Abstract
The absorption of K+ by excised roots of barley (Hordeum vulgare L. cv California Mariout) has been systematically compared with that of entire, undisturbed seedlings. Some experiments have also been done with wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) and an amphiploid obtained from a cross between it and salt-tolerant tall wheatgrass (Lophopyrum elongatum Host Löve [syn. Agropyron elongatum Host]). For all three genotypes, the rate of K+ absorption measured in a 20-min period was identical for entire 8-d-old seedlings and their excised roots within the experimental error. Manipulation gentler than root excision, viz. careful transfer of seedlings from one experimental solution to another, was also without effect on the rate of K+ absorption. Absorption of K+ measured by assay of its 86Rb label in the tissue was identical with that measured by K+ depletion of the experimental solutions assayed chemically. For the plant materials and conditions of these experiments, the excised root technique for studying ion transport into roots is validated. The advantages of the technique, and findings differing from the present ones, are discussed.
Full text
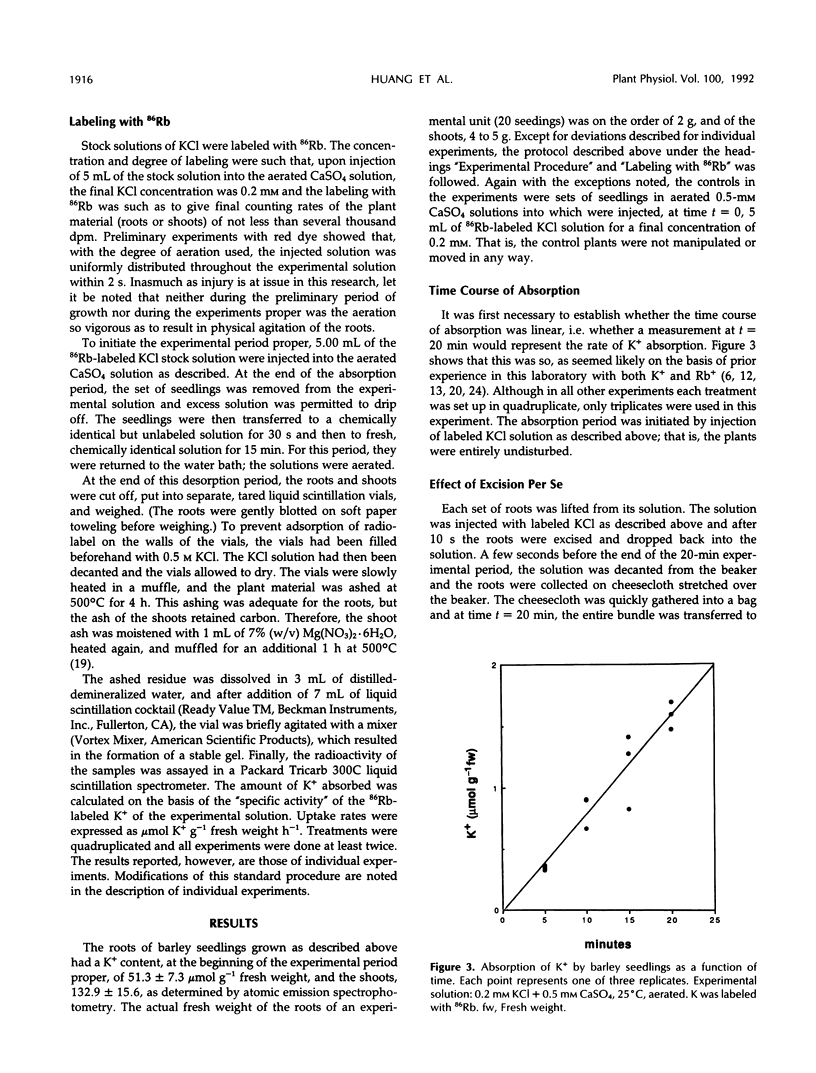
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
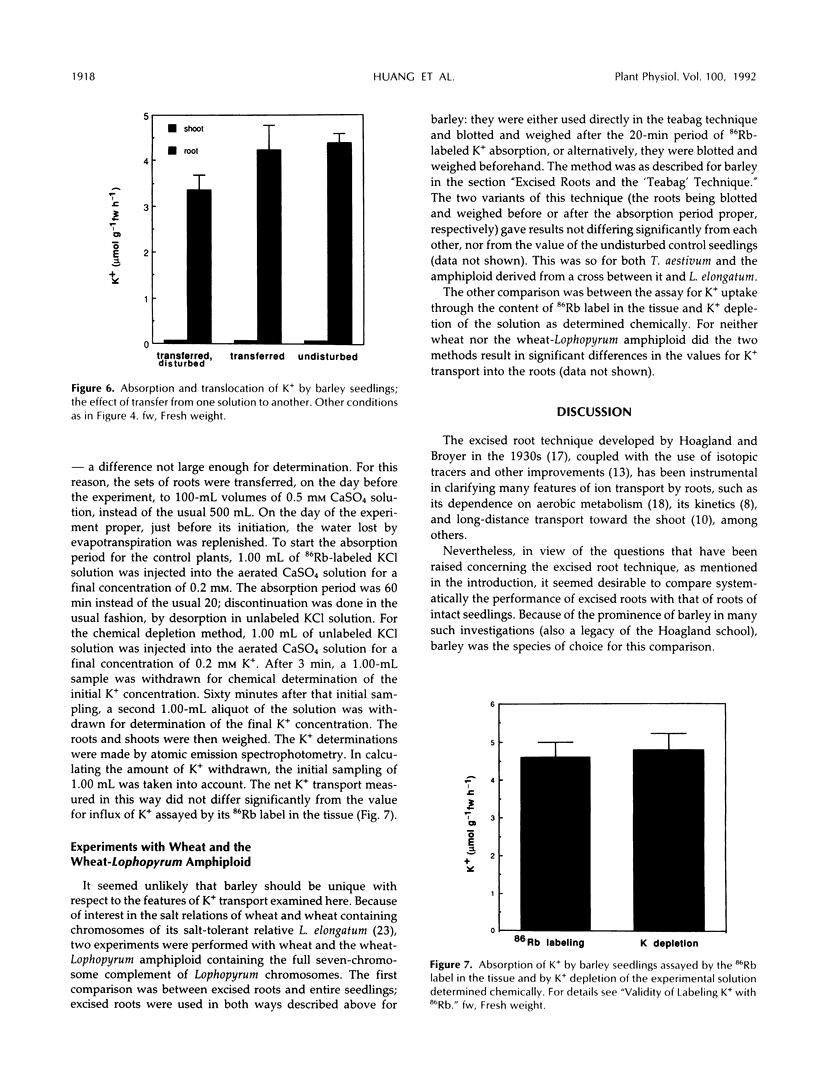
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom A. J., Caldwell R. M. Root excision decreases nutrient absorption and gas fluxes. Plant Physiol. 1988 Aug;87(4):794–796. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.4.794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom A. J., Sukrapanna S. S. Effects of Exposure to Ammonium and Transplant Shock upon the Induction of Nitrate Absorption. Plant Physiol. 1990 Sep;94(1):85–90. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.1.85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Norlyn J. D. The velocities of ion transport into and through the xylem of roots: findings with a two-point application pulse-chase technique. Plant Physiol. 1973 Oct;52(4):346–349. doi: 10.1104/pp.52.4.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E., Rains D. W., Schmid W. E. Course of Cation Absorption by Plant Tissue. Science. 1962 Jun 22;136(3521):1051–1052. doi: 10.1126/science.136.3521.1051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E. The essential role of calcium in selective cation transport by plant cells. Plant Physiol. 1961 Jul;36(4):437–444. doi: 10.1104/pp.36.4.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass A. D. Influence of Excision and Aging upon K Influx into Barley Roots: Recovery or Enhancement? Plant Physiol. 1978 Apr;61(4):481–483. doi: 10.1104/pp.61.4.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gronewald J. W., Cheeseman J. M., Hanson J. B. Comparison of the responses of corn root tissue to fusicoccin and washing. Plant Physiol. 1979 Feb;63(2):255–259. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.2.255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoagland D. R., Broyer T. C. GENERAL NATURE OF THE PROCESS OF SALT ACCUMULATION BY ROOTS WITH DESCRIPTION OF EXPERIMENTAL METHODS. Plant Physiol. 1936 Jul;11(3):471–507. doi: 10.1104/pp.11.3.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard R. T., Hanson J. B. Induction and development of increased ion absorption in corn root tissue. Plant Physiol. 1972 Mar;49(3):430–435. doi: 10.1104/pp.49.3.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Läuchli A., Epstein E. Transport of potassium and rubidium in plant roots: the significance of calcium. Plant Physiol. 1970 May;45(5):639–641. doi: 10.1104/pp.45.5.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. M. Errors in the Measurement of Root Pressure and Exudation Volume Flow Rate Caused by Damage during the Transfer of Unsupported Roots between Solutions. Plant Physiol. 1987 Sep;85(1):164–166. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.1.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rains D. W., Schmid W. E., Epstein E. Absorption of Cations by Roots. Effects of Hydrogen Ions and Essential Role of Calcium. Plant Physiol. 1964 Mar;39(2):274–278. doi: 10.1104/pp.39.2.274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



