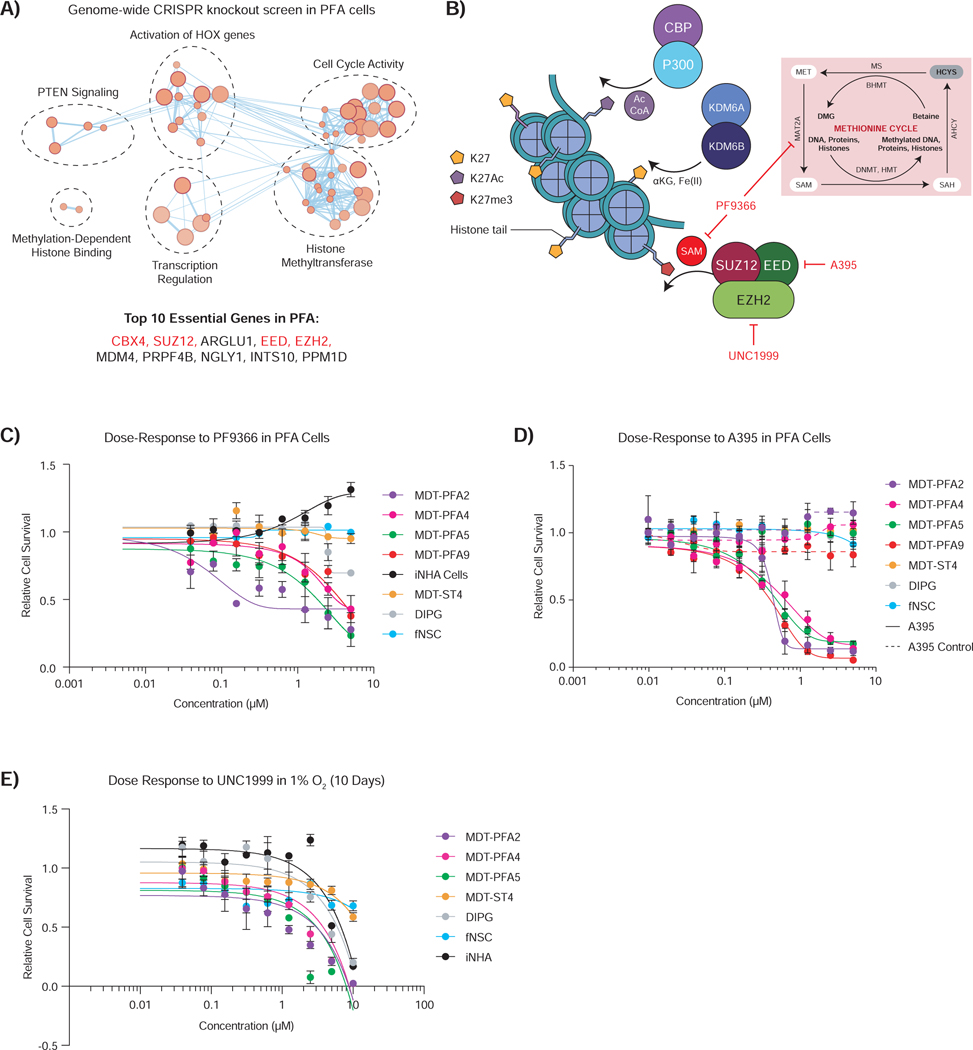
Figure 6 – Paradoxically, inhibition of the PRC2 complex also shows activity against PFA ependymoma.
A) Pathway analysis of significantly essential genes by genome-wide CRISPR knockout essentiality screen in PFA cells compared to GBM cells (z-score, p-value < 0.05). The top 10 hits ranked by average difference of quantile normalized Bayes Factor between PFA and GBM screens are listed. Genes associated with the PRC2 complex are denoted in red.
B) Cartoon depicting several mechanisms of K27 modification active in PFA ependymoma. Targeted inhibition of MAT2A by PF9366 and the PRC2 complex components EED and EZH2 by A395 and UNC1999 respectively are depicted.
C) Dose-dependent inhibition (7 days) of MAT2A by PF9366 inhibits SAM production, resulting in diminished PFA cell survival, while simultaneously augmenting iNHA control cell survival in 1% O2. ST, DIPG and fNSC control lines showed no effect upon treatment.
D) Dose-dependent inhibition (7 days) of EED by A395 diminishes PFA cell survival in 1% O2. An inactive analog of the A395 probe (dashed) did not affect PFA cell survival. ST, DIPG and fNSC control lines showed no effect upon treatment.
E) Dose-dependent inhibition (10 days) of EZH2 by UNC1999 diminishes PFA cell survival in 1% O2. ST, DIPG and fNSC control lines showed no effect upon treatment.
Curves show logistic regression line of fit for C-E.