Abstract
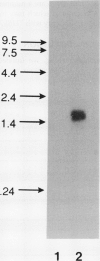
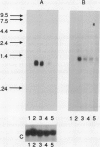
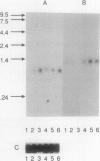
cDNA clones of two genes, TUBS19 and TUBL7, which show a 15- to 20-fold increase in transcript level in the stolon tip during the early stages of tuberization, have been isolated by differential screening. These genes are also expressed in leaves, stems, and roots, and the expression pattern in these organs changes on tuberization. Southern analysis shows that there are similar sequences in the genome of nontuberizing wild-type potato species Solanum brevidens and in Lycopersicon esculentum (tomato). Sequence analysis reveals a high degree of similarity between the TUBS19 cDNA and the eukaryotic S19 ribosomal protein gene. TUBL7 cDNA shows similarity to another eukaryotic ribosomal protein gene, L7.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amaldi F., Beccari E., Bozzoni I., Luo Z. X., Pierandrei-Amaldi P. Nucleotide sequences of cloned cDNA fragments specific for six Xenopus laevis ribosomal proteins. Gene. 1982 Mar;17(3):311–316. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90147-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisanz-Seyer C., Mache R. Organization and expression of the nuclear gene coding for the plastid-specific S22 ribosomal protein from spinach. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Jan;18(2):337–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00034960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L., Paz V., Olvera J., Wool I. G. The primary structure of rat ribosomal protein S24. FEBS Lett. 1990 Mar 26;262(2):253–255. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80203-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantt J. S., Thompson M. D. Plant cytosolic ribosomal protein S11 and chloroplast ribosomal protein CS17. Their primary structures and evolutionary relationships. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2763–2767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond M. L., Bowman L. H. Insulin stimulates the translation of ribosomal proteins and the transcription of rDNA in mouse myoblasts. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17785–17791. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hariharan N., Kelley D. E., Perry R. P. Equipotent mouse ribosomal protein promoters have a similar architecture that includes internal sequence elements. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1789–1800. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1789. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendriks T., Vreugdenhil D., Stiekema W. J. Patatin and four serine proteinase inhibitor genes are differentially expressed during potato tuber development. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Sep;17(3):385–394. doi: 10.1007/BF00040633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y., Zhang H., Scholl R. L. Two evolutionarily divergent genes encode a cytoplasmic ribosomal protein of Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene. 1990 Sep 14;93(2):177–182. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90222-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkin J. C., Hunsperger J. P., Culley D., Rubenstein I., Silflow C. D. The organization and expression of a maize ribosomal protein gene family. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):500–509. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebrun M., Freyssinet G. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of a maize cytoplasmic ribosomal protein S11 cDNA. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Aug;17(2):265–268. doi: 10.1007/BF00039502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A., Chan Y. L., McNally J., Peleg D., Meyuhas O., Wool I. G. The primary structure of rat ribosomal protein L7. The presence near the amino terminus of L7 of five tandem repeats of a sequence of 12 amino acids. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12665–12671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. Localization of surface peptide from ribosomal protein L7 on 80 S ribosome by biotinylation. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 5;287(1-2):121–124. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutsch G., Stahl J., Kärgel H. J., Noll F., Bielka H. Immunoelectron microscopic studies on the location of ribosomal proteins on the surface of the 40S ribosomal subunit from rat liver. Eur J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;51(1):140–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin C., Prescott A., Mackay S., Bartlett J., Vrijlandt E. Control of anthocyanin biosynthesis in flowers of Antirrhinum majus. Plant J. 1991 Jul;1(1):37–49. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313x.1991.00037.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyuhas O., Klein A. The mouse ribosomal protein L7 gene. Its primary structure and functional analysis of the promoter region. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11465–11473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolan D. R., Hershey J. W., Traut R. T. Crosslinking of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF3 to the 40S ribosomal subunit from rabbit reticulocytes. Biochimie. 1983 Jul;65(7):427–436. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(83)80062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]