Abstract
In Escherichia coli the genes encoding the anaerobic fumarate respiratory system are transcriptionally regulated by C4-dicarboxylates. The regulation is effected by a two-component regulatory system, DcuSR, consisting of a sensory histidine kinase (DcuS) and a response regulator (DcuR). DcuS and DcuR are encoded by the dcuSR genes (previously yjdHG) at 93.7 min on the calculated E. coli map. Inactivation of the dcuR and dcuS genes caused the loss of C4-dicarboxylate-stimulated synthesis of fumarate reductase (frdABCD genes) and of the anaerobic fumarate-succinate antiporter DcuB (dcuB gene). DcuS is predicted to contain a large periplasmic domain as the supposed site for C4-dicarboxylate sensing. Regulation by DcuR and DcuS responded to the presence of the C4-dicarboxylates fumarate, succinate, malate, aspartate, tartrate, and maleate. Since maleate is not taken up by the bacteria under these conditions, the carboxylates presumably act from without. Genes of the aerobic C4-dicarboxylate pathway encoding succinate dehydrogenase (sdhCDAB) and the aerobic succinate carrier (dctA) are only marginally or negatively regulated by the DcuSR system. The CitAB two-component regulatory system, which is highly similar to DcuSR, had no effect on C4-dicarboxylate regulation of any of the genes.
In Escherichia coli the switch from aerobic to anaerobic metabolism is regulated at the transcriptional level in response to the presence of the electron acceptors O2, nitrate, and fumarate (8, 9, 11, 25, 27, 28). This regulation ensures that in the presence of oxygen only aerobic metabolism and not anaerobic respiration or fermentation is functional. Under anoxic conditions, nitrate (and nitrite) represses the synthesis of the enzymes associated with fumarate respiration. The sensor-regulator systems controlling gene expression in response to O2 and nitrate are known and have been studied in detail. Regulation by O2 is effected by the two-component regulatory system ArcB/A (aerobic respiratory control) and by the cytoplasmic one-component regulator FNR (fumarate-nitrate reductase regulator) (8, 11, 27). Nitrate and nitrite regulate via two homologous two-component regulatory systems, NarX/L and NarP/Q (Nar is an acronym for nitrate reductase) (25).
Fumarate is also an important electron acceptor for respiration, and fumarate and related C4-dicarboxylates are known to induce a variety of genes required for anaerobic fumarate metabolism, such as the structural genes for fumarate reductase (frdABCD) (8, 12), the proton-pumping NADH dehydrogenase I (nuoA to -N) (3, 26, 28), and dicarboxylate carriers (dcu genes) (7, 24, 29). In aerobic growth, synthesis of succinate dehydrogenase (sdhCDAB) is stimulated by the same substrates (18). Therefore, there is a large group of genes which should be transcriptionally regulated by fumarate or other C4-dicarboxylates. For Rhizobium leguminosarum and Rhodobacter capsulatus, the two-component sensor-regulators, DctSR and DctBD, which control gene expression in response to C4-dicarboxylates are known (10, 21). In the present study a two-component regulatory system was identified in E. coli. It is responsible for regulation of the genes of fumarate respiration, including fumarate reductase and a fumarate carrier (DcuB), in response to the presence of C4-dicarboxylates.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains and growth.
For genetic experiments the bacteria (Table 1) were grown aerobically in Luria Bertani broth (22). For expression studies the bacteria were grown in M9 mineral medium (15) supplemented with acid-hydrolyzed casein (1 g/liter) (26). Anaerobic growth was performed in gastight stoppered tubes under an atmosphere of N2 (3). Aerobic growth was performed in flasks filled to 5% of the maximal volume with vigorous shaking. For anaerobic growth the carbon sources were added at 20 mM, and for aerobic growth the carbon sources were added at 10 mM. Cell densities were measured as the absorbance at 578 nm. Cells were harvested at an A578 of 0.5 to 0.7. β-Galactosidase assays were performed according to Miller (15).
TABLE 1.
Strains of E. coli and plasmids used
| Bacterial strain or plasmid | Genotype | Reference or source |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli K-12 | ||
| MC4100 | F−araD139 Δ(argF-lac)U169 rpsL150 relA1 flbB530 deoC1 ptsF25 rbsR | 23 |
| JC7623 | recB21 recC22 sbcB15 leu his thr pro arg ara | 16 |
| IMW205 | MC4100 but dcuR::Kanr | This study |
| IMW262 | MC4100 but dcuS::Camr | This study |
| IMW220 | MC4100 but citB::Spcr | This study |
| MC4100λJ100 | MC4100 λ [Φ(frdA′-′lacZ)] | 12 |
| IMW206 | MC4100 λ [Φ(frdA′-′lacZ)] but dcuR::Kanr | IMW205(P1) × MC4100λJ100 |
| IMW216 | MC4100 λ [Φ(frdA′-′lacZ)] but citB::Spcr | IMW220(P1) × MC4100λJ100 |
| MC4100λPC33 | MC4100 λ [Φ(sdhC′-′lacZ)] | 18 |
| IMW211 | MC4100 λ [Φ(sdhC′-′lacZ)] but dcuR::Kanr | IMW205(P1) × MC4100λPC33 |
| IMW33 | MC4100 λ [Φ(nuo′-′lacZ)] | 3 |
| IMW207 | MC4100 λ [Φ(nuo′-′lacZ)] but dcuR::Kanr | IMW205(P1) × IMW33 |
| IMW237 | MC4100 λ [Φ(dcuB′-′lacZ)] | This study |
| IMW238 | MC4100 λ [Φ(dcuB′-′lacZ)] but dcuR::Kanr | IMW205(P1) × IMW237 |
| IMW239 | MC4100 λ [Φ(dcuB′-′lacZ)] but citB::Spcr | IMW220(P1) × IMW237 |
| IMW240 | MC4100 λ [Φ(dcuC′-′lacZ)] | This study |
| IMW241 | MC4100 λ [Φ(dcuC′-′lacZ)] but dcuR::Kanr | IMW205(P1) × IMW240 |
| IMW260 | MC4100 λ [Φ(dcuB′-′lacZ)] but dcuS::Camr | IMW262(P1) × IMW237 |
| IMW261 | MC4100 λ [Φ(frdA′-′lacZ)] but dcuS::Camr | IMW262(P1) × MC4100λJ100 |
| Plasmids | ||
| pJL28 | ′lacZ, protein fusion vector (Apr) | 13 |
| pJL29 | ′lacZ, protein fusion vector (Apr) | 13 |
| pMW75 | pKS− but dcuR::Kanr | This study |
| pMW92 | pKS− but citB::Spcr | This study |
| pMW108 | pKS− but dcuS::Camr | This study |
| pMW99 | pJL29 but dcuB′-′lacZ | This study |
| pMW98 | pJL29 but dcuC′-′lacZ | This study |
| pMW103 | pJL28 but dctA′-′lacZ | This study |
Inactivation of dcuR (yjdG), dcuS (yjdH), and citB.
The genes were inactivated by replacing their central portions with resistance cassettes. The flanking regions upstream and downstream of the genes were amplified by PCR. The downstream region of dcuR was amplified with primers yjdG-Hin (5′-TGA CAT CAA GAC CGC CCG AAG CTT GCA AGG-3′) and yjdG-Eco (5′-GCG TCC AGT TTA CCG TTA CCG AAT TCA GGC-3′), generating a 848-bp fragment with flanking HindIII and EcoRI sites. The upstream region of dcuR was amplified with primers yjdG-Pst (5′-TGT TCG TTG GAG CTG CAG CCG TGG ATT AGC-3′) and yjdH-Xba (5′-CAG TGA AAG CCA GCT TCT AGA CAG CGG CAG-3′), producing a 815-bp fragment with flanking PstI and XbaI sites. The flanking region upstream of dcuS was amplified with primer YjdH-Eco (5′-CTC TCT GCG AAT TCT TTG TGC ATC-3′), introducing an EcoRI site, and primer YjdH-Bam-2 (5′-CTT CAG GAT CCG AGT AGC GAA GAC-3′), introducing a BamHI site, generating a 1,091-bp fragment. The downstream flanking region of dcuS was amplified with primer YjdH-Xba (5′-TGA GCG CCT CTA GAA AGC GGG AAG-3′), with a XbaI site, and primer YjdH-Bam-1 (5′-GGC GTT ATC ATC GGA TCC ATT TC-3′), with another BamHI site, generating a 1,020-bp fragment. The upstream region of citB was amplified with primers cri-Sac (5′-AAG ATG CTG GGG CTG AGC TCC-3′) and cri-Bam (5′-ATT CCG CAT GGA TCC CTG CC-3′), generating a 929-bp fragment with SacI and BamHI cloning sites. The downstream region of citB was amplified with primers cri-Hind (5′-ATG TTT AAA GCT TAT GCT CGC G-3′) and cri-Cla (5′ GAT CAT CGG TGT ATC GAT TTT TG-3′), producing a 918-bp fragment with HindIII and ClaI cloning sites. For each gene, the flanking regions were cloned into pKS− (Stratagene). For the dcuR and citB genes the Kanr and Spcr resistance cassettes derived from pGS607 and pGS606, respectively (24), were cloned into the EcoRI-PstI and the BamHI sites, respectively, resulting in dcuR::Kanr (pMW75) and citB::Spcr (pMW92). For dcuS, the flanking regions were separated by a single BamHI site (pMW107). A Camr resistance cassette was amplified from pACYC184 (6) by PCR with primers CAMLIB2 (5′-CAA TAA CTG GAT CCA AAA AAT TAC GC-3′) and CAMREB (5′-ATA TCC TGG ATC CCA TAT TCT GC-3′), both introducing a BamHI site. The resistance cassette was then cloned into the BamHI site of pMW107, resulting in pMW108 (dcuS::Camr). Any possible terminating sequences downstream of the Camr resistance cassette were removed to enable transcription of dcuR located downstream of dcuS. The plasmids were transformed into E. coli JC7623 and were used for replacement of the intact genes by homologous recombination (16). Presence of the dcuR::Kanr, dcuS::Camr, and citB::Spcr alleles was confirmed by PCR of the genomic DNA with the corresponding primers, yielding fragments corresponding to the sizes of the inactivated genes. The inactivated genes were transferred to strains with suitable genetic backgrounds by P1 transduction (15).
Construction of protein fusions.
For creating protein fusions (dcuB′-′lacZ, dcuC′-′lacZ, and dctA′-′lacZ) plasmid pJL28 or its derivative pJL29 was used (13). The dcuB′-′lacZ fusion was obtained by cloning the 0.65-kb PCR fragment generated with primer dcuB-Bam (5′-AAG TTG GAT CCT AAA TAA CAT GTG TGA ACC-3′) and primer yjdG-Eco into the BamHI and EcoRI sites of pJL29, yielding pMW99. For the dcuC′-′lacZ fusion (pMW98), the dcuB promoter region was amplified with primers dcuC-Bam (5′-CCC CAA TAA GGA TCC CAA TG-3′) and dcuC-Eco (5′-CCA GCG GTG AAT TCC AGA CC-3′), and the 1.1-kb fragment was cloned into the BamHI and EcoRI sites of pJL29. The dctA′-′lacZ fusion (pMW103) was obtained by cloning the 0.5-kb PCR fragment generated with primers dctA-Bam (5′-CAG AGA GGG ATC CAT AGG GTG TCC-3′) and dctA-Eco (5′-CGC TGG ATG AAT TCG GCA TGG G-3′) into the respective restriction sites of pJL28. The dcuB′- and dcuC′-′lacZ fusions were transferred to the chromosome with phage λRZ5 (12, 17), and monolysogens were identified and used for further work (3).
RESULTS
Fumarate induction of dcuB and frdA depends on the dcuSR regulatory genes.
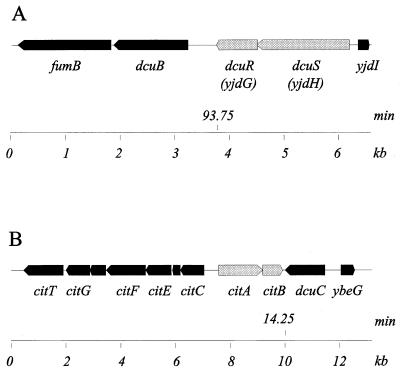
In a search for potential fumarate-responsive regulators, the E. coli data base was screened for gene products similar to the sensor-regulators DctRS and DctBD of R. capsulatus and Rhizobium leguminosarum, which stimulate the synthesis of the C4-dicarboxylate carriers in response to C4-dicarboxylates (10, 21). Both systems showed only low levels of similarity to two-component regulators of E. coli (<28% sequence identity). The genes for two of these systems, yjdHG and citAB, were located next to genes involved in anaerobic fumarate metabolism (Fig. 1). The yjdHG genes are in the dcuB fumB to lysU intergenic region at 93.7 min on the E. coli map (2). The dcuB fumB genes encode the anaerobically expressed fumarate carrier (dcuB) and fumarase (fumB) (1, 24). The citA citB (formerly criR) genes on the other hand are positioned at 14.1 min on the E. coli map between genes encoding an alternative fumarate carrier (dcuC) and the citC to citT gene cluster for anaerobic citrate metabolism (2, 20, 29). The citAB genes encode proteins homologous to the citrate sensor-regulators from Klebsiella pneumoniae (4, 5, 20). Anaerobic citrate metabolism of E. coli is related to C4-dicarboxylate metabolism due to the production and excretion of succinate (5, 14).
FIG. 1.
Map positions and arrangement of the dcuSR (previously yjdHG) (A) and citAB (B) genes on the E. coli genome. The scale gives the DNA length in kilobases. The positions of the dcuSR and the citAB genes on the calculated E. coli map are shown. Data are from reference 2 and the E. coli data bank.
The genes for the putative response regulator yjdG and the sensor kinase yjdH were genetically inactivated by replacement with genes carrying resistance cassettes. The mutant strains were tested for fumarate regulation of the dcuB and frdA genes (Table 2). Expression of the genes was determined with lacZ fusions, and growth was performed under anaerobic conditions on glucose or glycerol plus dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). DMSO has to be included as an electron acceptor for growth on glycerol, which cannot be fermented by E. coli. In the wild type, the expression of dcuB was stimulated 5.6-fold or 10.9-fold after growth on glucose or glycerol, respectively, when fumarate was present in the medium. When DMSO was omitted from the glycerol medium, a similar stimulation was found with the addition of fumarate. The lower expression of dcuB during growth on glucose could be due to glucose repression. In the yjdG (dcuR) and yjdH (dcuS) mutants the expression of dcuB was decreased to background levels, and the expression was not stimulated by fumarate (Table 2). Therefore both genes are required for fumarate stimulation of dcuB expression.
TABLE 2.
Regulation of dcuB and frdA expression by fumarate, dcuR (formerly yjdG), and dcuS (formerly yjdH) under anaerobic conditionsa
| Substrate(s) | Regulation of dcuB′-′lacZ expression by:
|
Regulation of frdA′-′lacZ expression by:
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WTb | dcuR | dcuS | WT | dcuR | dcuS | |
| Glucose | 8 | 5 | 2 | 150 | 130 | 130 |
| Glucose + fumarate | 45 | 3 | 1 | 300 | 155 | 150 |
| Glycerol + DMSO | 48 | 6 | 4 | 690 | 580 | 365 |
| Glycerol + DMSO + fumarate | 520 | 25 | 9 | NDc | ND | ND |
| Glycerol + fumarate | 560 | 7 | 18 | 1,010 | 400 | 430 |
Expression of dcuB and frdA is given in Miller units. Growth occurred in M9 medium with the indicated substrates.
WT, wild type.
ND, not determined.
Expression of frdA is stimulated by the presence of fumarate in the medium, too, but this stimulation is lower (about twofold [Table 2]). In the yjdG (dcuR) and yjdH (dcuS) mutants background expression of frdA was still high, but the fumarate-dependent stimulation was lost completely.
The citB gene encoding the response regulator of the second two-component system (CitAB) was inactivated, too. The inactivation of citB, however, had no effect on expression and fumarate stimulation of the dcuB and frdA genes (not shown). Therefore, the yjdHG genes, but not the citB gene, are required for fumarate stimulation of dcuB and frdA expression. For this reason the genes yjdH and yjdG were termed dcuS (sensor kinase) and dcuR (response regulator).
Genes regulated by DcuR: not all C4-dicarboxylate-regulated genes respond to DcuSR.
Other genes which are transcriptionally regulated by C4-dicarboxylates were tested in the same way for dcuR involvement (Table 3). The genes tested encode the proton-pumping NADH dehydrogenase I (nuoA to -N genes), an alternative anaerobic C4-dicarboxylate carrier (dcuC gene), succinate dehydrogenase (sdhCDAB), and a C4-dicarboxylate carrier for aerobic growth (dctA). The increase in the expression of the genes stimulated by fumarate or succinate was between 1.4- (nuoAB′-′lacZ) to 2.8-fold (dctA′-′lacZ) (Table 3). However, the fumarate- or succinate-dependent stimulation of nuoA, dcuC, and sdhC expression was not significantly affected in the dcuR mutant. Expression of the dctA′-′lacZ fusion was decreased in the dcuR mutant, but the succinate stimulation was retained and the increases were similar for the wild type (2.8-fold) and the mutant (3.2-fold). Thus, from the genes tested, only dcuB and frdA were clearly regulated by DcuR and DcuS. In the citB mutant neither of the genes was affected in C4-dicarboxylate-stimulated expression (not shown).
TABLE 3.
Effects of C4-dicarboxylates and DcuR on the expression of C4-dicarboxylate-regulated genes
| Gene fusiona | Substrate(s)c | β-Galactosidase activity (Miller units)
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
| WTd (dcuR+) | dcuR | ||
| nuoAB′-′lacZ | Glucose | 95 | 96 |
| Glucose + fumarate | 130 | 125 | |
| Glycerol + fumarate | 230 | 250 | |
| dcuC′-′lacZ | Glucose | 52 | 52 |
| Glucose + fumarate | 100 | 100 | |
| sdhC′-′lacZ | Glycerol + O2 | 3,580 | 3,680 |
| Succinate + O2 | 4,780 | 4,740 | |
| dctA′-′lacZb | Glycerol + O2 | 260 | 89 |
| Succinate + O2 | 730 | 286 | |
MC4100 derivatives with dcuR+ and dcuR backgrounds given in Table 1.
Strains MC4100pMW103 and IMW205pMW103, respectively.
M9 medium was used with the indicated substrates.
WT, wild type.
C4-dicarboxylates affecting regulation by DcuR.
The effects of various carboxylates on the expression of dcuB′-′lacZ were studied by including the respective substrates in the medium (Table 4). Growth was performed under anaerobic conditions in the presence of glycerol plus DMSO, which enables high expression of dcuB when suitable carboxylates are added (see Tables 2 and 4). Each of the C4-dicarboxylates fumarate, succinate, malate, tartrate, aspartate, and maleate caused a strong induction of dcuB expression compared to growth with glycerol plus DMSO alone. Even with succinate and maleate, which are not metabolized under the respective (anaerobic) conditions, the induction amounted to at least 63% of the maximal induction found with fumarate. Most remarkably, maleate, which is not even taken up by the anaerobic Dcu carriers (24), induced the expression of dcuB strongly. For all the C4-dicarboxylates the stimulation was completely lost in the dcuR mutant. Therefore neither uptake nor metabolism of the C4-dicarboxylates is required for induction by the DcuSR system. The results suggest that the C4-dicarboxylates bind to the sensor at the periplasmic aspect of the membrane and that the sensor is able to react with each of the C4-dicarboxylates. Butyrate and acetate, on the other hand, had no stimulating effect. During anaerobic growth on glucose, the respective C4-dicarboxylates and aspartate showed similar stimulating effects, but expression was generally lower, possibly due to glucose repression (not shown). Expression of frdA′-′lacZ responded in a similar way to the C4-dicarboxylates (not shown).
TABLE 4.
Effectors for dcuR-dependent regulation of dcuB′-′lacZ expression during anaerobic growth with glycerol plus DMSO
| Carboxylic acid in mediuma |
dcuB′-′lacZ expression (Miller units)
|
|
|---|---|---|
| IMW237 (dcuR+) | IMW238 (dcuR) | |
| None | 48 | 6 |
| Fumarate | 537 | 7 |
| Succinate | 437 | 4 |
| Malate | 435 | 4 |
| Tartrate | 382 | 13 |
| Aspartate | 434 | 10 |
| Maleate | 337 | 19 |
| Butyrate | 18 | 5 |
| Acetate | 26 | 3 |
M9 medium was used as the growth medium.
DISCUSSION
Physiology and significance of fumarate regulation in E. coli.
Transcriptional regulation by fumarate and other C4-dicarboxylates plays an important role in E. coli. The DcuSR two-component regulators identified here apparently exert this fumarate regulation for the genes of fumarate respiration, that is, frdABCD and dcuB. The expression of fumB (encoding anaerobic fumarase B), which is located downstream of dcuB and is possibly expressed from the dcuB promoter (1, 24), could also be subject to DcuR regulation. Expression of other genes which are transcriptionally stimulated by C4-dicarboxylates was not (nuoA to -N, sdhCDAB, and dcuC) or was only partially (dctA) dependent on DcuR. This indicates that DcuSR is required specifically for the regulation of the anaerobic fumarate respiratory pathway. The C4-dicarboxylate regulation of other genes apparently is effected by a different system, and the CitA-CitB two-component regulatory system obviously does not serve this function either, as shown here.
DcuRS as a C4-dicarboxylate-sensing two-component system.
The dcuSR genes, and the derived DcuS and DcuR proteins, show the typical properties of two-component regulatory systems. Both genes overlap by 4 bp, which is a strong indication for a joint transcription similar to that of the genes of other two-component regulators, which are mostly organized in one transcriptional unit. The DcuR protein contains a helix-turn-helix DNA-binding motif in the C-terminal half and an N-terminal receiver domain with a conserved aspartate residue (Asp56) as a potential phosphorylation site.
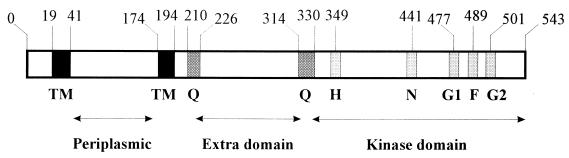
The DcuS protein contains the elements typical for sensory histidine kinases, and the arrangement is very similar to that found in the CitA protein of K. pneumoniae (4, 5) (Fig. 2). The CitA protein consists of an N-terminal sensory domain with two transmembrane helices which are separated by a long periplasmic domain of about 130 amino acids (5). The kinase domain is separated from the sensor domain by an extra domain of about 80 amino acids. The similarity of DcuS to CitA extends over the complete range, including the periplasmic and the extra domain. In the kinase domain the H, N, F, and G boxes, which are designated according to the characteristic amino acid residues (19), are present in an arrangement very similar to that of CitA. His349, which is supposed to be the phosphorylation site, is conserved in the H box.
FIG. 2.
Overview of the suggested domain structure of the sensor kinase DcuS. The positions of characteristic sequence features and of the domains are indicated by the numbers. The transmembrane helices (TM) were predicted from the sequence. The Q linkers (Q) and the signature segments of the kinase domain (H, N, G1, F, and G2) (19) were identified by sequence alignments. For the segments, the positions of the naming amino acid residue are given (drawn according to reference 5).
DcuS has significantly higher levels of similarity with the CitA citrate sensors of K. pneumoniae and E. coli than with the C4-dicarboxylate sensors DctB and DctS of Rhizobium sp. strains and R. capsulatus (not shown). Both the citrate (CitA) and the C4-dicarboxylate (DcuS, DctB, and DctS) sensors have similar N-terminal sensory domains consisting of two transmembrane helices and a long intervening periplasmic domain. The periplasmic domains of DctB and DctS, however, are about twice the size of the CitA or DcuS periplasmic domain, which presumably acts in ligand binding (5). Such a location of the sensory domain in the periplasm suggests sensing of the C4-dicarboxylates from without. This is also supported from the functioning of maleate as a signal which apparently is not taken up by the bacteria (24). In agreement with the postulated fumarate sensing by DcuSR from without, the fumarate carrier (DcuB) shows a strong induction by fumarate (up to 10.9-fold), whereas fumarate reductase shows only a weak induction by fumarate (up to twofold). These different responses to external fumarate appear to be sensible since DcuB is required in particular when external fumarate is present. FrdA on the other hand is also required when internal fumarate is produced from intermediary metabolism.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This study was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie.
REFERENCES
- 1.Bell P J, Andrews S C, Sivak M N, Guest J R. Nucleotide sequence of the FNR-regulated fumarase gene (fumB) of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1989;171:3494–3503. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3494-3503.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Blattner F R, et al. The complete genome sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science. 1997;277:1453–1463. doi: 10.1126/science.277.5331.1453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bongaerts J, Zoske S, Weidner U, Unden G. Transcriptional regulation of the proton translocating NADH dehydrogenase genes (nuoA-N) of Escherichia coli by electron acceptors, electron donors and gene regulators. Mol Microbiol. 1995;16:521–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02416.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bott M. Anaerobic citrate metabolism and its regulation in enterobacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1997;167:78–88. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bott M, Meyer M, Dimroth P. Regulation of anaerobic citrate metabolism in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol. 1995;18:533–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.mmi_18030533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chang A C Y, Cohen S N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978;134:1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Engel P, Krämer R, Unden G. Anaerobic fumarate transport in Escherichia coli by an fnr-dependent dicarboxylate uptake system which is different from aerobic dicarboxylate uptake. J Bacteriol. 1992;174:5533–5539. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.17.5533-5539.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Guest J R, Green J, Irvine A S, Spiro S. The FNR modulon and FNR-regulated gene expression. In: Lin E C C, Lynch A S, editors. Regulation of gene expression. New York, N.Y: Chapman & Hall; 1996. pp. 317–342. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gunsalus R P. Control of electron flow in Escherichia coli: coordinated transcription of respiratory pathway genes. J Bacteriol. 1992;174:7069–7074. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.22.7069-7074.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hamblin M J, Shaw J G, Kelly D J. Sequence analysis and interposon mutagenesis of a sensor-kinase (DctS) and a response-regulator (DctR) controlling synthesis of the high-affinity C4-dicarboxylate transport system in Rhodobacter capsulatus. Mol Gen Genet. 1993;237:215–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00282803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Iuchi S, Lin E C C. Adaptation of Escherichia coli to redox environments by gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1993;9:9–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jones H M, Gunsalus R P. Regulation of Escherichia coli fumarate reductase (frdABCD) operon expression by respiratory electron acceptors and the fnr gene product. J Bacteriol. 1987;169:3340–3349. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3340-3349.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lucht, J., and E. Bremer. Unpublished data.
- 14.Lüttgens M, Gottschalk G. Why a co-substrate is required for anaerobic growth of Escherichia coli on citrate. J Gen Microbiol. 1980;119:63–70. doi: 10.1099/00221287-119-1-63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Miller J H. A short course in bacterial genetics. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Oden K L, DeVaux L C, Vibaut C R T, Cronan J E, Jr, Gennis R B. Genomic replacement in Escherichia coli K-12 using covalently closed circular plasmid DNA. Gene. 1990;96:29–36. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90337-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ostrow K S, Silhavy T J, Garrett S. cis-acting sites required for osmoregulation of ompF expression in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1986;168:1165–1171. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1165-1171.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Park S J, Tseng C P, Gunsalus R P. Regulation of succinate dehydrogenase (sdhCDAB) operon expression in Escherichia coli in response to carbon supply and anaerobiosis: role of ArcA and FNR. Mol Microbiol. 1995;15:473–482. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1995.tb02261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Parkinson J S, Kofoid E C. Communication modules in bacterial signaling proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:71–112. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pos K M, Dimroth P, Bott M. The Escherichia coli citrate carrier CitT: a member of a novel eubacterial transporter family related to the 2-oxoglutarate/malate translocator from spinach chloroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1998;180:4160–4165. doi: 10.1128/jb.180.16.4160-4165.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ronson C W, Astwood P W, Nixon B T, Ausubel F M. Deduced products of C4-dicarboxylate transport regulatory genes of Rhizobium leguminosarum are homologous to nitrogen regulatory gene products. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987;15:7921–7934. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Sambrook J, Fritsch E F, Maniatis T. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1989. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Silhavy T J, Berman M, Enquist L W. Experiments with gene fusions. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 1984. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Six S, Andrews S C, Unden G, Guest J R. Escherichia coli possesses two homologous anaerobic C4-dicarboxylate membrane transporters (DcuA and DcuB) distinct from the aerobic dicarboxylate transport system (Dct) J Bacteriol. 1994;176:6470–6478. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.21.6470-6478.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Stewart V. Nitrate regulation of anaerobic respiratory gene expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1993;9:425–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01704.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Tran Q H, Bongaerts J, Vlad D, Unden G. Requirement for the proton-pumping NADH dehydrogenase I of Escherichia coli in NADH → fumarate respiration and bioenergetic implications. Eur J Biochem. 1997;244:155–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.00155.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Unden G, Bongaerts J, Becker S, Holighaus G, Schirawski J, Six S. O2-sensing and O2-dependent gene regulation in facultatively anaerobic bacteria. Arch Microbiol. 1995;164:81–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Unden G, Bongaerts J. Alternative respiratory pathways of Escherichia coli: energetics and transcriptional regulation in response to electron acceptors. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1997;1320:217–234. doi: 10.1016/s0005-2728(97)00034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zientz E, Six S, Unden G. Identification of a third secondary carrier (DcuC) for anaerobic C4-dicarboxylate transport in Escherichia coli: role of the three Dcu carriers in uptake and exchange. J Bacteriol. 1996;178:7241–7247. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.24.7241-7247.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]