Abstract
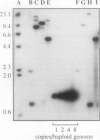
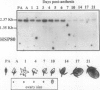
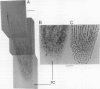
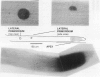
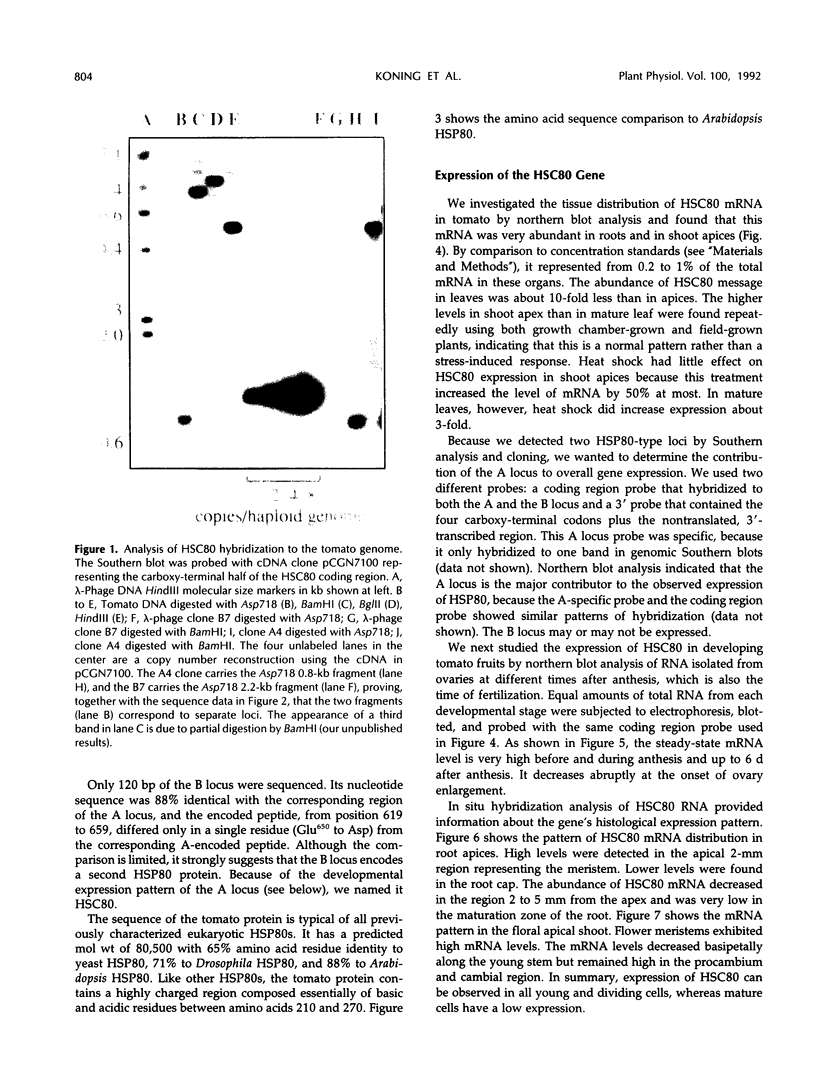
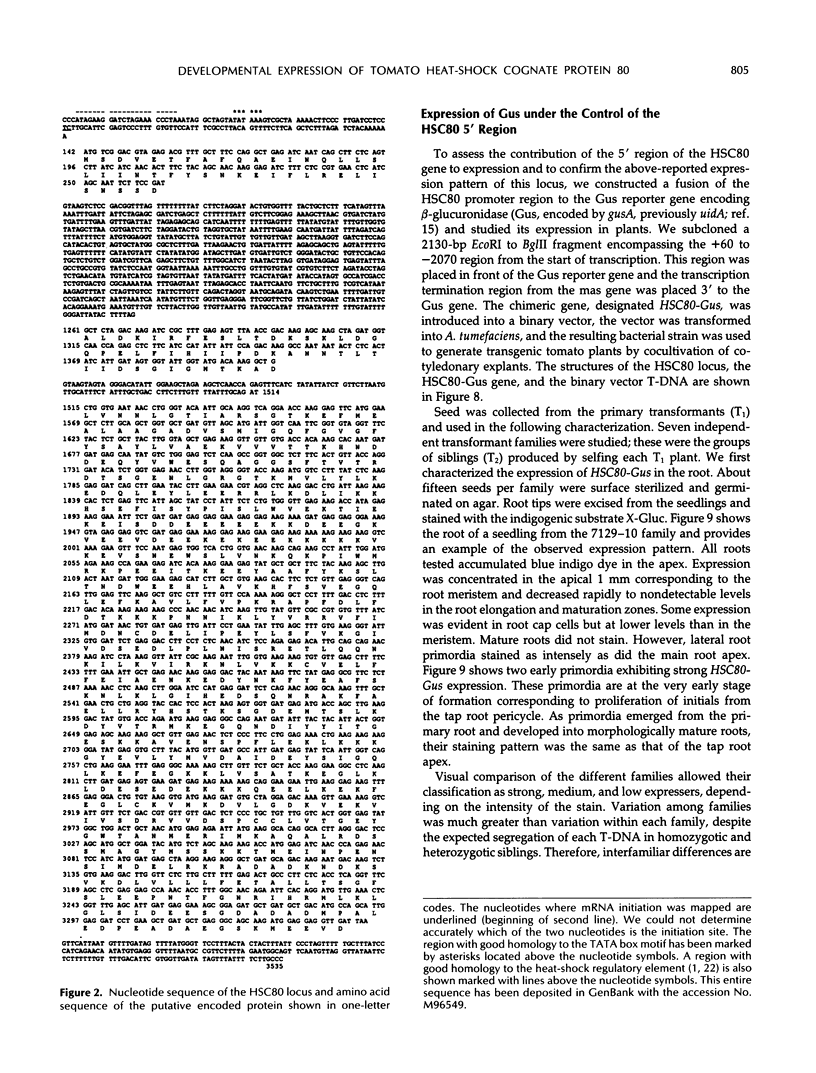
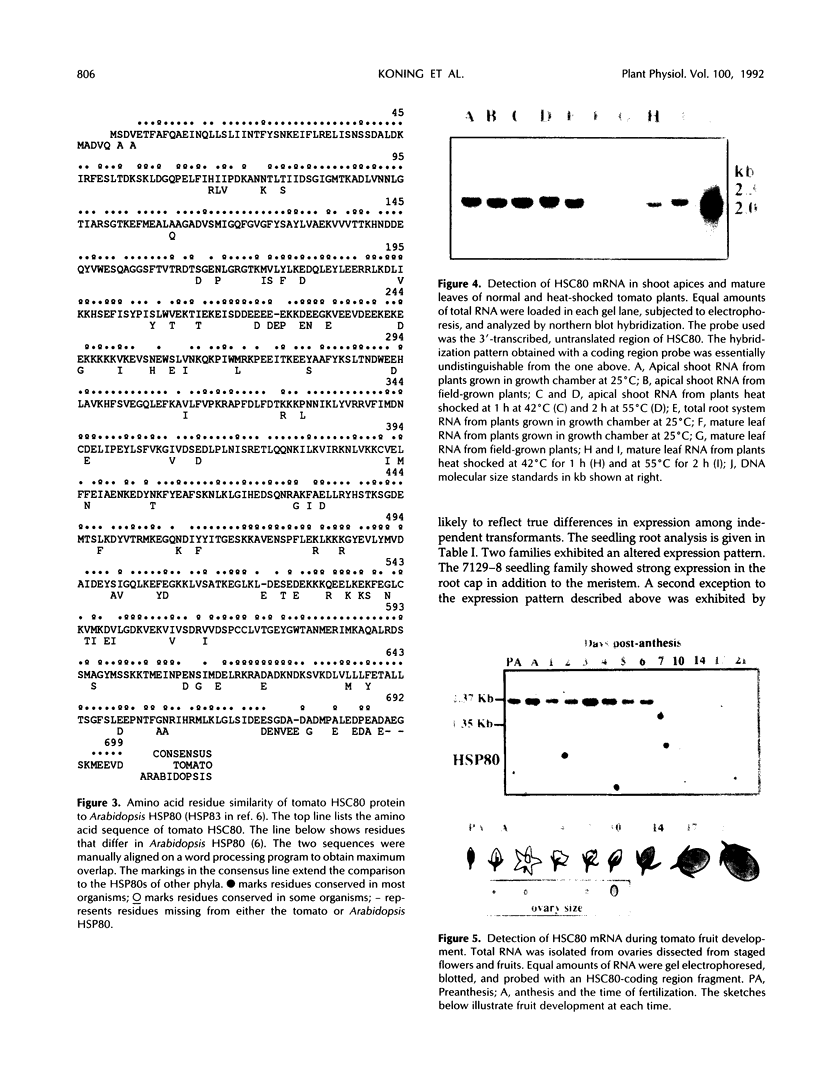
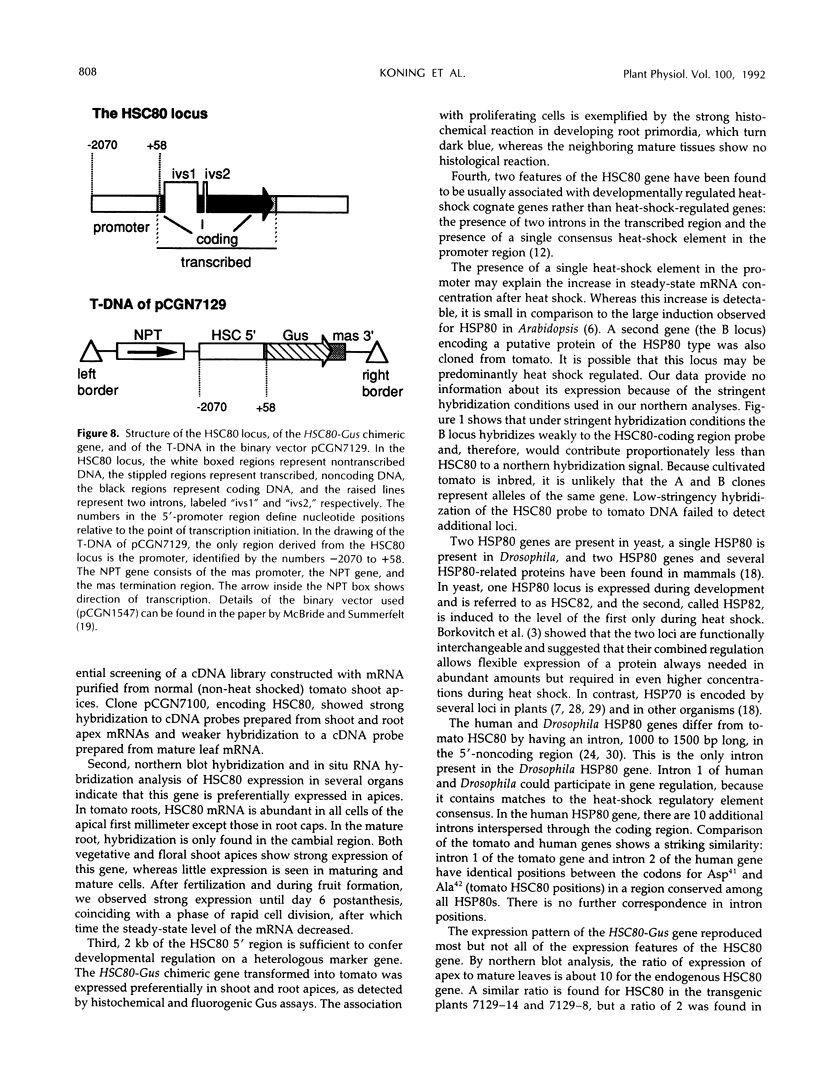
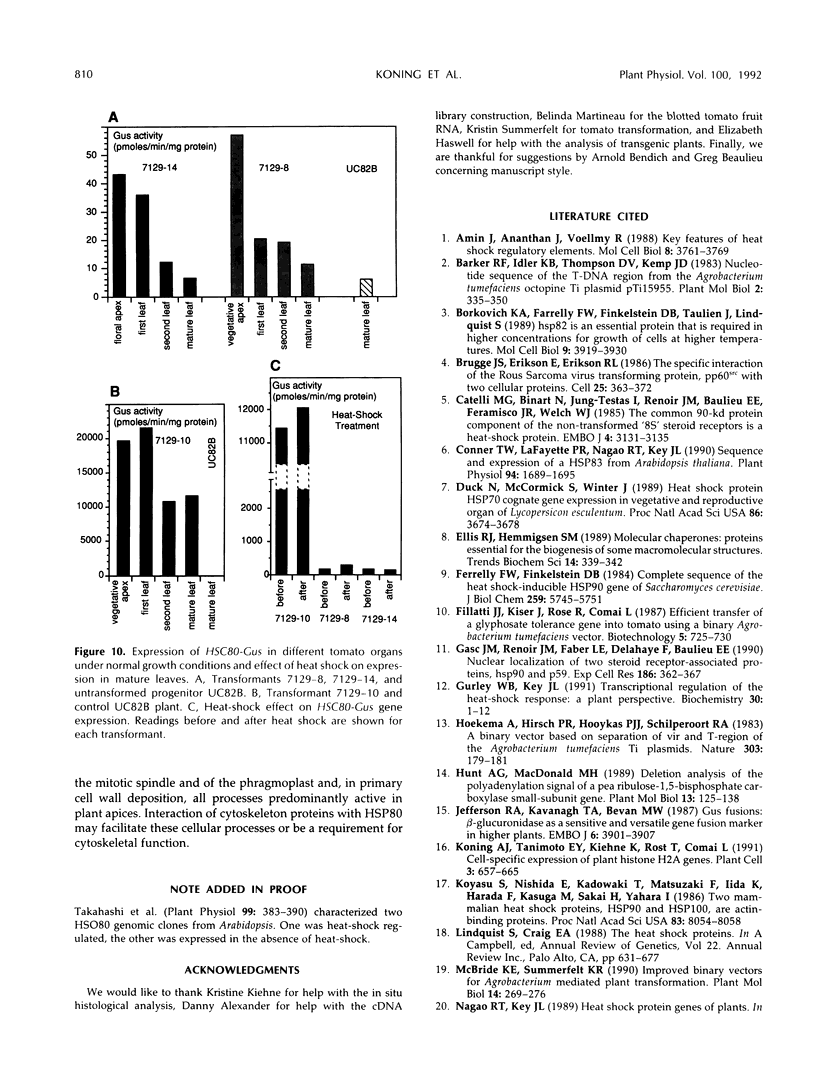
Heat-shock protein 80 (HSP80) is a major heat-shock protein induced in yeast and animals both by heat shock and by specific developmental events. In plants, a heat-shock-induced HSP80 cDNA has been described, although no information concerning developmental regulation of HSP80 genes is available. We have characterized a tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) gene encoding a typical HSP80 protein. This gene, called HSC80, is interrupted by two introns, 995 and 109 bp long. Northern blot analyses and in situ RNA hybridization show that HSC80 mRNA is abundant in shoot and root apices and in fertilized ovaries up to 6 d postanthesis but is rare in mature leaves. Heat shock increased mRNA levels in mature leaves but only 3-fold. Developmental regulation of the HSC80 gene was confirmed by fusing 2 kb of its 5′ region to the β-glucuronidase reporter gene and introducing the chimeric gene into tomatoes. The roots of transformants showed high β-glucuronidase expression in the apex and in lateral root primordia but not in mature tissue. Expression in the shoot was up to 10-fold higher in the apex than in mature leaves. Thus, HSC80 is preferentially expressed in shoot and root apices during normal development.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amin J., Ananthan J., Voellmy R. Key features of heat shock regulatory elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3761–3769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkovich K. A., Farrelly F. W., Finkelstein D. B., Taulien J., Lindquist S. hsp82 is an essential protein that is required in higher concentrations for growth of cells at higher temperatures. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3919–3930. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. The specific interaction of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, pp60src, with two cellular proteins. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):363–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catelli M. G., Binart N., Jung-Testas I., Renoir J. M., Baulieu E. E., Feramisco J. R., Welch W. J. The common 90-kd protein component of non-transformed '8S' steroid receptors is a heat-shock protein. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3131–3135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04055.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conner T. W., Lafayette P. R., Nagao R. T., Key J. L. Sequence and Expression of a HSP83 from Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 1990 Dec;94(4):1689–1695. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.4.1689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duck N., McCormick S., Winter J. Heat shock protein hsp70 cognate gene expression in vegetative and reproductive organs of Lycopersicon esculentum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3674–3678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. J., Hemmingsen S. M. Molecular chaperones: proteins essential for the biogenesis of some macromolecular structures. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Aug;14(8):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90168-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrelly F. W., Finkelstein D. B. Complete sequence of the heat shock-inducible HSP90 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5745–5751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasc J. M., Renoir J. M., Faber L. E., Delahaye F., Baulieu E. E. Nuclear localization of two steroid receptor-associated proteins, hsp90 and p59. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Feb;186(2):362–367. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90317-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurley W. B., Key J. L. Transcriptional regulation of the heat-shock response: a plant perspective. Biochemistry. 1991 Jan 8;30(1):1–12. doi: 10.1021/bi00215a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt A. G., MacDonald M. H. Deletion analysis of the polyadenylation signal of a pea ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small-subunit gene. Plant Mol Biol. 1989 Aug;13(2):125–138. doi: 10.1007/BF00016132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson R. A., Kavanagh T. A., Bevan M. W. GUS fusions: beta-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):3901–3907. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02730.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koning A. J., Tanimoto E. Y., Kiehne K., Rost T., Comai L. Cell-specific expression of plant histone H2A genes. Plant Cell. 1991 Jul;3(7):657–665. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.7.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyasu S., Nishida E., Kadowaki T., Matsuzaki F., Iida K., Harada F., Kasuga M., Sakai H., Yahara I. Two mammalian heat shock proteins, HSP90 and HSP100, are actin-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8054–8058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride K. E., Summerfelt K. R. Improved binary vectors for Agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Feb;14(2):269–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00018567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nover L., Scharf K. D. Synthesis, modification and structural binding of heat-shock proteins in tomato cell cultures. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Mar 1;139(2):303–313. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08008.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. A regulatory upstream promoter element in the Drosophila hsp 70 heat-shock gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):517–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Khursheed B., Garabedian M. J., Fortin M. G., Lindquist S., Yamamoto K. R. Reduced levels of hsp90 compromise steroid receptor action in vivo. Nature. 1990 Nov 8;348(6297):166–168. doi: 10.1038/348166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebbe N. F., Hickman W. S., Ley T. J., Stafford D. W., Hickman S. Nucleotide sequence and regulation of a human 90-kDa heat shock protein gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):15006–15011. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez E. R., Redmond T., Scherrer L. C., Bresnick E. H., Welsh M. J., Pratt W. B. Evidence that the 90-kilodalton heat shock protein is associated with tubulin-containing complexes in L cell cytosol and in intact PtK cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Aug;2(8):756–760. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-8-756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. H., Caspar T., Browse J., Lindquist S., Somerville C. Characterization of an HSP70 Cognate Gene Family in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 1988 Nov;88(3):731–740. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.3.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao H., Lis J. T. Heat shock and developmental regulation of the Drosophila melanogaster hsp83 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1746–1753. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]