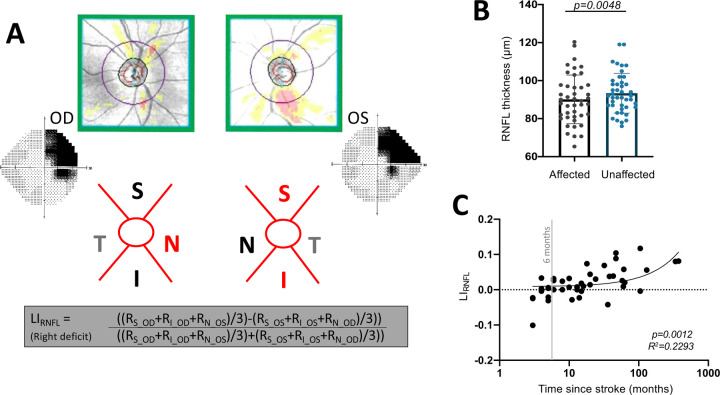
Figure 2.
A: Computation of LI using RNFL thickness values (R) from superior (S) and inferior (I) peripapillary regions comprised of uncrossed fibers, and nasal (N) peripapillary regions comprised of crossed fibers representing intact or blind hemifields. B: Plot comparing affected peripapillary RNFL segments carrying RGC axons representing the visual field defect to unaffected carrying predominantly intact field fibers (paired t-test, CI95 =1.046 to 5.450, t42 = 2.977, p = 0.0048). C: Plot of LIRNFL against time since stroke (linear regression, R2=0.2293, CI95=− 0.0004 to 0.0217, p=0.0012).