Abstract
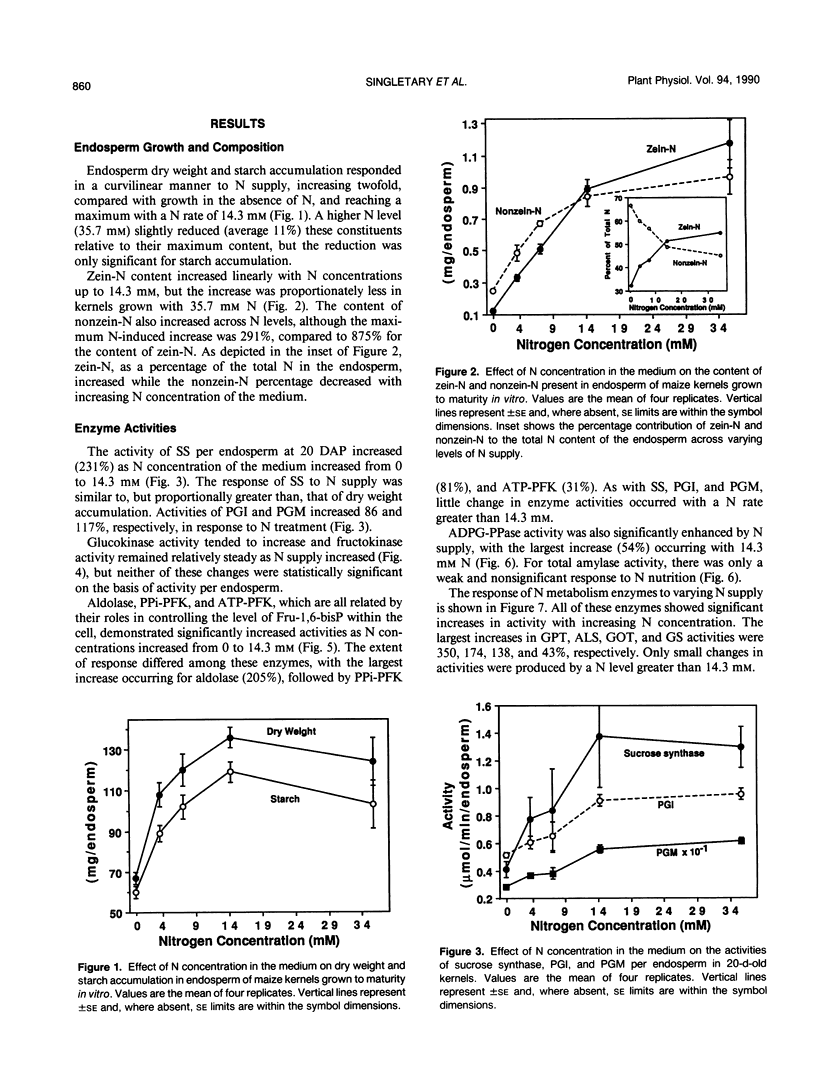
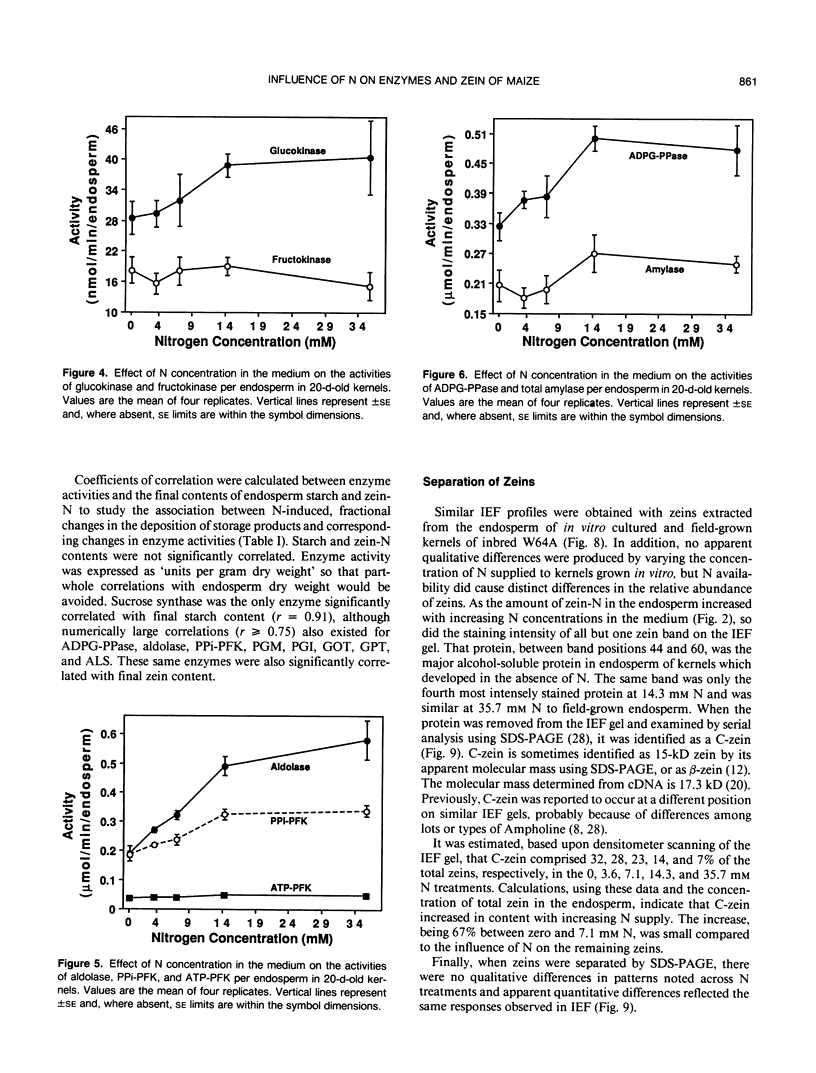
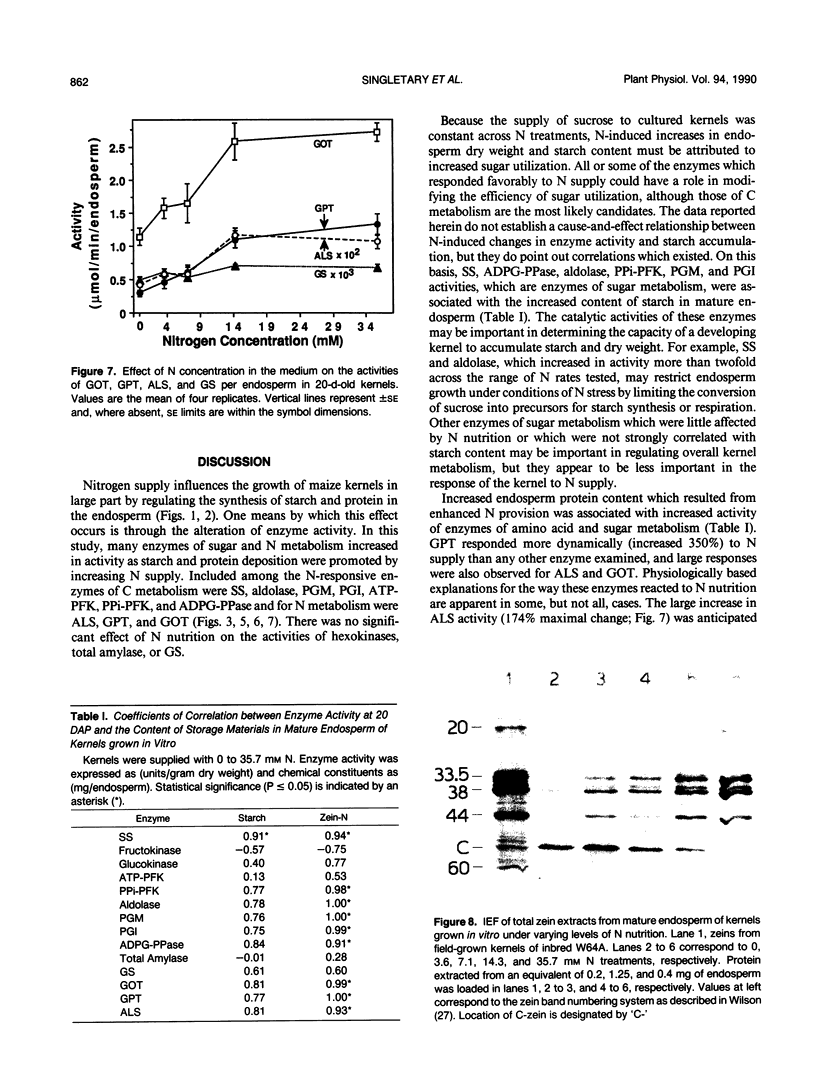
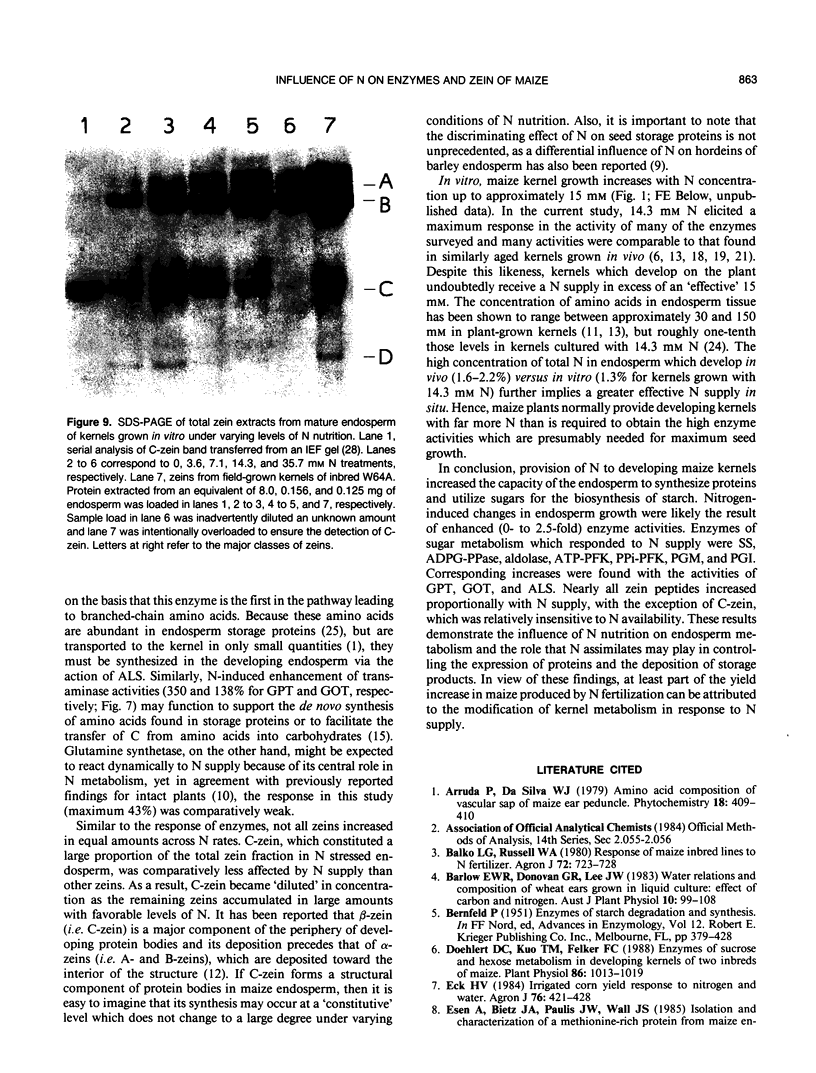
To examine the effects of N nutrition upon endosperm development, maize (Zea mays) kernels were grown in vitro with either 0, 3.6, 7.1, 14.3, or 35.7 millimolar N. Kernels were harvested at 20 days after pollination for determination of enzyme activities and again at maturity for quantification of storage products and electrophoretic separation of zeins. Endosperm dry weight, starch, zein-N, and nonzein-N all increased in mature kernels as N supply increased from zero to 14.3 millimolar. The activities of sucrose synthase, aldolase, phosphoglucomutase, glutamate-pyruvate transaminase, glutamate-oxaloacetate transaminase, and acetolactate synthase increased from 1- to 2.5-fold with increasing N supply. Adenosine diphosphate-glucose pyrophosphorylase and both ATP- and PPi-dependent phosphofructokinases increased to lesser extents, while no significant response was detected for hexose kinases and glutamine synthetase. Nitrogen-induced changes in enzyme activities were often highly correlated with changes in final starch and/or zein-N contents. Separation of zeins indicated that these peptides were proportionately enhanced by N supply, with the exception of C-zein, which was relatively insensitive to N. These data indicate that at least a portion of the yield increase in maize produced by N fertilization is induced by a modification of kernel metabolism in response to N supply.
Full text
PDF


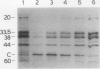
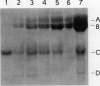
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Doehlert D. C., Kuo T. M., Felker F. C. Enzymes of sucrose and hexose metabolism in developing kernels of two inbreds of maize. Plant Physiol. 1988 Apr;86(4):1013–1019. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.4.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lending C. R., Larkins B. A. Changes in the zein composition of protein bodies during maize endosperm development. Plant Cell. 1989 Oct;1(10):1011–1023. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.10.1011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra S., Oaks A. Glutamine metabolism in corn kernels cultured in vitro. Plant Physiol. 1985 Mar;77(3):520–523. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.3.520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhitch M. J. Acetolactate Synthase Activity in Developing Maize (Zea mays L.) Kernels. Plant Physiol. 1988 Jan;86(1):23–27. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ou-Lee T. M., Setter T. L. Enzyme activities of starch and sucrose pathways and growth of apical and Basal maize kernels. Plant Physiol. 1985 Nov;79(3):848–851. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K., Argos P., Naravana S. V., Larkins B. A. Sequence analysis and characterization of a maize gene encoding a high-sulfur zein protein of Mr 15,000. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6279–6284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singletary G. W., Below F. E. Growth and composition of maize kernels cultured in vitro with varying supplies of carbon and nitrogen. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):341–346. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singletary G. W., Below F. E. Nitrogen-induced changes in the growth and metabolism of developing maize kernels grown in vitro. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jan;92(1):160–167. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. Y., Huber D. M., Warren H. L. A proposed role of zein and glutelin as N sinks in maize. Plant Physiol. 1980 Aug;66(2):330–333. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. M. Serial analysis of zein by isoelectric focusing and sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. Plant Physiol. 1986 Sep;82(1):196–202. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.1.196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]