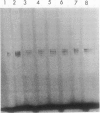
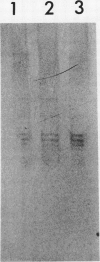
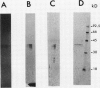
Abstract
A lactate dehydrogenase activity is present in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings and roots. Under aerobic conditions, lactate dehydrogenase activity is barely detectable in rice seedlings and is very low in rice roots. In 30 day old roots, the activity is increased two to three times by an anoxic or hypoxic treatment and can be detected on immunoblots by an antiserum raised against barley lactate dehydrogenase. The activity present in aerobic seedlings was partially purified. The native enzyme has a molecular mass of 160 kilodaltons, and is a tetramer of 2 subunit (38 and 39 kilodaltons) randomly associated. Studies of substrate specificity, native gel electrophoresis, and immunoblot analysis indicate that the partially purified enzyme is a typical lactate dehydrogenase. However, no increase of lactate dehydrogenase activity or protein was observed in seedlings transferred to anoxia.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeling M. Simultaneous induction by anaerobiosis or 2,4-D of multiple enzymes specificed by two unlinked genes: differential Adh1-Adh2 expression in maize. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Dec 31;127(3):215–227. doi: 10.1007/BF00333761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson A. D., Jacobsen J. V. Control of lactate dehydrogenase, lactate glycolysis, and alpha-amylase by o(2) deficit in barley aleurone layers. Plant Physiol. 1984 Jul;75(3):566–572. doi: 10.1104/pp.75.3.566. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman N. E., Bent A. F., Hanson A. D. Induction of lactate dehydrogenase isozymes by oxygen deficit in barley root tissue. Plant Physiol. 1986 Nov;82(3):658–663. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.3.658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman N. E., Hanson A. D. Purification and properties of hypoxically induced lactate dehydrogenase from barley roots. Plant Physiol. 1986 Nov;82(3):664–670. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond P., Al-Ani A., Pradet A. ATP Production by Respiration and Fermentation, and Energy Charge during Aerobiosis and Anaerobiosis in Twelve Fatty and Starchy Germinating Seeds. Plant Physiol. 1985 Nov;79(3):879–884. doi: 10.1104/pp.79.3.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. K., Andrade F. H., Anderson I. C. Further Evidence that Cytoplasmic Acidosis Is a Determinant of Flooding Intolerance in Plants. Plant Physiol. 1985 Feb;77(2):492–494. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.2.492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. K., Callis J., Jardetzky O., Walbot V., Freeling M. Cytoplasmic acidosis as a determinant of flooding intolerance in plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6029–6033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. K., Callis J., Wemmer D., Walbot V., Jardetzky O. Mechanisms of cytoplasmic pH regulation in hypoxic maize root tips and its role in survival under hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3379–3383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs M. M., Freeling M., Okimoto R. The anaerobic proteins of maize. Cell. 1980 Jul;20(3):761–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]