Abstract
Several thousand plant species, including many economically important food plants, synthesize cyanogenic glycosides and cyanolipids. Upon tissue disruption, these natural products are hydrolyzed liberating the respiratory poison hydrogen cyanide. This phenomenon of cyanogenesis accounts for numerous cases of acute and chronic cyanide poisoning of animals including man. This article reviews information gathered during the past decade about the enzymology and molecular biology of cyanogenesis in higher plants. How compartmentation normally prevents the large-scale, suicidal release of HCN within the intact plant is discussed. A renewed interest in the physiology of these cyanogenic compounds has revealed that, in addition to providing protection for some species against herbivory, they may also serve as storage forms for reduced nitrogen.
Full text
PDF
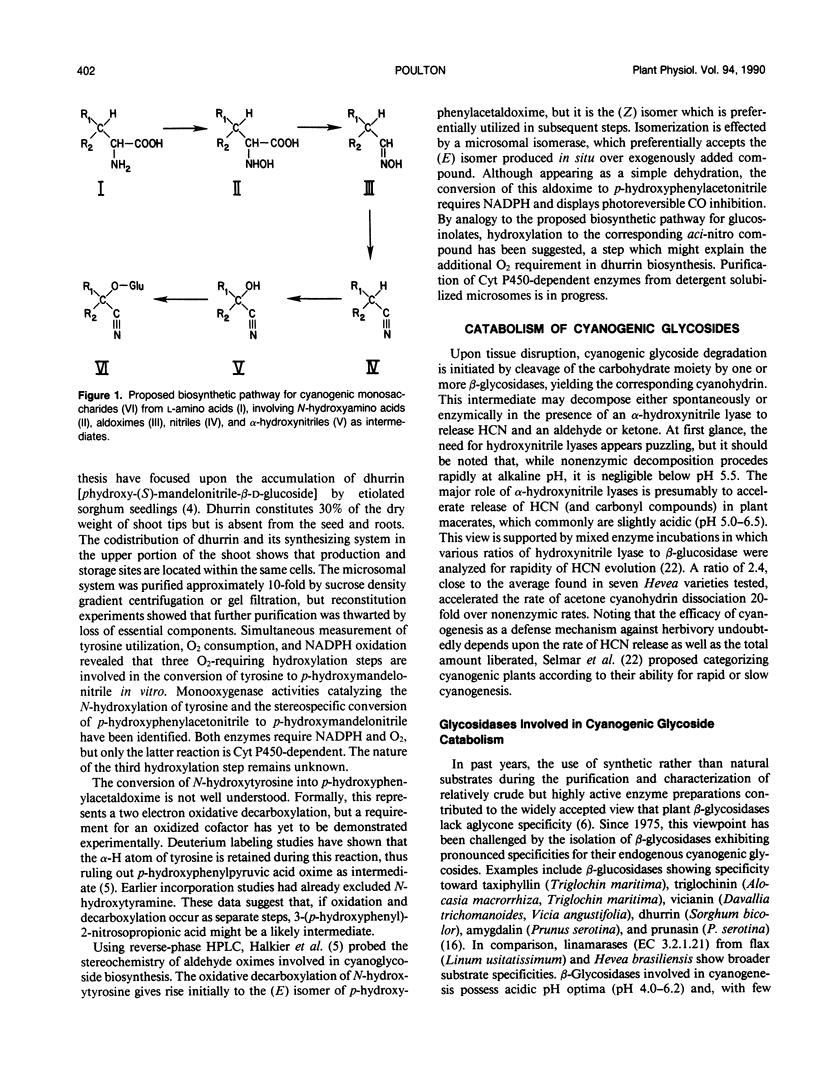



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fan T. W., Conn E. E. Isolation and characterization of two cyanogenic beta-glucosidases from flax seeds. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Dec;243(2):361–373. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90513-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frehner M., Conn E. E. The Linamarin beta-Glucosidase in Costa Rican Wild Lima Beans (Phaseolus lunatus L.) Is Apoplastic. Plant Physiol. 1987 Aug;84(4):1296–1300. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.4.1296. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halkier B. A., Olsen C. E., Møller B. L. The biosynthesis of cyanogenic glucosides in higher plants. The (E)- and (Z)-isomers of p-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde oxime as intermediates in the biosynthesis of dhurrin in Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19487–19494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halkier B. A., Scheller H. V., Møller B. L. Cyanogenic glucosides: the biosynthetic pathway and the enzyme system involved. Ciba Found Symp. 1988;140:49–66. doi: 10.1002/9780470513712.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes M. A., Sharif A. L., Dunn M. A., Oxtoby E. The molecular biology of cyanogenesis. Ciba Found Symp. 1988;140:111–130. doi: 10.1002/9780470513712.ch8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kende H. Enzymes of ethylene biosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 1989 Sep;91(1):1–4. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima M., Iwatsuki N., Data E. S., Villegas C. D., Uritani I. Changes of cyanide content and linamarase activity in wounded cassava roots. Plant Physiol. 1983 May;72(1):186–189. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.1.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima M., Poulton J. E., Thayer S. S., Conn E. E. Tissue Distributions of Dhurrin and of Enzymes Involved in Its Metabolism in Leaves of Sorghum bicolor. Plant Physiol. 1979 Jun;63(6):1022–1028. doi: 10.1104/pp.63.6.1022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki G. W., Conn E. E. Mandelonitrile lyase from Ximenia americana L.: stereospecificity and lack of flavin prosthetic group. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6978–6981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmar D., Grocholewski S., Seigler D. S. Cyanogenic Lipids: Utilization during Seedling Development of Ungnadia speciosa. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jun;93(2):631–636. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.2.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selmar D., Lieberei R., Biehl B. Mobilization and utilization of cyanogenic glycosides: the linustatin pathway. Plant Physiol. 1988 Mar;86(3):711–716. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


