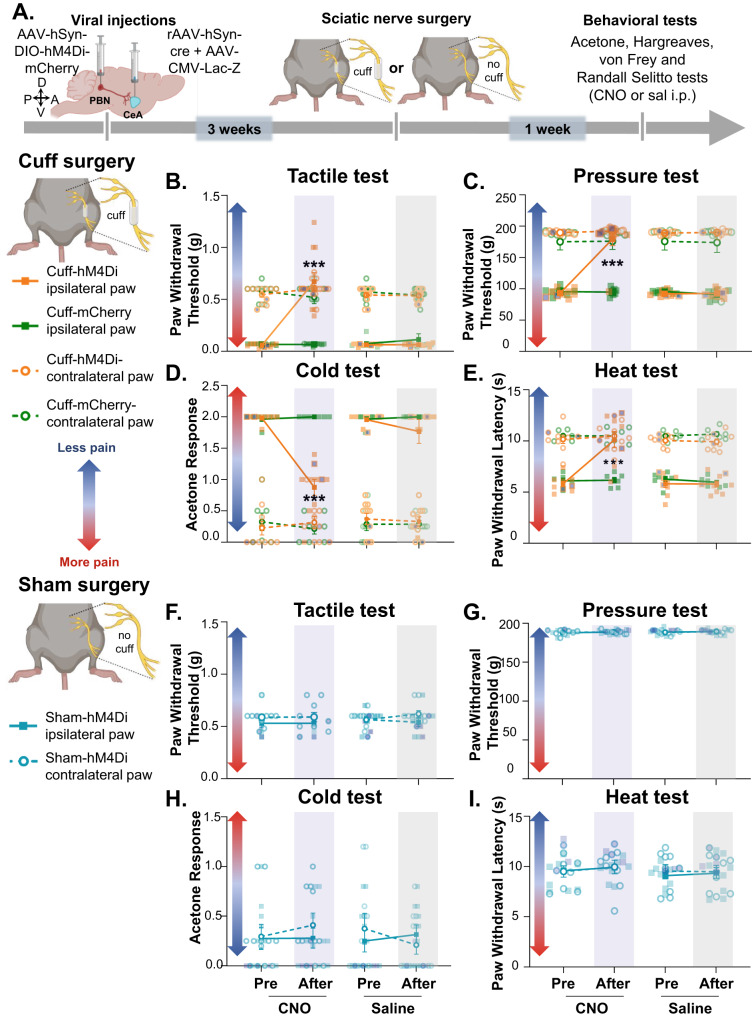
Fig. 3. Chemogenetic inhibition of CeA-projecting PBN neurons reverses nerve injury-induced hypersensitivity without affecting baseline nociception.
A Experimental timeline. Male and female C57BL/6J mice were stereotaxically co-injected with AAV8-hSyn-DIO-hMD4i or AAV8-hSyn-DIO into the right PBN and a mix (1:1) of AAV.hSyn.HI.eGFP-Cre and pAAV.CMV.LacZ.bGH into the right CeA. Sciatic nerve surgery was performed 3 weeks after viral injections. Following 1 week of recovery, von Frey, Randall-Selitto, Acetone and Hargreaves tests were used to address sensitivity to tactile, deep tissue pressure, cold and heat stimulation, respectively, in the hind paws ipsilateral and contralateral to cuff and sham treatment. Mice were intraperitoneally (i.p.) injected with CNO or saline prior to behavior testing in a counterbalanced way. Paw withdrawal threshold in response to tactile (B, F) or deep tissue pressure (C, G) stimulation, acetone response score (D, H) and paw withdrawal latency after heat stimulation (E, I) of the hind paw ipsilateral or contralateral to cuff (B–E) and sham(F–I) treatment before and 30 min after i.p. injection of CNO (blue bar) or saline (gray bar). n = 10 mice for cuff-hM4Di and sham-hM4di (2 females and 8 males), n = 9 mice for cuff-mCherry for both, ipsilateral and contralateral paws in all tests. Two-way repeated measures ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; ***p < 0.001 for before and after CNO in the ipsilateral paw of cuff-hMd4i mice; Individual mice are represented by scatter points and female mice are identified in purple. All data are presented as means ± SEM.