Abstract
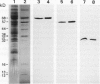
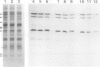
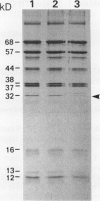
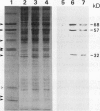
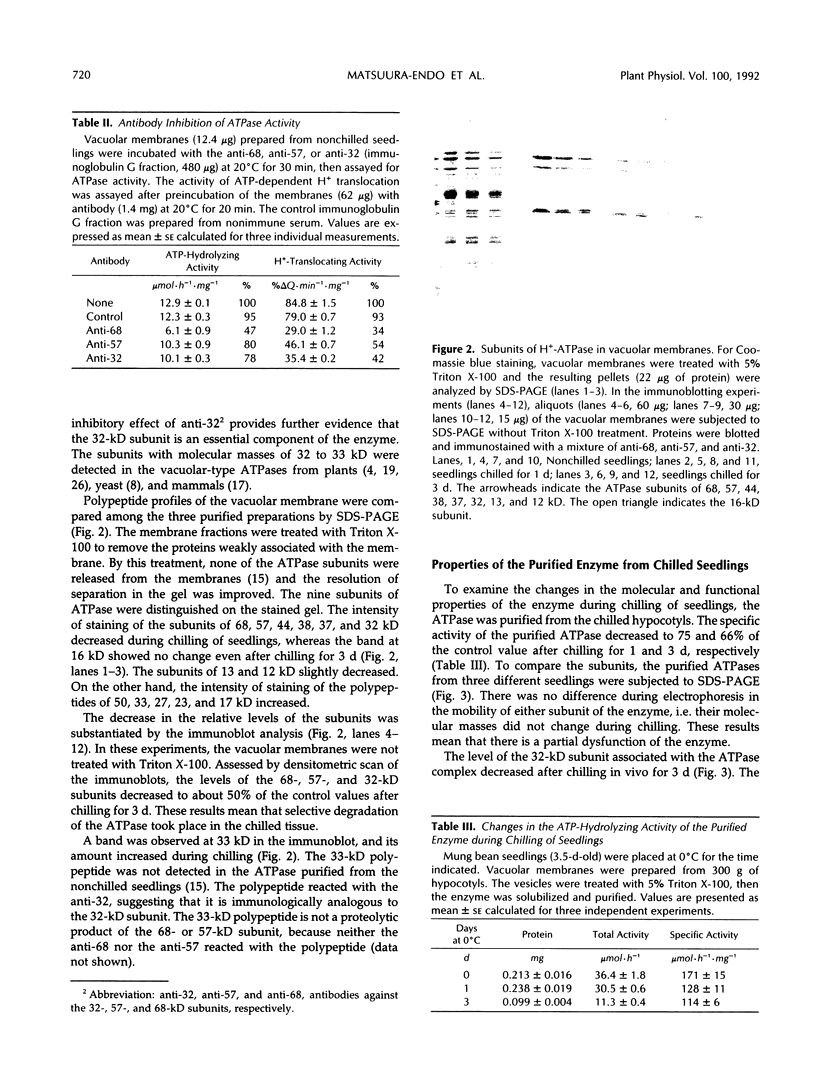
The mechanism responsible for the decrease in the activity of vacuolar H+ -ATPase during chilling was investigated in seedlings of mung bean (Vigna radiata). After chilling at 0°C for 3 d, the activity of vacuolar H+ -ATPase, calculated on the basis of membrane protein, decreased to 47% of the original value. Of the nine subunits of the ATPase, the specific contents of at least six subunits, of 68, 57, 44, 38, 37, and 32 kD, decreased in vacuolar membranes after chilling, as judged by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. These subunits were released by treatment with chaotropic anions such as thiocyanate. The level of the 16-kD subunit did not change. Immunoblot analyses showed the decrease in the levels of the subunits of 68, 57, and 32 kD. Furthermore, the specific activity of the ATPase purified from chilled hypocotyls was two-thirds of that of the enzyme from nonchilled seedlings, and the enzyme from chilled tissue retained only a small amount of the 32-kD subunit. These results suggest that a selective release of the peripheral subunits of the ATPase from the membrane and a partial degradation of the ATPase complex may occur in vivo during chilling.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi I., Puopolo K., Marquez-Sterling N., Arai H., Forgac M. Dissociation, cross-linking, and glycosylation of the coated vesicle proton pump. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 15;265(2):967–973. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman B. J., Dschida W. J., Harris T., Bowman E. J. The vacuolar ATPase of Neurospora crassa contains an F1-like structure. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 15;264(26):15606–15612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gogarten J. P., Kibak H., Dittrich P., Taiz L., Bowman E. J., Bowman B. J., Manolson M. F., Poole R. J., Date T., Oshima T. Evolution of the vacuolar H+-ATPase: implications for the origin of eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6661–6665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrich R., Kurkdjian A., Guern J., Flügge U. I. Comparative studies on the electrical properties of the H+ translocating ATPase and pyrophosphatase of the vacuolar-lysosomal compartment. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2835–2841. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08430.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane P. M., Yamashiro C. T., Stevens T. H. Biochemical characterization of the yeast vacuolar H(+)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 15;264(32):19236–19244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai S. P., Randall S. K., Sze H. Peripheral and integral subunits of the tonoplast H+-ATPase from oat roots. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16731–16737. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandala S., Taiz L. Characterization of the subunit structure of the maize tonoplast ATPase. Immunological and inhibitor binding studies. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12850–12855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manolson M. F., Rea P. A., Poole R. J. Identification of 3-O-(4-benzoyl)benzoyladenosine 5'-triphosphate- and N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-binding subunits of a higher plant H+-translocating tonoplast ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12273–12279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura-Endo C., Maeshima M., Yoshida S. Subunit composition of vacuolar membrane H(+)-ATPase from mung bean. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Feb 14;187(3):745–751. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15362.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama Y., Nelson N. Cold inactivation of vacuolar proton-ATPases. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3577–3582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N. Structure, molecular genetics, and evolution of vacuolar H+-ATPases. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1989 Oct;21(5):553–571. doi: 10.1007/BF00808113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N., Taiz L. The evolution of H+-ATPases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Mar;14(3):113–116. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry R. V., Turner J. C., Rea P. A. High purity preparations of higher plant vacuolar H+-ATPase reveal additional subunits. Revised subunit composition. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):20025–20032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall S. K., Sze H. Properties of the partially purified tonoplast H+-pumping ATPase from oat roots. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 25;261(3):1364–1371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida E., Ohsumi Y., Anraku Y. Purification and properties of H+-translocating, Mg2+-adenosine triphosphatase from vacuolar membranes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1090–1095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida S., Matsuura C., Etani S. Impairment of Tonoplast H-ATPase as an Initial Physiological Response of Cells to Chilling in Mung Bean (Vigna radiata [L.] Wilczek). Plant Physiol. 1989 Feb;89(2):634–642. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.2.634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]