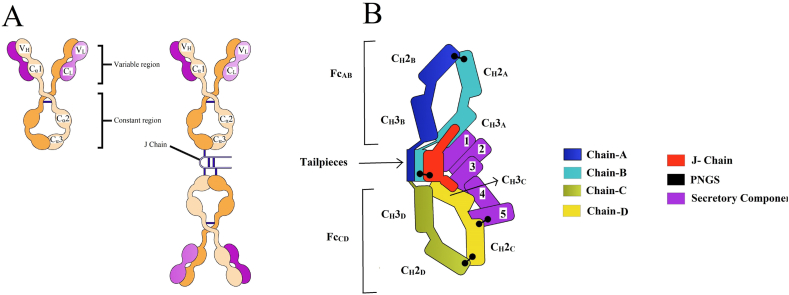
Fig. 1.
Monomeric and dimeric IgA. A) Left: The monomeric IgA (mIgA). The heavy chains are shown in orange and the light chains in purple. V: Variable region, C: Constant region. Right: The dimeric IgA (dIgA). dIgA contains the joining chain (J-CHAIN) linked by two disulfide bonds to the Fc region in the two different monomers. B) Schematic representation of the complex structure of SIgA with the secretory component. Chain names and corresponding CH domains and Fcs are labeled with SC domains (1–5). Each SIgA component is depicted in a unique color. This figure is based on recently published papers [46]. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)