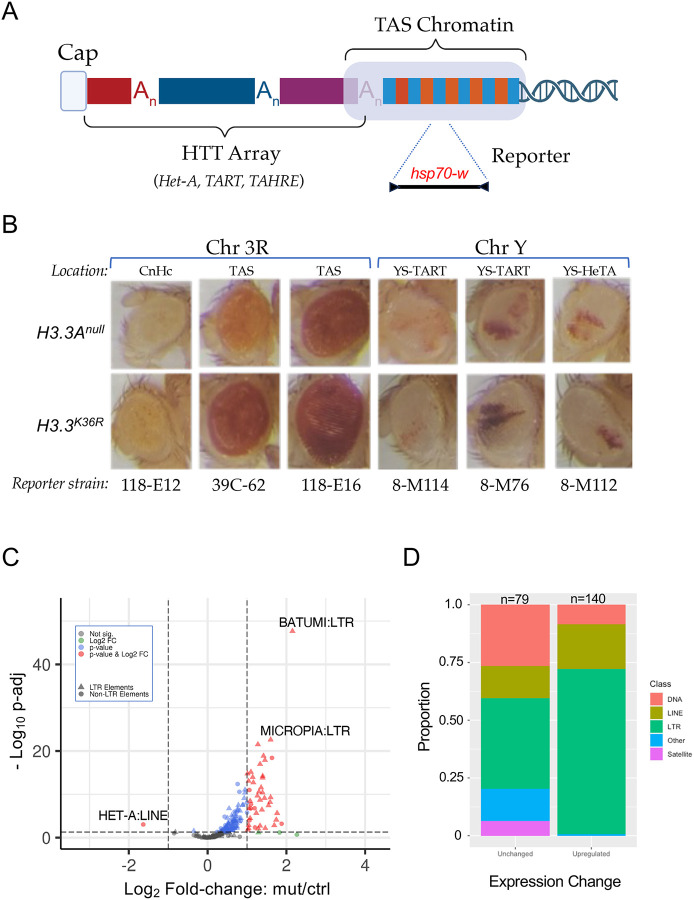
Figure 6. Telomeric position effect and transposable element expression analysis.
(A) Cartoon depicting key features of Drosophila telomeres. At the distal end of the telomere, a capping complex assembles adjacent to arrays of Het-A, TAHRE, and TART retrotransposons (HTT array). Proximal to that is the TAS (Telomere Associated Sequence) Chromatin, which is characterized by the presence of complex satellite repeats that vary by chromosome. (B) Images of adult eyes. For each column, representative examples are shown for a particular reporter strain. Rows correspond to genotype (H3.3Anull control or H3.3K36R mutant). The location and type of chromatin for each reporter strain is also indicated: Pericentric heterochromatin (CnHc), Telomere Associated Sequences (TAS), YS-TART (Y chromosome TART), and YS-HeTA (Y chromosome HeT-A). n-values for each experiment ranged from 16 to 44, see Fig. S5 for details. (C) Volcano plot of annotated transposable elements (TEs) analyzed using the TEcounts tool within TEtranscripts. Each dot or triangle represents the combined reads from all loci for a given TE subtype. Dotted lines represent significance cutoffs for adjusted p-value and Log2 fold-change. Symbols are color coded according to the key in the upper left. LTR-type transposons are represented by triangles, non-LTR elements are shown as dots. (D) Stacked bar graph, binned by whether TEs were upregulated or unchanged in the H3.3K36R mutant. The relative proportion of a given type of transposable element (DNA, LINE, LTR, Satellite, and Other) in each bin are shaded as indicated in the legend.