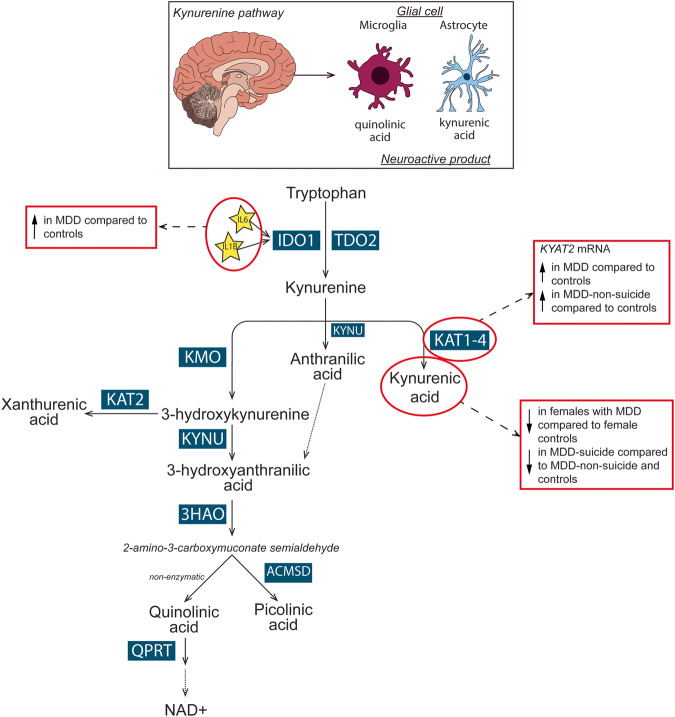
Fig. 4. Overview of the kynurenine pathway in the brain and key findings in MDD.
In the brain, tryptophan can be metabolised in glial cells via the kynurenine pathway. Dependent on the cell type different neuroactive metabolites will be produced. Predominantly in microglia, kynurenine is metabolised into quinolinic acid whereas kynurenic acid is primarily produced in astrocytes. In the anterior cingulate cortex, IL6, IL1B and KYAT2 mRNAs were increased in major depressive disorder (MDD) overall. KYAT2 mRNA was increased in MDD subjects that did not die by suicide in comparison to controls. Kynurenic acid was decreased in females with MDD in comparison to female controls and was decreased in MDD subjects that died by suicide in comparison to MDD-non-suicide and controls. Abbreviations: 3-HAO 3-hydroxyanthranilate 3,4-dioxygenase, ACMSD α-amino-β-carboxymuconate-ε-semialdehyde, IDO1 indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase, IL interleukin, KAT kynurenine aminotransferase, KMO kynurenine 3-monoxygenase, KYNU kynurinase, MDD major depressive disorder, NAD+ nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, TDO tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase, QPRT quinolinic acid phosphoribosyltransferase.