Abstract
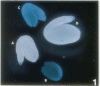
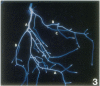
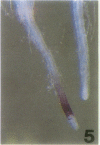
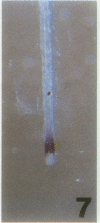
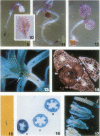
The vacuolar membrane (tonoplast) contains an abundant intrinsic protein with six membrane-spanning domains that is encoded by a small gene family. Different isoforms of tonoplast intrinsic protein (TIP) are expressed in different tissues or as a result of specific signals. Using promoter-β-glucuronidase (GUS) fusions and in situ hybridization, we have examined the expression of γ-TIP in Arabidopsis thaliana. GUS staining of plants transformed with promoter-GUS fusions showed that γ-TIP gene expression is high in recently formed tissues of young roots. In the shoot, γ-TIP gene expression was highest in the vascular bundles of stems and petioles, as well as in the stipules and in the receptacle of the flower. No GUS activity was detected in root or shoot meristems or in older tissues, suggesting temporal control of γ-TIP gene expression associated with cell elongation and/or differentiation. In situ hybridization carried out with whole seedlings confirmed that in root tips, γ-TIP mRNA was present only in the zone of cell elongation just behind the apical meristem. In seedling shoots, mRNA abundance was also found to be correlated with cell expansion. These results indicate that γ-TIP may be expressed primarily at the time when the large central vacuoles are being formed during cell enlargement.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Denecke J., Botterman J., Deblaere R. Protein secretion in plant cells can occur via a default pathway. Plant Cell. 1990 Jan;2(1):51–59. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.1.51. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehring G. R., Zampighi G., Horwitz J., Bok D., Hall J. E. Properties of channels reconstituted from the major intrinsic protein of lens fiber membranes. J Gen Physiol. 1990 Sep;96(3):631–664. doi: 10.1085/jgp.96.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero F. D., Jones J. T., Mullet J. E. Turgor-responsive gene transcription and RNA levels increase rapidly when pea shoots are wilted. Sequence and expression of three inducible genes. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Jul;15(1):11–26. doi: 10.1007/BF00017720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höfgen R., Willmitzer L. Storage of competent cells for Agrobacterium transformation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9877–9877. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höfte H., Hubbard L., Reizer J., Ludevid D., Herman E. M., Chrispeels M. J. Vegetative and Seed-Specific Forms of Tonoplast Intrinsic Protein in the Vacuolar Membrane of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 1992 Jun;99(2):561–570. doi: 10.1104/pp.99.2.561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. D., Chrispeels M. J. Tonoplast-bound protein kinase phosphorylates tonoplast intrinsic protein. Plant Physiol. 1992 Dec;100(4):1787–1795. doi: 10.1104/pp.100.4.1787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. D., Herman E. M., Chrispeels M. J. An abundant, highly conserved tonoplast protein in seeds. Plant Physiol. 1989 Nov;91(3):1006–1013. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.3.1006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K. D., Höfte H., Chrispeels M. J. An intrinsic tonoplast protein of protein storage vacuoles in seeds is structurally related to a bacterial solute transporter (GIpF). Plant Cell. 1990 Jun;2(6):525–532. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.6.525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang L. J., Whelan J., Weaver C. D., Roberts D. M., Day D. A. Protein phosphorylation stimulates the rate of malate uptake across the peribacteroid membrane of soybean nodules. FEBS Lett. 1991 Nov 18;293(1-2):188–190. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81183-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pao G. M., Wu L. F., Johnson K. D., Höfte H., Chrispeels M. J., Sweet G., Sandal N. N., Saier M. H., Jr Evolution of the MIP family of integral membrane transport proteins. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):33–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01823.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M., Agre P. Isolation of the cDNA for erythrocyte integral membrane protein of 28 kilodaltons: member of an ancient channel family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11110–11114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M., Carroll T. P., Guggino W. B., Agre P. Appearance of water channels in Xenopus oocytes expressing red cell CHIP28 protein. Science. 1992 Apr 17;256(5055):385–387. doi: 10.1126/science.256.5055.385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandal N. N., Marcker K. A. Soybean nodulin 26 is homologous to the major intrinsic protein of the bovine lens fiber membrane. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9347–9347. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Pfeifle C. A non-radioactive in situ hybridization method for the localization of specific RNAs in Drosophila embryos reveals translational control of the segmentation gene hunchback. Chromosoma. 1989 Aug;98(2):81–85. doi: 10.1007/BF00291041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valvekens D., Van Montagu M., Van Lijsebettens M. Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana root explants by using kanamycin selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5536–5540. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Aelst L., Hohmann S., Zimmermann F. K., Jans A. W., Thevelein J. M. A yeast homologue of the bovine lens fibre MIP gene family complements the growth defect of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutant on fermentable sugars but not its defect in glucose-induced RAS-mediated cAMP signalling. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2095–2104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07742.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verkman A. S. Water channels in cell membranes. Annu Rev Physiol. 1992;54:97–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.54.030192.000525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y. T., Cheng C. L., Conkling M. A. Root-specific genes from tobacco and Arabidopsis homologous to an evolutionarily conserved gene family of membrane channel proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 25;18(24):7449–7449. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.24.7449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto Y. T., Taylor C. G., Acedo G. N., Cheng C. L., Conkling M. A. Characterization of cis-acting sequences regulating root-specific gene expression in tobacco. Plant Cell. 1991 Apr;3(4):371–382. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.4.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]