Abstract
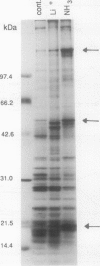
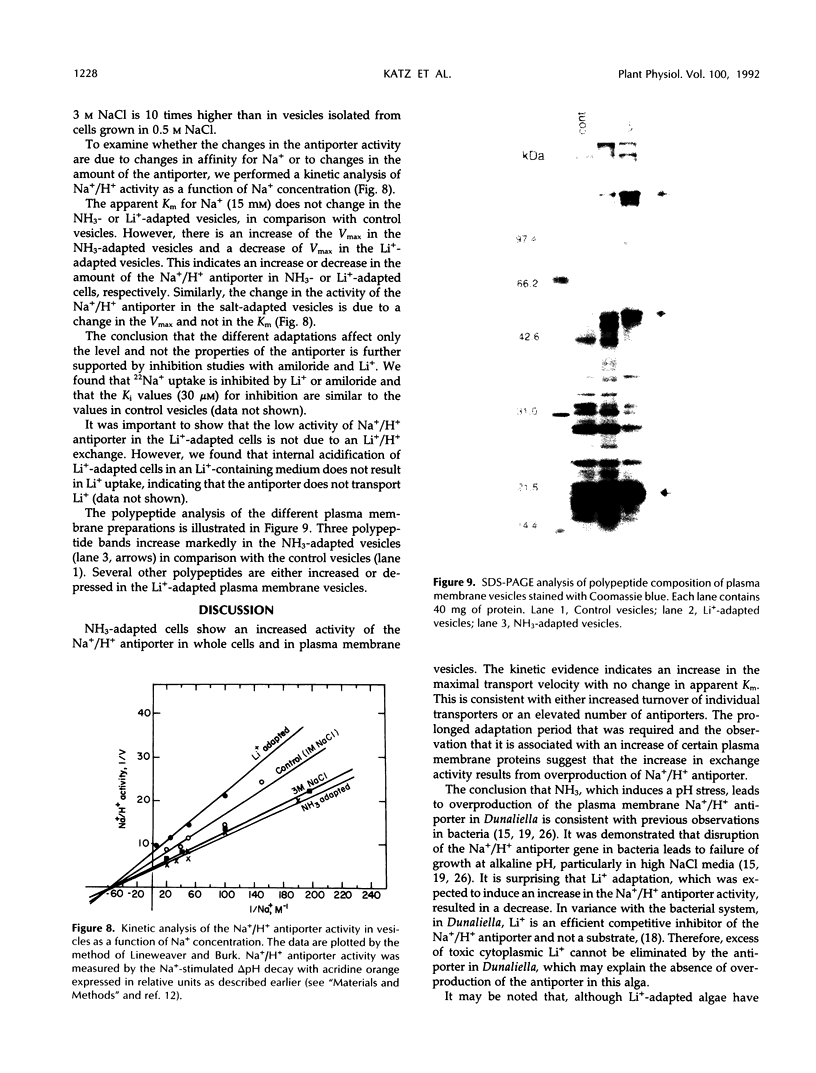
The effect of different growth conditions on the activity of the Na+/H+ antiporter in Dunaliella salina has been investigated. Adaptation of D. salina cells to ammonia at alkaline pH or to high NaCl concentrations is associated with a pronounced increase in the plasma membrane Na+/H+ exchange activity. The enhanced activity is manifested both in vivo, by stimulation of Na+ influx into intact cells in response to internal acidification, and in vitro, by a larger 22Na accumulation in plasma membrane vesicles in response to an induced pH gradient. Kinetic analysis shows that the stimulation does not result from a change of the Km for Na+ but from an increase in the Vmax. In contrast, adaptation of cells to a high LiCl concentration (0.8 m) depresses the activity of the Na+/H+ antiporter. Adaptation to ammonia is also associated with a large increase of three polypeptide bands in purified plasma membrane preparations, indicating that they may compose the antiporter polypeptides. These results suggest that adaptation to ammonia or to high salinity induces overproduction of the plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter in Dunaliella.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bensadoun A., Weinstein D. Assay of proteins in the presence of interfering materials. Anal Biochem. 1976 Jan;70(1):241–250. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(76)80064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bental M., Degani H., Avron M. Na-NMR Studies of the Intracellular Sodium Ion Concentration in the Halotolerant Alga Dunaliella salina. Plant Physiol. 1988 Aug;87(4):813–817. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.4.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumwald E., Poole R. J. Salt tolerance in suspension cultures of sugar beet : induction of na/h antiport activity at the tonoplast by growth in salt. Plant Physiol. 1987 Apr;83(4):884–887. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.4.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun Y., Hassidim M., Lerner H. R., Reinhold L. Evidence for a Na/H Antiporter in Membrane Vesicles Isolated from Roots of the Halophyte Atriplex nummularia. Plant Physiol. 1988 May;87(1):104–108. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.1.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garbarino J., Dupont F. M. Rapid induction of na/h exchange activity in barley root tonoplast. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):1–4. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Rothstein A. Mechanisms of regulation of the Na+/H+ exchanger. J Membr Biol. 1986;90(1):1–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01869680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. K., Johnson E. J., MacElroy R. D., Speer H. L., Bruff B. S. Effects of salts on the halophilic alga Dunaliella viridis. J Bacteriol. 1968 Apr;95(4):1461–1468. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.4.1461-1468.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Avron M. Determination of intracellular osmotic volume and sodium concentration in dunaliella. Plant Physiol. 1985 Aug;78(4):817–820. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.4.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Bental M., Degani H., Avron M. In Vivo pH Regulation by a Na/H Antiporter in the Halotolerant Alga Dunaliella salina. Plant Physiol. 1991 May;96(1):110–115. doi: 10.1104/pp.96.1.110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Pick U., Avron M. Characterization and reconstitution of the Na+/H+ antiporter from the plasma membrane of the halotolerant alga Dunaliella. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 24;983(1):9–14. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90373-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleiner D. The transport of NH3 and NH4+ across biological membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 9;639(1):41–52. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(81)90004-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A. Bioenergetics of alkalophilic bacteria. J Membr Biol. 1986;89(2):113–125. doi: 10.1007/BF01869707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanyi J. K. The role of Na+ in transport processes of bacterial membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 20;559(4):377–397. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(79)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niiya S., Yamasaki K., Wilson T. H., Tsuchiya T. Altered cation coupling to melibiose transport in mutants of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8902–8906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Maisler N., Taglicht D., Karpel R., Schuldiner S. Deletion of ant in Escherichia coli reveals its function in adaptation to high salinity and an alternative Na+/H+ antiporter system(s). J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20297–20302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Schuldiner S. Intracellular pH and membrane potential as regulators in the prokaryotic cell. J Membr Biol. 1987;95(3):189–198. doi: 10.1007/BF01869481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U., Karni L., Avron M. Determination of Ion Content and Ion Fluxes in the Halotolerant Alga Dunaliella salina. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):92–96. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U., Zeelon O., Weiss M. Amine Accumulation in Acidic Vacuoles Protects the Halotolerant Alga Dunaliella salina Against Alkaline Stress. Plant Physiol. 1991 Nov;97(3):1226–1233. doi: 10.1104/pp.97.3.1226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadka A., Himmelhoch S., Zamir A. A 150 Kilodalton Cell Surface Protein Is Induced by Salt in the Halotolerant Green Alga Dunaliella salina. Plant Physiol. 1991 Mar;95(3):822–831. doi: 10.1104/pp.95.3.822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M., Bental M., Pick U. Hydrolysis of polyphosphates and permeability changes in response to osmotic shocks in cells of the halotolerant alga dunaliella. Plant Physiol. 1991 Nov;97(3):1241–1248. doi: 10.1104/pp.97.3.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein D., Padan E., Schuldiner S. A single locus in Escherichia coli governs growth in alkaline pH and on carbon sources whose transport is sodium dependent. FEBS Lett. 1980 Jul 28;116(2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80637-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]