively spliced mRNAs encoding related sex-specific polypeptides. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):997–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90633-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callis J., Fromm M., Walbot V. Heat Inducible Expression of a Chimeric Maize hsp70CAT Gene in Maize Protoplasts. Plant Physiol. 1988 Dec;88(4):965–968. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P., Ho T. H. Heat shock proteins in maize. Plant Physiol. 1983 Feb;71(2):215–222. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.2.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Regulatory pathways governing HIV-1 replication. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90420-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
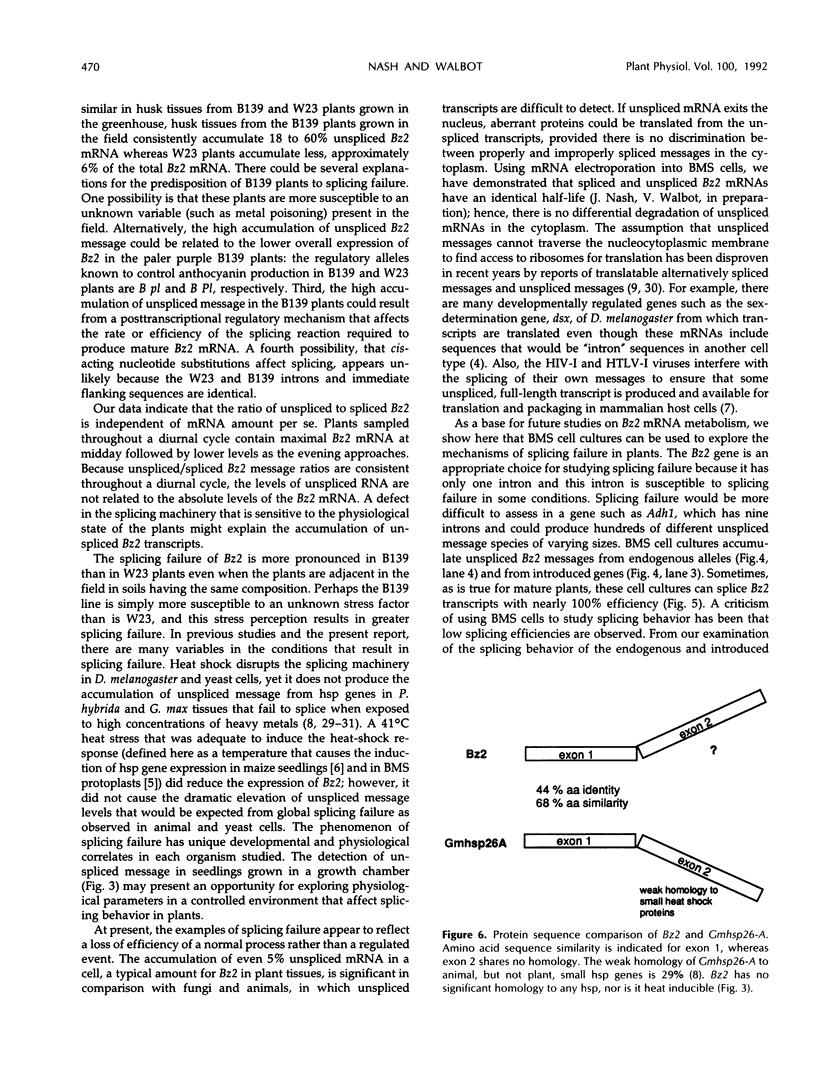
- Czarnecka E., Nagao R. T., Key J. L., Gurley W. B. Characterization of Gmhsp26-A, a stress gene encoding a divergent heat shock protein of soybean: heavy-metal-induced inhibition of intron processing. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1113–1122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey M., Reinecke J., Grant S., Saedler H., Gierl A. Excision of the En/Spm transposable element of Zea mays requires two element-encoded proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):4037–4044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07625.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall G. J., Filipowicz W. Different effects of intron nucleotide composition and secondary structure on pre-mRNA splicing in monocot and dicot plants. EMBO J. 1991 Sep;10(9):2635–2644. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07806.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodall G. J., Filipowicz W. The minimum functional length of pre-mRNA introns in monocots and dicots. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 May;14(5):727–733. doi: 10.1007/BF00016505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotewold E., Athma P., Peterson T. Alternatively spliced products of the maize P gene encode proteins with homology to the DNA-binding domain of myb-like transcription factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4587–4591. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Complex transcriptional units: diversity in gene expression by alternative RNA processing. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1091–1117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logemann J., Schell J., Willmitzer L. Improved method for the isolation of RNA from plant tissues. Anal Biochem. 1987 May 15;163(1):16–20. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90086-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luehrsen K. R., Walbot V. Insertion of Mu1 elements in the first intron of the Adh1-S gene of maize results in novel RNA processing events. Plant Cell. 1990 Dec;2(12):1225–1238. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.12.1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luehrsen K. R., Walbot V. Intron enhancement of gene expression and the splicing efficiency of introns in maize cells. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jan;225(1):81–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00282645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin M., Walbot V. Cloning of a mutable bz2 allele of maize by transposon tagging and differential hybridization. Genetics. 1987 Dec;117(4):771–776. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.4.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash J., Luehrsen K. R., Walbot V. Bronze-2 gene of maize: reconstruction of a wild-type allele and analysis of transcription and splicing. Plant Cell. 1990 Nov;2(11):1039–1049. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.11.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz D. F., Strommer J. N. The Mu1 maize transposable element induces tissue-specific aberrant splicing and polyadenylation in two Adh1 mutants. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2090–2095. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paz-Ares J., Ghosal D., Saedler H. Molecular analysis of the C1-I allele from Zea mays: a dominant mutant of the regulatory C1 locus. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):315–321. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08113.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochester D. E., Winer J. A., Shah D. M. The structure and expression of maize genes encoding the major heat shock protein, hsp70. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):451–458. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04233.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheen J. Molecular mechanisms underlying the differential expression of maize pyruvate, orthophosphate dikinase genes. Plant Cell. 1991 Mar;3(3):225–245. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.3.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. C., Howlett B., Boyes D. C., Nasrallah M. E., Nasrallah J. B. Molecular cloning of a putative receptor protein kinase gene encoded at the self-incompatibility locus of Brassica oleracea. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8816–8820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost H. J., Lindquist S. Heat shock proteins affect RNA processing during the heat shock response of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;11(2):1062–1068. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.2.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost H. J., Lindquist S. Translation of unspliced transcripts after heat shock. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1544–1548. doi: 10.1126/science.3201243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yost H. J., Petersen R. B., Lindquist S. RNA metabolism: strategies for regulation in the heat shock response. Trends Genet. 1990 Jul;6(7):223–227. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90183-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]