Abstract
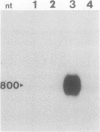
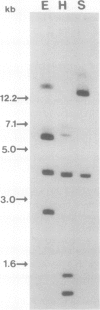
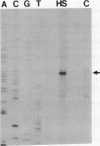
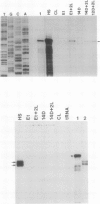
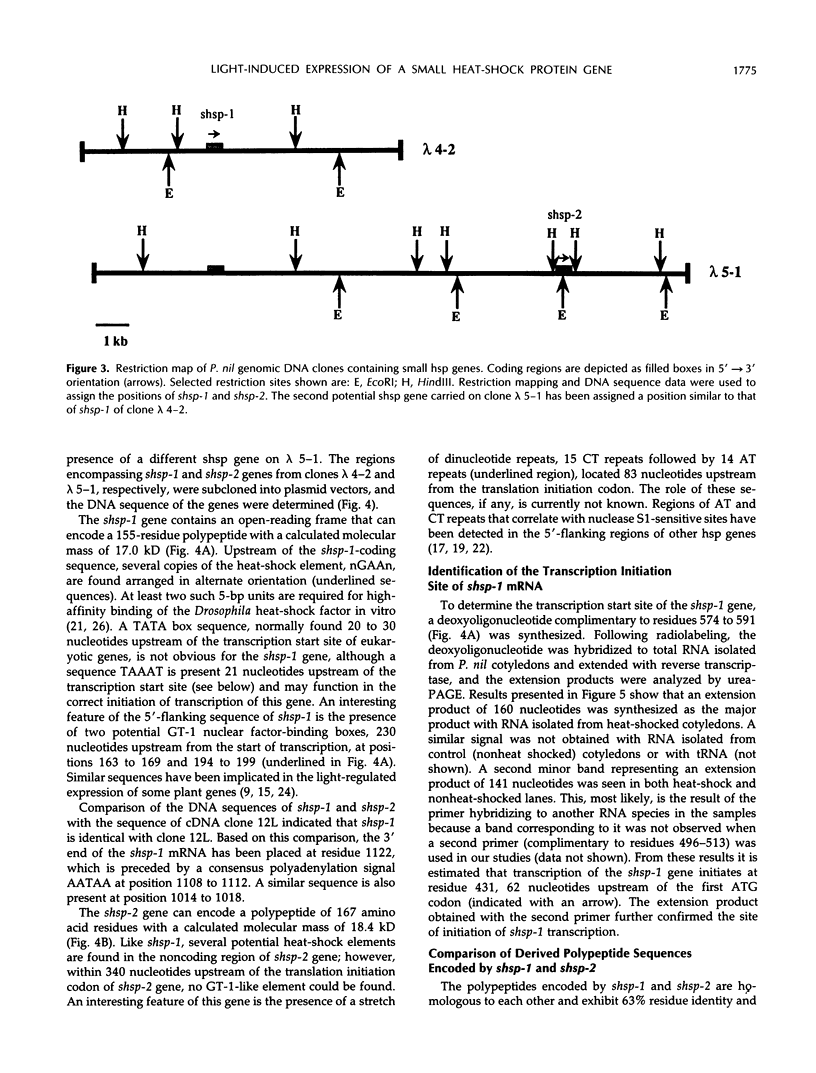
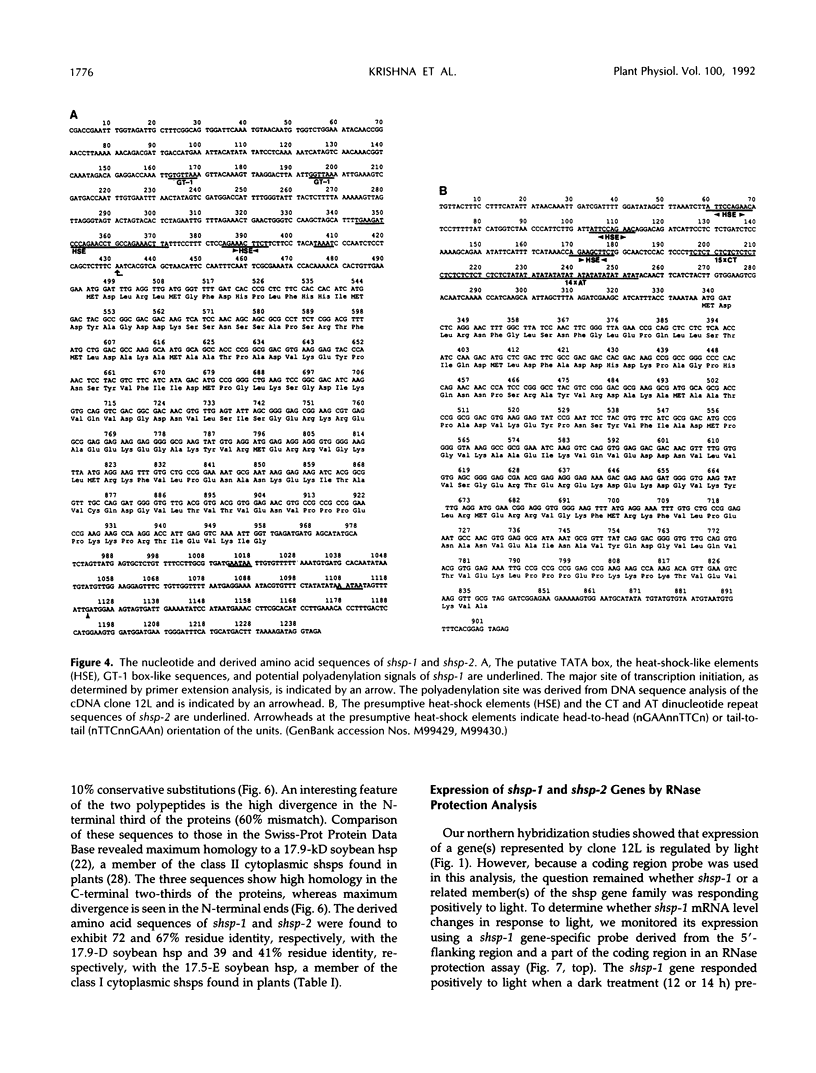
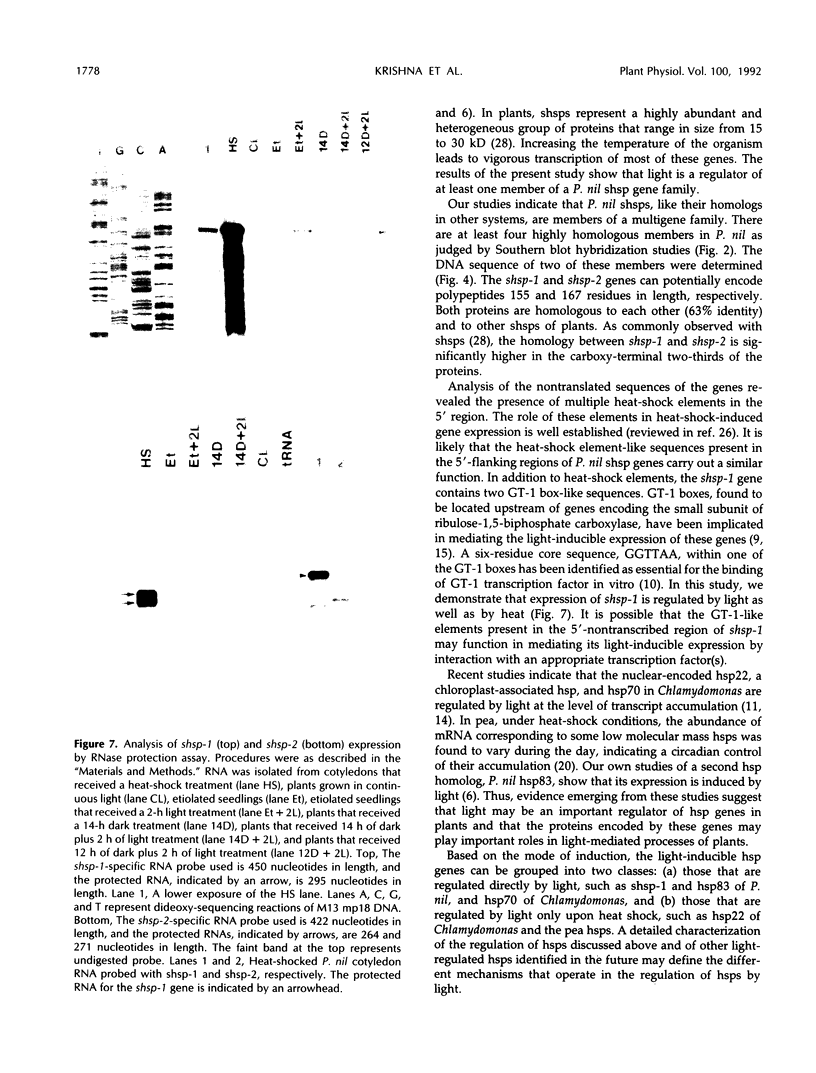
To isolate genes that are regulated by a photoperiod that promotes flowering in Pharbitis nil, a cDNA library representing mRNA of induced cotyledons was screened by differential hybridization. The DNA sequence of one cDNA clone isolated by this approach, clone 12L, showed homology to plant small heat-shock protein (hsp) genes. P. nil genomic clones hybridizing to clone 12L were isolated, and the DNA sequences of two P. nil small hsp (shsp) genes, shsp-1 and shsp-2, were determined. The derived amino acid sequences of shsp-1 and shsp-2 showed maximum homology to the 17.9-kD soybean hsp, a member of the class II cytoplasmic hsps found in plants. A study of the expression of shsp-1 and shsp-2 genes by RNase protection assay indicated that shsp-1 is induced by photoperiod, by light treatment of dark-grown P. nil seedlings, and by heat shock, and that shsp-2 is induced only by heat shock. Analysis of the sequences of the nontranscribed region indicates that both genes contain multiple heat-shock elements. The shsp-1 gene, in addition, contains sequences homologous to the GT-1-binding site, which may play a role in its light-regulated expression.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bouchard R. A. Characterization of expressed meiotic prophase repeat transcript clones of Lilium: meiosis-specific expression, relatedness, and affinities to small heat shock protein genes. Genome. 1990 Feb;33(1):68–79. doi: 10.1139/g90-012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felsheim R. F., Das A. Structure and Expression of a Heat-Shock Protein 83 Gene of Pharbitis nil. Plant Physiol. 1992 Dec;100(4):1764–1771. doi: 10.1104/pp.100.4.1764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firestein G. S., Gardner S. M., Roeder W. D. Quantitative molecular hybridization with unfractionated, solubilized cells using RNA probes and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1987 Dec;167(2):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fray R. G., Lycett G. W., Grierson D. Nucleotide sequence of a heat-shock and ripening-related cDNA from tomato. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):7148–7148. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.7148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin P. M., Sarokin L., Memelink J., Chua N. H. Molecular light switches for plant genes. Plant Cell. 1990 May;2(5):369–378. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.5.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. J., Yong M. H., Cuozzo M., Kano-Murakami Y., Silverstein P., Chua N. H. Binding site requirements for pea nuclear protein factor GT-1 correlate with sequences required for light-dependent transcriptional activation of the rbcS-3A gene. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4035–4044. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03297.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Shalom D., Kloppstech K., Ohad I. Light regulation of the 22 kd heat shock gene transcription and its translation product accumulation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2657–2661. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07450.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E., Chua N. H. GT-1 binding site confers light responsive expression in transgenic tobacco. Science. 1990 Apr 27;248(4954):471–474. doi: 10.1126/science.2330508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mace H. A., Pelham H. R., Travers A. A. Association of an S1 nuclease-sensitive structure with short direct repeats 5' of Drosophila heat shock genes. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):555–557. doi: 10.1038/304555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao R. T., Czarnecka E., Gurley W. B., Schöffl F., Key J. L. Genes for low-molecular-weight heat shock proteins of soybeans: sequence analysis of a multigene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3417–3428. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto B., Grimm B., Ottersbach P., Kloppstech K. Circadian Control of the Accumulation of mRNAs for Light- and Heat-Inducible Chloroplast Proteins in Pea (Pisum sativum L.). Plant Physiol. 1988 Sep;88(1):21–25. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.1.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perisic O., Xiao H., Lis J. T. Stable binding of Drosophila heat shock factor to head-to-head and tail-to-tail repeats of a conserved 5 bp recognition unit. Cell. 1989 Dec 1;59(5):797–806. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90603-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raschke E., Baumann G., Schöffl F. Nucleotide sequence analysis of soybean small heat shock protein genes belonging to two different multigene families. J Mol Biol. 1988 Feb 20;199(4):549–557. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90300-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler U., Cashmore A. R. Photoregulated gene expression may involve ubiquitous DNA binding proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3415–3427. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster G., Even D., Kloppstech K., Ohad I. Evidence for protection by heat-shock proteins against photoinhibition during heat-shock. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):1–6. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02776.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K. Heat shock factor and the heat shock response. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):363–366. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90452-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gromoff E. D., Treier U., Beck C. F. Three light-inducible heat shock genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3911–3918. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]