Correction : Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2018) 23:29 10.1186/s11658-018-0095-z
Following publication of the original article [1], the authors informed us that there is in Fig. 3C. The pictures used in the AngII and AngII + Negative groups in Fig. 3C were repeated. Neither of these changes affects the results and conclusions of this study.
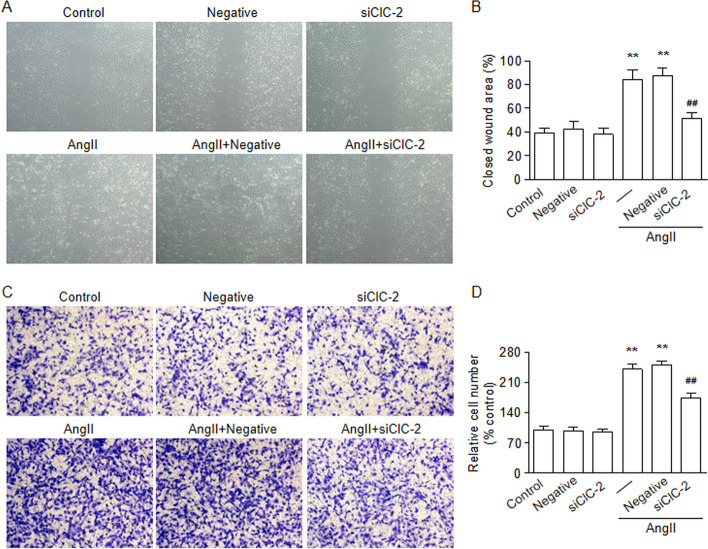
The correct Fig. 3 is given below:
Fig. 3.
ClC-2 downregulation prevented AngII-induced HBVSMC migration and invasion. a HBVSMCs transfected with ClC-2 siRNA (siClC-2; 20 nM) or negative siRNA (negative; 20 nM) were subjected to angiotensin II (AngII) treatment (10 − 7 M). The wound healing assay was performed. Representative images are shown (× 100). b The quantification results for the wound closure. c HBVSMC migration was examined via transwell analysis. Representative images are shown (× 100). d The columns represent the relative numbers of invasive cells. **p < 0.01 vs. control, ##p < 0.01 vs. AngII alone, n = 6
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Reference
- 1.Lu J, Xu F, Zhang Y, Lu H, Zhang J. ClC-2 knockdown prevents cerebrovascular remodeling via inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2018;23:29. doi: 10.1186/s11658-018-0095-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]