Abstract
We have inactivated the ospC, oppAIV, and guaB genes on the 26-kb circular plasmid of Borrelia burgdorferi (cp26) by allelic exchange. On several occasions following such transformations, the cp26 of transformants had an aberrant mobility through agarose gels. Characterization of these cp26 molecules showed that the plasmid had dimerized. These dimers were quite stable during either selective or nonselective passage. Subsequent transformations with dimer DNA supported the hypothesis that in B. burgdorferi, transforming cp26 DNA most likely does not displace the resident homologous plasmid but rather must recombine in order to donate sequences that it carries. These serendipitous findings provide a mechanism for obtaining heterozygous complemented control strains when mutant phenotypes are characterized.
Borrelia burgdorferi, the causative agent of Lyme disease, is a spirochete with a genome composed of a linear chromosome and both linear and circular plasmids (1, 4, 5, 8, 9, 11, 13, 14). At least several of the plasmids have been considered to be minichromosomes (2), since they are invariably present in natural isolates, are very stable in vitro, and are the loci of genes presumed to be essential for growth in some phase of the bacterial life cycle, which alternates between ticks and small mammals.
Among the plasmids is a circular one of approximately 26 kb (14, 18, 21, 24, 28, 30). This plasmid (called cp26) carries the guaA and guaB genes, encoding the last two enzymes involved in guanine nucleotide biosynthesis (22). Guanine levels are high in ticks (32), but free nucleotides are rare in mammalian blood and, presumably, other tissues (6); therefore, expression of the guaA and guaB genes may be responsive to this environmental variable. Also on cp26 is the ospC gene, encoding an outer surface protein that may be involved in tick-mammal transmission, since its synthesis increases after an infected tick begins a blood meal (12, 29). The plasmid also carries a gene for a homolog of OppA, the peptide binding component of oligopeptide permease (23). This gene (oppAIV) is one of five oppA genes in the B. burgdorferi genome, three of which are located on the chromosome, with the fifth on a linear plasmid (7). The genes encoding the other components of oligopeptide permease (oppB, oppC, oppD, and oppF) are located downstream of the three linked chromosomal oppA genes (7). Several other bacteria use oligopeptide permease for environmental sensing (10, 17, 31, 34).
We have undertaken a genetic analysis of the above genes, in part because they may be involved in transmission of the spirochete from the tick to the mouse. We have inactivated the guaB (this report), oppAIV (7), and ospC genes (33) by allelic exchange with recombinant plasmids in which the appropriate gene had an insertion of the gyrBr gene, encoding coumermycin-resistant gyrase (23, 27).
Although we obtained targeted insertions in all of the genes attempted, allelic exchange occurred in the minority of transformants (0.1 to 0.4%) (7, 23, 33); the remainder had converted the wild-type chromosomal gyrB locus to gyrBr. Transforming with B. burgdorferi total plasmid DNA containing gyrBr inserted into cp26 increased the frequency of targeted insertions (23). Further experiments suggested targeted insertion was facilitated by increasing the sequences flanking the insertion site, although the possibility that the transforming cp26::gyrBr displaced the resident cp26 was not definitively excluded (23). No other studies addressing the mechanism of stable transformation or preferred DNA substrates have been reported.
Some of the transformants that we obtained in these and other experiments had cp26 that migrated aberrantly through agarose gels (called cp26*). We characterized these plasmids to shed light on mechanisms of plasmid replication and establishment of transformants. In this paper, we show that these plasmids are stable dimers of cp26 and describe some unusual features of their formation and stability.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains, growth, and transformations.
B. burgdorferi strains used in this study are described in Table 1. They were grown in BSK-H medium (Sigma, St. Louis, Mo.) with 6% rabbit serum (Sigma) at 34°C. Transformations by electroporation were performed as described previously (23, 25). Strain B31, the prototype for B. burgdorferi sensu stricto, was high passage and uncloned. When we assessed the stability of plasmids in the absence of selection, we passaged cultures by diluting them 1/100 every 3 to 4 days and assuming six to seven doublings per passage.
TABLE 1.
B. burgdorferi strains used in this study
| Strain | Relevant genotype | cp26 type |
|---|---|---|
| B31 | Wild type | Monomer |
| B31-86 | gyrBr | Monomer |
| B31-9 | gyrBr | Dimer |
| B31-82 | ΔoppAIV::gyrBr | Monomer |
| B31-34 | oppAIV+/ΔoppAIV::gyrBr | Dimer |
| B31-80.22, B31-80.87 | ΔguaB::gyrBr | Monomer |
| B31-80.74 | guaB+/ΔguaB::gyrBr | Dimer |
| B31-89 | ospC::gyrBr | Monomer |
| B31-2 | ospC+/ospC::gyrBr | Dimer |
guaB gene inactivation.
The recombinant plasmid for inactivating the guaB gene (pKK75) was constructed by three-way ligation. First, the gyrBr gene (encoding a coumermycin-resistant B subunit of gyrase) and its promoter were amplified from strain NGR (23), using primers U173F-NcoI and 1905R-BclI (Table 2), and cloned into pCRII (Invitrogen Corp., San Diego, Calif.). After digestion with NcoI and BclI (New England Biolabs, Beverly, Mass.), the gyrBr-containing fragment was purified from an agarose minigel by using an NA45 membrane (Schleicher & Schuell, Keene, N.H.). A BglII-XhoI fragment of pDH63 (23) (which contains most of the oppAIV gene and pBluescript [Stratagene, La Jolla, Calif.] sequences) and an NcoI-XhoI fragment of pDH68 (which includes the 5′ end of the guaB gene, the guaA gene, and most of the region between the guaA and ospC genes [22]) were also isolated. The three fragments were mixed and ligated. The resulting plasmid, pKK75, contains 1.75 kb of cp26 sequences downstream of the gyrBr gene and about 2.1 kb of cp26 sequences upstream of the site of gyrBr insertion. Deleted in this plasmid are about 700 bp of the guaB gene and 261 bp of the region between the termini of the oppAIV and guaB genes. This plasmid was digested with PvuI (to remove the bla gene, which can confer ampicillin resistance), and the large fragment was electroeluted from an agarose gel by using a model UEA unidirectional electroelutor (International Biotechnologies, Inc., New Haven, Conn.). One microgram of the eluted DNA was used to transform electrocompetent B. burgdorferi B31 as described previously (23, 25). The resulting coumermycin-resistant colonies were screened for the presence of targeted insertion by PCR, using the primer pair gb.18-gb.6 (Table 2) in previously described conditions (33).
TABLE 2.
Oligonucleotide primers used in this study
| Primer | Sequence (5′→3′) | Gene |
|---|---|---|
| U173F+NcoI | AGGCCATGGTTTTAGCACTATACTTTT | 5′-gyrB |
| 1905R+BclI | ACCTTGATCATTACACATCAAGATTAATTAC | 3′-gyrB |
| pc.10 | AAATATGAATATCTCAGGAA | guaA |
| pc.11 | TAGCTAGTCCTGGGCCGGGA | guaA |
| gb.18 | GCAATAATAATTGAAAGAGATT | oppAIV |
| gb.6 | TTAACACTAATGGAGATACA | guaB |
| CP-0 | GAAAAAGATAACATGCAAGATACG | cp32 orf13 |
| CP-1 | AGGAATACAAAAATAAATATGGAG | cp32 orf13 |
| osp 1 | AAGCTTAATTAGAACCAAAC | ospA |
| osp 14 | GTTCCTTCTTTAACCACCAA | ospA |
Agarose gel electrophoresis.
Agarose gels for analysis of PCR products were 1% in TBE buffer (89 mM Tris-borate, 89 mM boric acid, 1 mM EDTA). B. burgdorferi plasmid DNA was prepared for analysis using Qiagen columns (Chatsworth, Calif.); 0.3% Seakem agarose (FMC Bioproducts, Rockland, Maine) gels were run in TAE buffer (40 mM Tris-acetate, 2 mM EDTA) at 0.5 to 1.0 V/cm for approximately 18 h, followed by ethidium bromide staining or Southern blot analysis (33). Transfer to nylon membranes, probe preparation, and hybridization were as described previously (33). The guaA probe was a PCR fragment synthesized by using primers pc.10 and pc.11 (Table 2).
Two-dimensional agarose gel electrophoresis.
In a modification of the procedure described by Samuels and Garon (26), a 0.3% agarose gel in TAE buffer was run normally in the first dimension and then soaked for 1 h in ice water and 4 h in TAE buffer containing 15 μM chloroquine. The gel was rotated 90° and electrophoresed for an additional 18 h; the DNA was then transferred to a Biotrans membrane (ICN, Irvine, Calif.) and hybridized as described previously (33). Probes for the two-dimensional gel were labeled by random priming (Life Technologies, Gaithersburg, Md.), and the fragments were derived from the following sources: the cp26* probe was the gyrBr fragment used in constructing pKK75, the cp32 probe was an orf13 fragment made by PCR using primers CP-0 and CP-1 (Table 2), the lp56 probe was an ospA fragment made by PCR using primers osp 1 and osp 14, and the lp16 probe was p5 (3).
Electron microscopy.
Samples were eluted from agarose gel slices by freezing at −70°C and squeezing the frozen agarose until a liquid phase formed. They were then spread for electron microscopy analysis using the Kleinschmidt aqueous spreading technique (15, 16) as follows. A 15-μl aliquot of the DNA was brought to 500 μM EDTA–0.5 M ammonium acetate–0.1 mg of cytochrome c per ml in a 50-μl volume. This solution was mechanically spread over a fluid-air interface of 0.25 M ammonium acetate for 30 s, and the DNA was transferred to a 2.7 to 3.0% Parlodion-coated copper-palladium grid. The DNA was subsequently stained with 5% aqueous uranylformate (1.57 × 10−5 M) for 30 s, rinsed in 90% ethanol, blotted with filter paper, and air dried. The grids were rotary shadowed with an 80:20 platinum-palladium mixture for contrast enhancement and viewed in a JEOL100B transmission electron microscope at magnifications of ×10,000 to ×15,000. Relaxed circular DNA was obtained by treating 7 μl of the DNA squeezed from an agarose gel slice with 1.5 × 10−3 U of DNase (Boehringer Mannheim, Mannheim, Germany) in the presence of 10 mM MgCl2 and 100 mM Tris (pH 8). Contour lengths were measured, with pBR322 as a size standard, with a Numonics Graphic (Lansdale, Pa.) calculator that was interfaced with a Tektronix (Beaverton, Oreg.) 4052A computer.
RESULTS
Inactivation of the guaB gene.
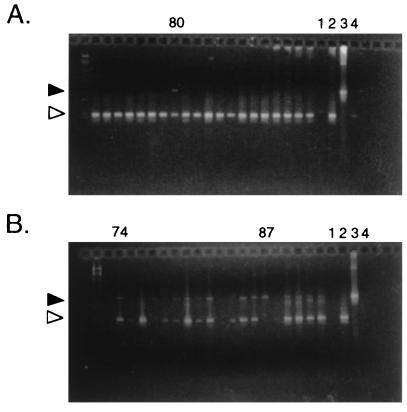
As part of our continuing genetic analysis of putative environmentally regulated genes on cp26, we inactivated the guaB gene with a deletion and insertion of the gyrBr allele. In our previous experiments (7, 23, 33), the majority of the transformants had undergone gene conversion of the chromosomal gyrB gene, rather than the desired allelic exchange, and so we used PCR with primers flanking the insertion site to screen the coumermycin-resistant colonies that arose after electroporation. One colony (B31-80, the only guaB mutant that we isolated out of about 1,000 colonies screened) yielded products corresponding to both the wild-type and mutant versions of the guaB gene (Fig. 1A). To determine if the apparent heterozygosity resulted from contamination with an adjacent colony, we transferred colony B31-80 into 10 ml of liquid medium, grew the culture to log phase, and replated the bacteria at low density. When individual colonies were retested for their guaB genotype by PCR, 82% (54 of 66) retained both bands (e.g., Fig. 1B, 74), whereas 18% (12 of 66) had only the mutant band (e.g., Fig. 1B, 87). When a heterozygote colony was again grown up and replated, all of the 92 resultant colonies tested remained heterozygous. Agarose gel analysis of the plasmid DNA of one of the heterozygous colonies showed that it lacked cp26 at the expected position and had a potential new DNA species at another location, since a DNA band that migrated with an apparent size of about 35 kb broadened as if it had become a doublet (data not shown).
FIG. 1.
Agarose gels of PCR products to identify guaB genotype of individual B. burgdorferi colonies. (A) Initial screen of coumermycin-resistant colonies, showing identification of B31-80, with bands indicating the presence of both wild-type (white arrowhead) and mutant (guaB::gyrBr; black arrowhead) copies of the guaB gene. The PCR product corresponding to the mutant locus is consistently weaker than that derived from the wild-type locus, most likely because the larger fragment is poorly amplified in the conditions used. (B) Rescreen of individual colonies derived from B31-80. Most (e.g., 74) remain heterozygous, whereas 87 represents a homozygous mutant colony. Amplification controls: lanes 1, reagent blank; 2, wild-type DNA; 3, guaB::gyrBr DNA; 4, blank spot on transformation plate.
Isolation of additional B. burgdorferi clones with cp26*.
On three other occasions during our inactivation of genes on cp26 by allelic exchange, we also isolated clones with cp26 that migrated aberrantly (called cp26*; see below). One of these had no gyrBr insertion on cp26 but had the gyrBr allele at the chromosomal gyrB locus (reference 23 and Table 1), and the other two had gyrBr inserted at either the oppAIV or ospC locus (Table 1). Since allelic exchange is a rare event in these experiments (0.1 to 0.4% of coumermycin-resistant transformants), obtaining clones with aberrantly migrating cp26 among the few mutants that we isolated was a striking result.
To exclude the possibility that the apparent heterozygosity of the oppAIV and ospC mutants resulted from mixed colonies of B. burgdorferi, composed of bacteria with wild-type and mutant cp26 (or background derived from dead wild-type bacteria in the electroporation mix), bacteria from the colonies were grown and replated, as described for the guaB heterozygote. The resultant colonies were screened by PCR for their oppAIV or ospC genotype (data not shown). All of the colonies derived from the oppAIV and ospC heterozygotes (92 of 92 and 74 of 74, respectively) retained copies of both wild-type and mutant genes.
Characterization of cp26*.
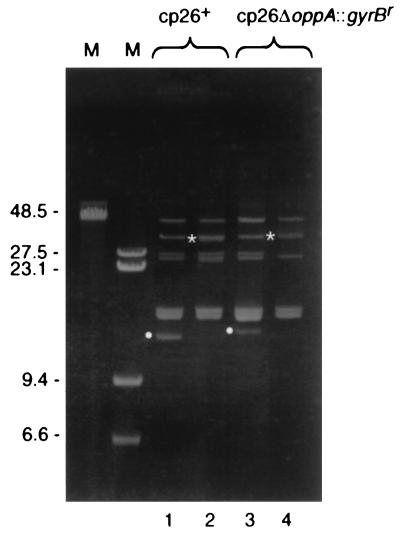
Since the oppAIV, ospC, and guaB mutants with cp26* appeared to have two copies of their respective loci, the simplest explanation for the aberrant migration through agarose gels was that in all three cases, cp26 had formed a heterozygous dimer. The clone with no gyrBr insertion on cp26 (B31-9) could not be shown by PCR to have two copies of any cp26 locus because all of the genes would be identical on both copies. By ethidium bromide staining, however, all of these clones lacked cp26 migrating at its normal position (or the position of cp26 with the corresponding mutation) in 0.3% agarose gels, and all had cp26* bands that migrated more slowly (Fig. 2 and data not shown; also see below).
FIG. 2.
Agarose gel of plasmid DNA from B. burgdorferi clones with normal cp26 and cp26*. Plasmid preparations from the indicated strains were separated by electrophoresis through a 0.3% agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide. cp26 and cp26* are indicated by white circles and asterisks, respectively, to the left of the bands. Lanes: M, markers (sizes in kilobases); 1, B31; 2, B31-9; 3, B31-82; 4, B31-34.
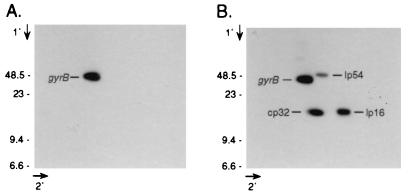
In the case of the guaB heterozygote, two-dimensional agarose gel electrophoresis of B. burgdorferi plasmid DNA showed that a gyrB probe hybridized to a single species of plasmid DNA (Fig. 3A), which comigrated in the first dimension with cp26*. Subsequent hybridization of the blot with probes derived from cp32, lp16, and lp54 showed that the hybridizing DNA behaved as a large circular molecule, since it migrated more slowly than cp32 in the first dimension and was retarded from the linear axis in the second dimension (Fig. 3B).
FIG. 3.
Southern blot analysis of two-dimensional gel of guaB heterozygote plasmid DNA. (A) B31-80.74 plasmid DNA was electrophoresed through 0.3% agarose before and after being soaked in chloroquine and rotated 90°. DNA was transferred to a nylon membrane and sequentially hybridized with probes derived from guaB (A) and then cp32 (orf12-13), lp16 (p5 [3]), and lp54 (ospA) (B). Marker sizes are in kilobases.
Confirmation that cp26* is a dimer.
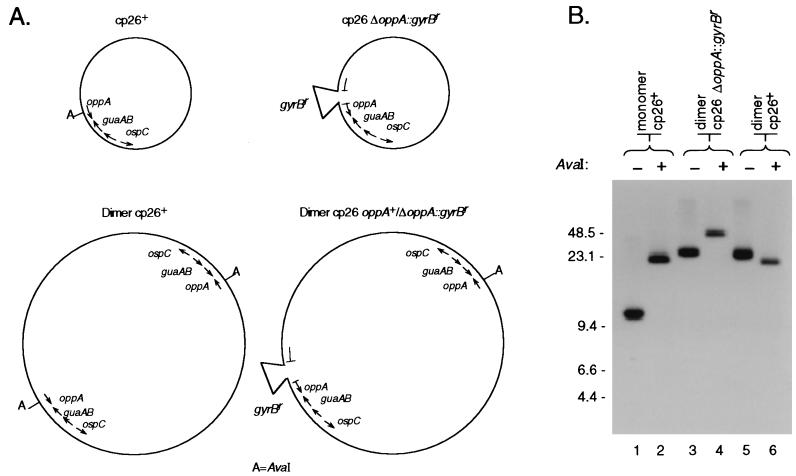
Confirming that cp26* is actually a dimer plasmid required that the two versions be distinguishable by a molecular technique. In the case of the plasmid heterozygous for the oppAIV mutation, the unique AvaI site in cp26 (7, 14) was deleted during mutant construction (Fig. 4A). Because of this, digesting a cp26 dimer containing wild-type and mutant copies of oppAIV with AvaI should yield a linear band of about 52 kb, in contrast to the 26-kb band formed by digesting wild-type cp26 (Fig. 4A). A 52-kb band hybridized to the cp26 probe after AvaI digestion of B31-34 DNA (Fig. 4B), confirming that cp26* was a dimer in this case. The cp26* of B31-9, which has no mutations, migrated with approximately the same mobility as was found for the cp26* of B31-34, but AvaI digestion yielded a band identical to that for the clone with normal cp26 (B31-86) (Fig. 4B), as expected, since both copies of oppAIV in cp26* of B31-9 retained the AvaI site. Similar results were obtained with the guaB heterozygote B31-80 (data not shown).
FIG. 4.
AvaI digestion patterns of various plasmid preparations. (A) Schematic showing the positions of AvaI sites on wild-type and ΔoppAIV::gyrBr cp26. (B) Southern blot analysis of uncut and AvaI-digested cp26 and cp26* from wild-type bacteria and ΔoppAIV::gyrBr mutants. Plasmid preparations from the indicated clones were electrophoresed through a 0.3% agarose gel with (+) or without (−) AvaI digestion. DNA was transferred to a nylon membrane and hybridized with a guaA probe (Table 2). Lanes: 1 and 2, B31-86; 3 and 4, B31-34; 5 and 6, B31-9. Marker sizes are in kilobases.
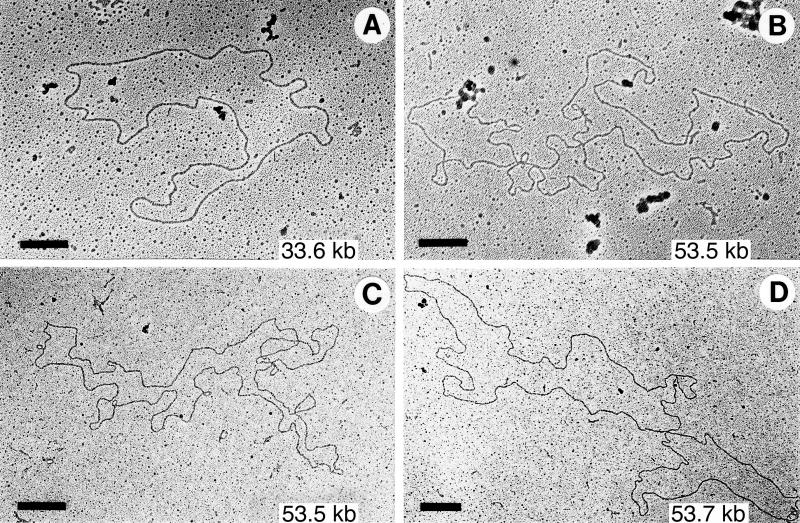
Since it was not possible to show by linearization that cp26* from guaB and ospC heterozygotes or B31-9 were dimers, we directly examined their DNA by electron microscopy after eluting the cp26* regions from agarose gels. In all of these cases, in addition to that of the oppAIV heterozygote cp26, we were able to find circular supercoiled molecules of 52 to 57 kb. With gentle DNase nicking, relaxed molecules of 52 to 57 kb were observed in DNA from the cp26* region for the guaB and ospC heterozygotes (Fig. 5). No supercoiled or relaxed molecules of greater than 50 kb were observed in the corresponding fraction of DNA derived from wild-type B31 bacteria. The simplest interpretation of all of these results is that the cp26* represents circular cp26 dimers. The AvaI digestion patterns suggest that the dimers have head-tail structures, as depicted in Fig. 4A.
FIG. 5.
Electron micrographs of DNA eluted from the cp26 and cp26* regions of agarose gels. DNA was nicked with DNase before spreading for microscopy. Sources of molecules: (A) cp26 region (which is difficult to resolve from the cp32 region) from wild-type B31 DNA; (B) cp26* region from a guaB heterozygote; (C and D) cp26* region from an ospC heterozygote. Bars = 0.5 μM.
Dimer stability assessment.
The oppAIV, guaB, and ospC heterozygote dimers appeared to be stable, since 100% of the colonies derived from a single colony remained heterozygous. To roughly measure stability of the oppAIV heterozygote plasmid, a culture of B31-34 was grown for 20 passages (120 to 130 generations) without coumermycin. After plating in the absence of coumermycin, single colonies were tested for their oppAIV genotypes, using PCR with primers flanking the insertion-deletion site (7). Ninety-one percent retained both wild-type and mutant oppAIV loci, whereas 9% had just the mutant locus. All of the homozygous mutant colonies had monomer cp26. No colonies had only the wild-type oppAIV locus, although such bacteria should have been viable during growth in culture without selection for the presence of the gyrBr locus. When the ospC heterozygote B31-2 was grown up again and replated (an additional 30 generations), all of 34 colonies tested remained heterozygous.
Allelic exchange with dimer plasmid as a source of mutant DNA.
We previously found that transforming with total B. burgdorferi mutant plasmid DNA, which has extensive sequence flanking the gyrBr insertion site, resulted in a higher frequency of allelic exchange than recombinant plasmid DNA derived from E. coli, even if the B. burgdorferi DNA had been digested with an enzyme that linearizes cp26 (23). These results suggested that transformation with circular B. burgdorferi plasmids led to recombination with the resident cp26, rather than displacement of the resident plasmid. Having heterozygous mutant dimer cp26 allowed us to readdress the question of displacement versus recombination, since donor and recipient DNA could be easily distinguished by PCR. We used plasmid DNA derived from bacteria containing monomer oppAIV mutant cp26 or oppAIV heterozygous dimer cp26 to transform a clone of B31 that had only monomer cp26. Single coumermycin-resistant colonies were tested by PCR for the presence of the mutant oppA gene. Whether the donor DNA was monomer or dimer, the frequency of allelic exchange was about 7% of the transformants (Table 3). The proportion of these mutants with dimer plasmids was the same (20 to 25%) whether monomer or dimer cp26 was used as the donor DNA (Table 3). These results support our hypothesis that the transforming DNA does not displace the resident plasmid, but rather recombines using the homologous flanking sequences.
TABLE 3.
Transformation with monomer or dimer cp26
| Donor DNA | No./total tested (%)
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Cour transformants with gyrBr at plasmid locus | Mutants with dimer cp26 | |
| Dimer | 5/76 (6.6) | 1/5 (20) |
| Monomer | 4/60 (6.7) | 1/4 (25) |
Source of dimer plasmids.
We identified dimer plasmids after transformation because they are heterozygous for the mutation being screened, but we had not assessed the frequency of dimer plasmids in a normal population of B. burgdorferi. To do this, we prepared plasmids from cultures derived from individual colonies of B31 (about half of which were derived from control electroporations with no DNA that had been plated without coumermycin) and analyzed them by agarose gel electrophoresis. We found that none of 38 B31 clones tested had dimer cp26, showing that the frequency with which we obtained cp26 dimers after transformation did not reflect their frequency within untransformed bacteria.
Since cp26 dimers were not detected in a normal population of B31 bacteria, we tested to see if a coumermycin-resistant strain was more likely to contain plasmid dimers. We found that none of 22 colonies derived from a coumermycin-resistant clone (with gyrBr at the chromosomal gyrB locus) had dimer cp26. These results show that the frequency of cp26 dimer formation was not significantly increased by the presence of the gyrBr allele.
DISCUSSION
This report describes experiments showing that dimers of cp26 arise at a surprisingly high frequency after transformations of B. burgdorferi B31. We have used this knowledge to readdress the mechanism of transformation with B. burgdorferi plasmid DNA, in studies that confirm that transforming DNA recombines with resident DNA, rather than displacing it, even if the donor DNA is capable of doing so.
Although we have not identified the mechanism by which dimers arise, we hypothesize that only a small subpopulation of the cells in a transformation is proficient for recombination. In this case, transformants that have undergone two separate recombination events would be found at a higher than expected frequency, meaning that dimers would be overrepresented in bacteria in which allelic exchange and gene conversion are likely. We assume that dimers are formed by recombination, although other mechanisms have not been excluded. This model explains a number of our findings, including why we were unable to find dimers in untransformed bacteria, while 20 to 50% of transformants had dimer cp26. Also explained by this model is how dimers would be isolated after transformation with small fragments of B. burgdorferi DNA cloned into E. coli plasmids, which are unable to generate dimers by recombining with the resident DNA. This model predicts that recombination events involving multiple plasmids, or plasmids and the chromosome, might be common in transformants. Our finding of B31-9, a coumermycin-resistant clone that had dimer cp26 without any targeted mutation on cp26 (which presumably had independent recombination events involving the chromosome and cp26), is consistent with the existence of a recombinationally active subpopulation. When a second selectable marker for use in B. burgdorferi genetic studies becomes available, we will be able to further test this model by determining the frequencies of double allelic exchange events involving either single or multiple plasmids.
Another potential source of heterozygosity in cp26 would be catenanes, with interlocked molecules of wild-type and mutant plasmids. Catenanes of 26- and 29-kb circular plasmids were observed previously (30), and the presence in our strains of an altered form of gyrase, an enzyme that breaks and rejoins DNA, might lead to higher levels of such molecules. Catenanes are clearly excluded in the case of the oppAIV heterozygote, because AvaI digestion yielded a 52-kb linear molecule, and seem unlikely to explain our other results, since large circular molecules were seen by electron microscopy of cp26* (Fig. 5). Differences between the previous study and ours in the method of plasmid purification may explain why we have not found catenanes in our DNA preparations.
Two other descriptions of B. burgdorferi sensu lato plasmid dimers have been published (19, 20). Restriction analysis of a 9.2-kb circular plasmid in isolate CT1 showed that the plasmid appeared to be a tandem duplication of a 4.6-kb sequence (19), but no further studies of this plasmid have been published. Dimers were also described for the linear plasmid known as lp54 (20). The lp54 dimers in B. japonica isolate HO14 could have been formed by incomplete resolution of replication intermediates or by recombination in the terminal inverted repeats of the plasmids. In both cases, plasmid dimers are characteristic of the isolate and did not arise during the course of experimentation. Although interesting, these previous reports do not clarify the mechanisms of formation or maintenance of cp26 dimers.
The stability of the cp26 plasmid dimers is surprising, since they are essentially tandem 26-kb duplications. We have not measured the stability of the wild-type cp26 dimers found in B31-9, since we cannot distinguish monomer from dimer by a simple method. This dimer is probably also stable, since Southern hybridization of a plasmid preparation by using a cp26 probe does not detect cp26 migrating at the monomer position (data not shown), excluding a high frequency of monomerization. Some plasmids from other bacteria carry site-specific recombination systems specifically designed to reduce multimers to monomers and thereby increase plasmid stability (35). If present, such a system seems to be ineffective on cp26 dimers, given their stability in the dimer state.
A plasmid heterozygous for a mutation on cp26 may confer a selective advantage for growth in culture over the respective homozygous mutant. We are testing this hypothesis by creating isogenic mutants derived from a clone of B31, in which we can compare the growth rates of homozygous and heterozygous mutants. Dimers of cp26 are also not lost from the cell at a detectable frequency, perhaps because cp26 contains genes essential for growth in culture, since it is omnipresent in B. burgdorferi isolates.
Dimer plasmids are obviously useful for genetic studies in B. burgdorferi, especially with the few available genetic tools. The spontaneous generation of the cp26 dimers, as was found among our mutant and control strains, should provide us with heterozygotes, even after transforming strains containing monomer cp26. In attempts to inactivate essential genes, inability to recover homozygous mutant strains, either after transformation or after nonselective growth, would be evidence that the targeted gene was essential. When both heterozygous and homozygous mutant strains are obtained (as we have found for guaB, ospC, and oppAIV inactivation), the heterozygous strain serves as a useful complemented control for phenotypic analysis.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
We thank George Weinstock, Sherwood Casjens, Brian Stevenson, James Bono, and Abdallah Elias for helpful discussions. Carol Carter, Brian Stevenson, and James Bono provided probes. Scott Samuels helped formulate the strategy for guaB inactivation and provided the oligonucleotide primers used in amplifying the gyrBr gene. Robert Evans and Gary Hettrick prepared the figures, and Beth Fischer helped with the electron micrograph figure. We thank Tom Schwan, Joe Hinnebusch, Michael Chaussee, Brian Stevenson, James Bono, and Scott Samuels for comments on the manuscript.
REFERENCES
- 1.Barbour A G. Plasmid analysis of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. J Clin Microbiol. 1988;26:475–478. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.3.475-478.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Barbour A G. Linear DNA of Borrelia species and antigenic variation. Trends Microbiol. 1993;1:236–239. doi: 10.1016/0966-842x(93)90139-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Barbour A G, Carter C J, Bundoc V, Hinnebusch J. The nucleotide sequence of a linear plasmid of Borrelia burgdorferi reveals similarities to those of circular plasmids of other prokaryotes. J Bacteriol. 1996;178:6635–6639. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.22.6635-6639.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Barbour A G, Garon C F. Linear plasmids of the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi have covalently closed ends. Science. 1987;237:409–411. doi: 10.1126/science.3603026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Baril C, Richaud C, Baranton G, Saint Girons I. Linear chromosome of Borrelia burgdorferi. Res Microbiol. 1989;140:507–516. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90083-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bishop C, Rankine D M, Talbott J H. The nucleotides in normal human blood. J Biol Chem. 1959;234:1233–1237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bono J L, Tilly K, Stevenson B, Hogan D, Rosa P. Oligopeptide permease in Borrelia burgdorferi: putative peptide-binding components encoded by both chromosomal and plasmid loci. Microbiology. 1998;144:1033–1044. doi: 10.1099/00221287-144-4-1033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Casjens S, DeLange M, Ley H L, III, Rosa P, Huang W M. Linear chromosomes of Lyme disease agent spirochetes: genetic diversity and conservation of gene order. J Bacteriol. 1995;177:2769–2780. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.10.2769-2780.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Casjens S, Huang W M. Linear chromosomal physical and genetic map of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. Mol Microbiol. 1993;8:967–980. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Clewell D B. Bacterial sex pheromone-induced plasmid transfer. Cell. 1993;73:9–12. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90153-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Davidson B E, MacDougall J, Saint Girons I. Physical map of the linear chromosome of the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi 212, a causative agent of Lyme disease, and localization of rRNA genes. J Bacteriol. 1992;174:3766–3774. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3766-3774.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.de Silva A M, Fikrig E. Growth and migration of Borrelia burgdorferi in Ixodes ticks during blood feeding. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1995;53:397–404. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1995.53.397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ferdows M S, Barbour A G. Megabase-sized linear DNA in the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989;86:5969–5973. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Fraser C M, Casjens S, Huang W M, Sutton G G, Clayton R, Lathigra R, White O, Ketchum K A, Dodson R, Hickey E K, Gwinn M, Dougherty B, Tomb J-F, Fleischmann R D, Richardson D, Peterson J, Kerlavage A R, Quackenbush J, Salzberg S, Hanson M, van Vugt R, Palmer N, Adams M D, Gocayne J, Weidmann J, Utterback T, Watthey L, McDonald L, Artiach P, Bowman C, Garland S, Fujii C, Cotton M D, Horst K, Roberts K, Hatch B, Smith H O, Venter J C. Genomic sequence of a Lyme disease spirochaete, Borrelia burgdorferi. Nature. 1997;390:580–586. doi: 10.1038/37551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Garon C. Electron microscopy of nucleic acids. In: Chirikjian J, Papas T, editors. Gene amplification and analysis. New York, N.Y: Elsevier/North-Holland; 1981. pp. 573–589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Garon C. Electron microscopy of nucleic acids. In: Aldrich H, Todd D, editors. Ultrastructure techniques for microorganisms. New York, N.Y: Plenum Publishing Corporation; 1986. pp. 161–181. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Grossman A D, Ireton K, Hoff E F, LeDeaux J R, Rudner D Z, Magnuson R, Hicks K A. Signal transduction and the initiation of sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. Semin Dev Biol. 1991;2:31–36. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hinnebusch J, Barbour A G. Linear- and circular-plasmid copy numbers in Borrelia burgdorferi. J Bacteriol. 1992;174:5251–5257. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.16.5251-5257.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hyde F W, Johnson R C. Characterization of a circular plasmid from Borrelia burgdorferi, etiologic agent of Lyme disease. J Clin Microbiol. 1988;26:2203–2205. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.10.2203-2205.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Marconi R T, Casjens S, Munderloh U G, Samuels D S. Analysis of linear plasmid dimers in Borrelia burgdorferi sensu lato isolates: implications concerning the potential mechanism of linear plasmid replication. J Bacteriol. 1996;178:3357–3361. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.11.3357-3361.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Marconi R T, Samuels D S, Garon C F. Transcriptional analyses and mapping of the ospC gene in Lyme disease spirochetes. J Bacteriol. 1993;175:926–932. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.4.926-932.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Margolis N, Hogan D, Tilly K, Rosa P A. Plasmid location of Borrelia purine biosynthesis gene homologs. J Bacteriol. 1994;176:6427–6432. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.21.6427-6432.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rosa P, Samuels D S, Hogan D, Stevenson B, Casjens S, Tilly K. Directed insertion of a selectable marker into a circular plasmid of Borrelia burgdorferi. J Bacteriol. 1996;178:5946–5953. doi: 10.1128/jb.178.20.5946-5953.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sadziene A, Wilske B, Ferdows M S, Barbour A G. The cryptic ospC gene of Borrelia burgdorferi B31 is located on a circular plasmid. Infect Immun. 1993;61:2192–2195. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2192-2195.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Samuels D S. Electrotransformation of the spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi. In: Nickoloff J A, editor. Methods in molecular biology. Totowa, N.J: Humana Press, Inc.; 1995. pp. 253–259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Samuels D S, Garon C F. Coumermycin A1 inhibits growth and induces relaxation of supercoiled plasmids in Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993;37:46–50. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.1.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Samuels D S, Mach K E, Garon C F. Genetic transformation of the Lyme disease agent Borrelia burgdorferi with coumarin-resistant gyrB. J Bacteriol. 1994;176:6045–6049. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.19.6045-6049.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Schwan T G, Burgdorfer W, Garon C F. Changes in infectivity and plasmid profile of the Lyme disease spirochete, Borrelia burgdorferi, as a result of in vitro cultivation. Infect Immun. 1988;56:1831–1836. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1831-1836.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schwan T G, Piesman J, Golde W T, Dolan M C, Rosa P A. Induction of an outer surface protein on Borrelia burgdorferi during tick feeding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:2909–2913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.7.2909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Simpson W J, Garon C F, Schwan T G. Analysis of supercoiled circular plasmids in infectious and non-infectious Borrelia burgdorferi. Microb Pathog. 1990;8:109–118. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(90)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Solomon J M, Lazazzera B A, Grossman A D. Purification and characterization of an extracellular peptide factor that affects two different developmental pathways in Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 1996;10:2014–2024. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.16.2014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sonenshine D E. Biology of ticks. New York, N.Y: Oxford University Press; 1991. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Tilly K, Casjens S, Stevenson B, Bono J L, Samuels D S, Hogan D, Rosa P. The Borrelia burgdorferi circular plasmid cp26: conservation of plasmid structure and targeted inactivation of the ospC gene. Mol Microbiol. 1997;25:361–373. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.4711838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wirth R, Muscholl A, Wanner G. The role of pheromones in bacterial interactions. Trends Microbiol. 1996;4:96–103. doi: 10.1016/0966-842X(96)81525-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Yarmolinsky M B, Sternberg N. Bacteriophage P1. In: Calendar R, editor. The bacteriophages. New York, N.Y: Plenum Publishing Corporation; 1988. pp. 291–438. [Google Scholar]