In the published article, there was a missing citation of “The Crosstalk Between Tumor Cells and the Immune Microenvironment in Breast Cancer: Implications for Immunotherapy, doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.610303”in the legend for Figure 1 as published. The corrected Figure 1 legend appears below.
Figure 1.
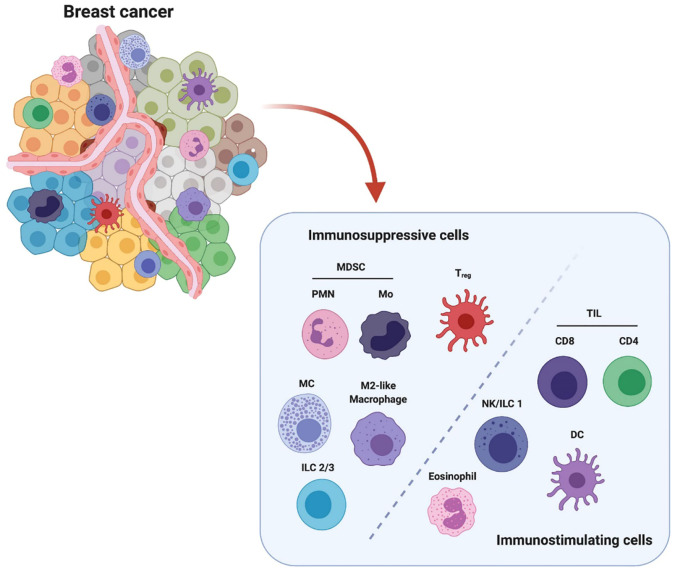
Breast cancer microenvironment is populated by diverse infiltrating immune cells. These immune cells are categorized into immunosuppressive population and immunostimulating population (e.g.) according to their major characteristics in modulating breast cancer. The immunosuppressive cells include polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells (PMN-MDSCs), monocytic MDSC (Mo-MDSC), regulatory T cells (Treg), mast cells (MC), M2-like macrophages and type 2/3 innate lymphoid cells (ILC 2/3). The immunostimulating cells include tumor infiltrating lymphocytes CD8+ and CD4+ T cells, nature killer cells/type 1 innate lymphoid cells (NK/ILC1), dendritic cells (DCs) and eosinophils. This figure is reproduced with permission from “The Crosstalk Between Tumor Cells and the Immune Microenvironment in Breast Cancer: Implications for Immunotherapy, doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.610303” Copyright ©2021 Frontiers.
The authors apologize for this error and state that this does not change the scientific conclusions of the article in any way. The original article has been updated.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.