Abstract
Background
Orthodontic relapse can be defined as the tendency for teeth to return to their pre‐treatment position, and this occurs especially in lower front teeth (lower canines and lower incisors). Retention, to maintain the position of corrected teeth, has become one of the most important phases of orthodontic treatment. However, 10 years after the completion of orthodontic treatment, only 30% to 50% of orthodontic patients effectively retain the satisfactory alignment initially obtained. After 20 years, satisfactory alignment reduces to 10%. When relapse occurs, simple effective strategies are required to effectively manage the problem. The periodontal, physiological or psychological conditions may be different from those before orthodontic treatment, so re‐treatment methods may also need to be different.
Objectives
To assess the effects of interventions used to manage relapse of the lower front teeth after first fixed orthodontic treatment.
Search methods
The following electronic databases were searched: the Cochrane Oral Health Group Trials Register (to 9 November 2012), the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library 2012, Issue 10), MEDLINE via OVID (1950 to 9 November 2012), EMBASE via OVID (1980 to 9 November 2012). There were no restrictions regarding language or date of publication. A thorough handsearch was done in relation to the following journals: American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics (1970 to 9 November 2012), Angle Orthodontist (1978 to 9 November 2012), European Journal of Orthodontics (1979 to 9 November 2012), Journal of Orthodontics (1978 to 9 November 2012), Chinese Journal of Stomatology (1953 to 9 November 2012), West China Journal of Stomatology (1983 to 9 November 2012), Chinese Journal of Dental Materials and Devices (1992 to 9 November 2012) and Chinese Journal of Orthodontics (1994 to 9 November 2012).
Selection criteria
We would have included randomised controlled trials (RCTs) which compared any of the following: fixed options (including labial braces, lingual braces and fixed lingual wire), removable options (including Hawley's retainer with active components such as Hawley's retainer with spring elastomeric module, Bloore removable aligner and any other modifications on the Hawley's retainer to correct the lower front teeth, and invisible removable aligners such as Invisalign and Clearstep) and no active treatment for the management of relapsed lower front teeth after orthodontic treatment. We excluded RCTs of participants with craniofacial deformities/syndromes or serious skeletal deformities who received prior surgical/surgical orthodontic treatment.
Data collection and analysis
Two review authors, independently and in duplicate, assessed the results of the searches to identify studies for inclusion. The Cochrane Collaboration statistical guidelines were to be followed for data synthesis.
Main results
We did not identify any RCTs which met the inclusion criteria for this review.
Authors' conclusions
This review has revealed that there was no evidence from RCTs to show that one intervention was superior to another to manage the relapse of the alignment of lower front teeth using any method or index, aesthetic assessment by participants and practitioners, treatment time, patient's discomfort, quality of life, cost‐benefit considerations, stability of the correction, and side effects including pain, gingivitis, enamel decalcification and root resorption. There is an urgent need for RCTs in this area to identify the most effective and safe method for managing the relapse of alignment of the lower front teeth.
Plain language summary
Treatment options to manage relapse of lower front teeth after orthodontic treatment
Review question The main question addressed by this review is how effective are fixed braces or removable retainers for managing relapse of lower front teeth after orthodontic treatment, compared to each other or no treatment.
Background An important problem for patients completing orthodontic treatment is maintaining their lower front teeth in the corrected position (known as managing relapse) and preventing teeth from returning to their original positions. After orthodontic treatment, less than half of patients maintain alignment of their lower front teeth for the next 10 years, and even fewer (10%) maintain alignment for 20 years. Managing relapse is important in order to avoid wasting time, money and resources, and to maintain both the appearance and function of well‐aligned teeth. There are two types of appliances (retainers) used to manage relapse; retainers which are fixed to the teeth or retainers able to be removed for cleaning.
The most commonly used fixed retainers are:
• normal braces that have brackets attached to the lips‐side of teeth (labial braces); • braces with brackets attached to the tongue‐side of teeth (lingual braces); or • a fixed flexible wire attached to the tongue‐side of teeth without using brackets.
The most common removable retainers are:
• retainers made from wire and acrylic (Hawley’s retainer), with or without the addition of springs to apply force; or • clear 'invisible' aligners, free from metal brackets and wires, which are computer‐generated to fit over the patient's lower teeth and move teeth in order.
Study characteristics This review of existing studies was carried out by the Cochrane Oral Health Group and the evidence is current up to 9 November 2012.
In this review there are no trials published between 1950 and 2012 in which patients were randomly treated with either fixed braces, removable retainers or no treatment.
Key results No trials were found that were suitable for inclusion in this review.
Quality of the evidence Currently there is no evidence to support using one form of treatment for managing relapse over another.
Background
Description of the condition
Orthodontic relapse can be defined as the tendency for teeth to return to their pre‐treatment position (Rygh 1988), and this particularly occurs in the lower front teeth (lower canines and lower incisors). Retention, to maintain teeth in their corrected position, has become one of the most important phases of orthodontic treatment (Rygh 1988; Joondeph 1994), however, studies have revealed that there was an unsatisfactory long‐term alignment of the lower front teeth following orthodontic treatment (Shah 2003).
Post‐treatment alignment (assessed by Little's irregularity index (Figure 1) Little 1975) may be maintained in only 30% to 50% of orthodontic patients over 10 years (Little 1981; Artun 1996). Another study, which followed up patients 20 years after treatment, found only 10% of treatments could be considered clinically satisfactory (Little 1988).
1.
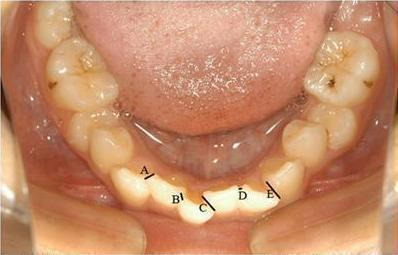
Little's irregularity index (= A + B + C + D + E). This photograph was taken by the review authors, in reference to Little 1975.
Certain critical factors may contribute to the relapse of the lower front teeth. These include reorganisation of the periodontal tissue (Boese 1980; Southard 1992), decrease of the crestal alveolar bone level (Sharpe 1987), overexpansion of the arch dimension (Rossouw 1993; Kahl‐Nieke 1995; Canut 1999), occlusal changes due to mandibular growth, eruption of the third mandibular molars (Perera 1987; Richardson 1994; Hansen 1997; Al‐Balkhi 2004), type of malocclusion being treated and adverse effects of tooth movement during treatment (Moss 1980a; Moss 1980b).
Description of the intervention
When relapse occurs, simple yet effective strategies are required to manage the problem. The periodontal, physiological or psychological conditions after treatment may be different from those before treatment, so the re‐management methods may also need to be different.
The following are alternative strategies to manage the relapse of the lower front teeth.
Fixed options
Labial braces (Figure 2): Labial braces are conventional braces where the patient's brackets are placed on the outer surfaces of the teeth. This may be the most effective method to re‐treat the lower front teeth, but patients may be reluctant to go through the whole procedure again due to aesthetic or other concerns.
Lingual braces (Figure 3): Lingual orthodontics came into existence as a viable option for orthodontic patients in 1970s with the pioneering works of Craven Kurz of USA and Kinya Fujita of Japan (Kurz 1998). The lingual orthodontic system is an almost invisible kind of orthodontic therapy in which braces are placed behind the teeth. It has been used to treat nearly all kinds of malocclusion, such as: impacted maxillary canine (Chaushu 2008); bimaxillary protrusion (Kawakami 2004); severe skeletal Class III with crowding; severe class II, division 2 (Pauls 2008); deep‐bite (Carano 2001); open bite (Fillion 1997), and so on. Lingual orthodontic treatment outcomes have become similar and comparable to those produced by labial orthodontic treatment (Gorman 1991; Pauls 2010; Grauer 2011). Compared to the conventional buccal appliances, the lingual orthodontic system has many advantages (Poon 1998; van der Veen 2010): invisibility (these appliances provide the ultimate in aesthetics for patients), better biomechanics, improved patient compliance, more predictable 'bodily' movement and fewer white spot lesions. However, it also has many disadvantages (Sinclair 1986; Poon 1998; Hohoff 2003; Caniklioglu 2005; Wu 2011): difficult to clean, higher rating of tongue pain, more oral discomfort, dietary changes, swallowing difficulty, speech disturbances, social problems, more clinical chair‐side time, and cost. Taking account of the merits and shortcomings, patients may hope to find another more comfortable, and also invisible, appliance to correct the relapse of their lower front teeth.
Fixed lingual wire (Figure 4): A nickel titanium (NiTi) mandibular bonded lingual 3‐3 retainer can be used to re‐treat the lower front teeth without the use of lingual brackets. The patients are seen once a month and the ligature wires are retied, changed, or removed as needed. After completion of the re‐treatment, the ligature wires are removed and the NiTi arch wires are left in situ for permanent retention. The NiTi mandibular bonded lingual 3‐3 retainer may be an effective tool for resolving the relapse of the lower front teeth rapidly. It does not require patient compliance or the use of brackets (Liou 2001).
2.
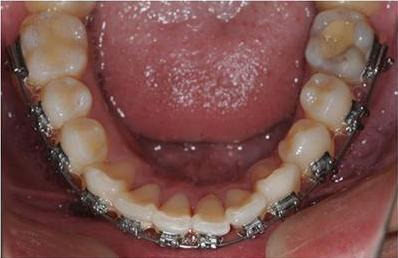
Labial braces. This photograph was taken by the review authors.
3.
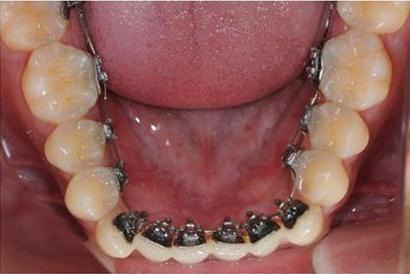
Lingual braces. This photograph was taken by the review authors.
4.
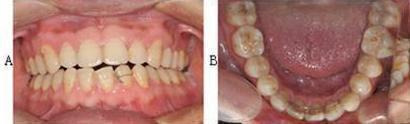
Fixed lingual wire. Clinical application of fixed lingual flexible wire to re‐correct lower front teeth in a 31‐year‐old male. A: Front view after placing the fixed lingual flexible wire. B: Occlusal surface view after placing the fixed lingual flexible wire. These photographs were taken by the review authors, in reference to Liou 2001.
Removable options
Hawley's retainer with active component
Hawley's retainer with spring elastomeric module (Figure 5): Removable spring retainers like the Hawley's retainer can be used to correct rotations and buccolingual malpositions. First, the Hawley's retainer is drilled on the place matching the malpositioned teeth, and then the elastomeric module is placed on the hole. After the retainer is fixed, the teeth will align. Fixed retainers can then be bonded on the teeth (Cureton 1996).
Bloore removable aligner (Figure 6): The Bloore removable aligner can control and move any incisor due to the addition of lingual 0.026 inch eyelet arm springs and 0.030 inch and 0.045 inch stainless steel reinforcing wires. Requirements for successful use of this technique include: good posterior occlusion, incisor crowding of no more than 2.5 mm, adequate crown anatomy, incisor apices in adequate positions, and healthy periodontium (Bloore 1998).
Other kinds with modifications on the Hawley's retainer to correct the lower front teeth, such as adding hyperbolic lingual springs to the Hawley's retainer.
5.
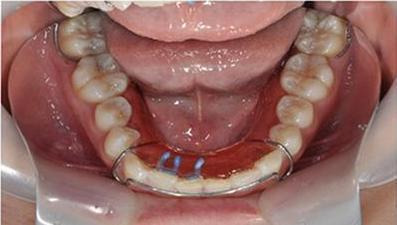
Hawley's retainer with spring elastomeric module. Figure depicts a 29‐year‐old female, whose right central incisor is rotated mesial‐in and right lateral incisor is labial‐lingual malpositioned. The picture shows the occlusal review after placing the Hawley's retainer with spring elastomeric module. Adjustment of the outer bow of the retainer allows facial movement of the incisors and assists in the rotation and alignment. This photograph was taken by the review authors, in reference to Cureton 1996.
6.
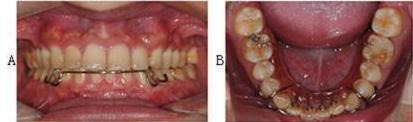
Bloore removable aligner. Clinical application of Bloore removable aligner to treat the relapse of lower front teeth. This figure shows Bloore removable aligner prior to activation of 0.026 inch eyelet arm springs. A: Front view after placing the Bloore Removable Aligner. B: Occlusal surface view after placing the Bloore removable aligner. These photographs were taken by the review authors, in reference to Bloore 1998.
Invisible removable aligners
Invisalign (Figure 7): In 1999, AIign Technology Inc addressed the demand for an aesthetic alternative to brackets by developing an invisible method of orthodontic treatment that uses a series of computer‐generated clear removable aligners to move the dentition. Since then, Invisalign has been used to treat over 300,000 orthodontic patients with a variety of malocclusions. The primary benefit of the Invisalign system is the superior aesthetic during treatment compared to metal brackets. Other advantages of the system include: the ability to remove aligners to eat, brush and floss, the superior comfort, and ease of use (Invisalign 2006). Based on case reports, this technique appears effective in treating mild malocclusions and is more visually appealing than conventional brackets (Joffe 2003). Align Technology Inc claims that 90% of orthodontic patients are candidates for Invisalign. These include patients with mild to moderate crowding, mild to moderate spacing, non‐skeletal constricted arches, and those who have experienced relapse after fixed appliance therapy (Vlaskalic 2001).
Clearstep: This is a type of invisible appliance, similar to Invisalign, which is easy to wear and attractive to look at. It is mainly worn for cosmetic purposes, as it is unnoticeable when worn over the teeth. This appliance is worn for a period of two weeks before being removed and replaced with a new brace. This process is repeated until the teeth have moved into the correct position. Compared to Invisalign, ClearStep positioners are smooth and have no ridges, making them more hygienic and very easy to clean.
7.
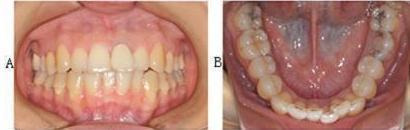
Invisalign. Clinical application of Invisalign to re‐retreat the mandibular anterior crowding teeth. As figures show this appliance is invisible. A: Front view after placing the Invisalign. B: Occlusal surface view after placing the Invisalign. These photographs were taken by the review authors.
No active treatment
If the relapse of the lower front teeth is minimal, intervention may not be required. Some patients may choose to accept a small degree of relapse.
Why it is important to do this review
While labial braces and lingual braces may be the most effective method to correct relapse of lower front teeth, their use may be undesirable and painful for patients, and the chances of root resorption are high, together with other side effects. Fixed lingual wire, Hawley's retainer with spring elastomeric module, or Bloore removable aligner are potentially simpler and cheaper, but they may not be as effective as fixed appliances. Invisalign and Clearstep may address the demand for an aesthetic alternative to brackets, but could prove to be a very expensive option for the patient. The option of not having any further intervention does not expose the patient to any detrimental side effects, but it does not provide a solution to the problem of the relapse of the lower front teeth.
Re‐managing the lower front teeth to correct relapse has been regarded as an additional, extended period of active treatment, which is often associated with substantial additional costs, hence consideration should be given to its cost‐benefit ratio. This systematic review is important to evaluate the merits, shortcomings and costs of each of the re‐management options.
Objectives
To asses the effects of the different interventions used to manage relapse of the lower front teeth after first fixed orthodontic treatment.
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
We would only have included randomised controlled trials (RCTs) in this review.
Types of participants
We would have included RCTs of participants who previously underwent orthodontic treatment, with subsequent crowding of the lower front teeth (lower incisors and lower canines). We would have excluded RCTs of participants with craniofacial deformities/syndromes or serious skeletal deformities who received prior surgical/orthodontic treatment.
Types of interventions
We would have assessed the following interventions: fixed options (including labial braces, lingual braces and fixed lingual wire), removable options (including Hawley's retainer with active components such as Hawley's retainer with spring elastomeric module, Bloore removable aligner and any other modifications on the Hawley's retainer to correct the lower front teeth and invisible removable aligners such as Invisalign and Clearstep) and no active treatment. All interventions would have been compared against each other in any combination.
Types of outcome measures
Primary outcomes
Assessment of the alignment of the lower front teeth using any method or index.
Secondary outcomes
Aesthetic assessment by participants and practitioners.
Treatment time.
Patient discomfort.
Quality of life.
Cost‐benefit consideration.
Stability of the correction.
We would have assessed adverse effects (including pain, gingivitis, enamel decalcification and root resorption).
Search methods for identification of studies
For the identification of studies included or considered for this review, detailed search strategies were developed for each database searched. These were based on the search strategy developed for MEDLINE (OVID) but revised appropriately for each database. The search strategy used a combination of controlled vocabulary and free text terms and was linked with the Cochrane Highly Sensitive Search Strategy (CHSSS) for identifying randomised controlled trials in MEDLINE: sensitivity maximising version (2011 revision) as detailed in box 6.4.c of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011) (Higgins 2011).
Electronic searches
We searched the following databases:
The Cochrane Oral Health Group's Trials Register (to 9 November 2012) (see Appendix 1)
The Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library 2012, Issue 10) (see Appendix 2)
MEDLINE (1950 to 9 November 2012) (see Appendix 3)
EMBASE (1980 to 9 November 2012) (see Appendix 4).
There were no restrictions on language or date of publication. Non‐English papers would have been translated.
Searching other resources
Handsearching
The following journals were handsearched as part of this review. We have read all the abstracts of these journals' papers.
American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics (1970 to 9 November 2012)
The Angle Orthodontist (1978 to 9 November 2012)
European Journal of Orthodontics (1979 to 9 November 2012)
Journal of Orthodontics (1978 to 9 November 2012)
Chinese Journal of Stomatology (1953 to 9 November 2012)
West China Journal of Stomatology (1983 to 9 November 2012)
Chinese Journal of Dental Materials and Devices (1992 to 9 November 2012)
Chinese Journal of Orthodontics (1994 to 9 November 2012)
Unpublished studies
We would have checked the reference lists of all eligible trials, review articles and conference proceedings for additional trials on the topic. We would have contacted the authors of RCTs to identify unpublished or ongoing trials.
Data collection and analysis
Selection of studies
Two review authors, independently and in duplicate, screened the titles, abstracts and keywords (when available) of all reports identified by the searching process. For studies appearing to meet the inclusion criteria or for which insufficient data existed in the title and abstract to make a clear decision, we would have obtained the full reports and assessed them independently and in duplicate. Disagreements would have been resolved by discussion. Where agreement could not be reached, a third review author would have been consulted. All studies meeting the inclusion criteria then would have undergone a risk of bias assessment and data would have been extracted. Studies rejected at this or subsequent stages would have been excluded and the reasons for exclusion would have been noted.
Data extraction and management
Data from eligible reports would have been extracted independently and in duplicate by two review authors using a previously piloted data extraction form. Any discrepancies between review authors in data extracted would have been resolved by discussion. Where agreement could not be reached, a third review author would have been consulted. Where the reported data were unclear, the authors of the studies would have been contacted for clarification.
Data extraction would have included the following: patients' characteristics (total number, age, sex, occupation, socioeconomic condition and diagnosis); methods (total study duration, sequence generation, allocation concealment, blinding of outcomes assessment, completeness of follow‐up, and the source of the information); interventions (specific description); outcomes (assessment of the alignment of the lower front teeth, aesthetic assessment after treatment by participants and practitioners, treatment time, patient discomfort, side effects, quality of life, cost‐benefit consideration and stability of the correction); results and relevant data. Study authors would have been contacted to provide missing data if necessary.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
Two review authors would have assessed the risk of bias in the included studies, independently and in duplicate, using The Cochrane Collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias as outlined in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011). Risk of bias would have been assessed and judged for six separate domains.
Sequence generation: was the allocation sequence adequately generated?
Allocation concealment: was allocation adequately concealed?
Blinding of outcome assessors: was knowledge of the allocated intervention adequately prevented during the study?
Incomplete outcome data: were incomplete outcome data adequately addressed?
Selective outcome reporting: were reports of the study free of suggestion of selective outcome reporting?
Other sources of bias: was the study apparently free of other problems that could put it at a high risk of bias?
Each study would have received a judgement of low risk, high risk or unclear risk of bias (indicating either lack of sufficient information to make a judgement or uncertainty over the risk of bias) for each of the six domains. We would have contacted the authors of the included studies for missing information if necessary. After taking into account the additional information provided by the authors of the trials, studies would have been grouped into the following categories:
Low risk of bias (plausible bias unlikely to seriously alter the results) if all key domains of the study were at low risk of bias
Unclear risk of bias (plausible bias that raises some doubt about the results) if one or more key domains of the study were unclear
High risk of bias (plausible bias that seriously weakens confidence in the results) if one or more key domains were at high risk of bias.
Measures of treatment effect
We would have analysed and reported data as described in Chapter 9 of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011). For dichotomous data (e.g. pain: yes/no), we would have calculated risk ratios (RR) and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs). For continuous data (e.g. pain on a visual analogue scale), we would have calculated the mean difference (MD) and 95% CIs. For ordinal data (e.g. quality of life: poor, reasonable, good or excellent), these would have been dichotomised, when appropriate, and then RRs and their 95% CIs would have been calculated accordingly.
Unit of analysis issues
The patient/participant would have been the unit of analysis.
Dealing with missing data
We would have contacted study authors to request missing data where necessary. If they could not provide the missing data, only the available data would have been analysed.
Assessment of heterogeneity
We would have assessed heterogeneity using a Chi² test and the I² statistic where I² values over 50% indicated substantial heterogeneity. We would have considered heterogeneity to be significant when the P value was less than 0.1 (Higgins 2011).
Assessment of reporting biases
If there had been more than 10 studies in any meta‐analyses, we would have investigated the possible presence of publication bias. For continuous outcomes with intervention effects measured using MDs, a test for funnel plot asymmetry, proposed by Egger et al (Egger 1997), would have been used. For dichotomous outcomes with intervention effects measured using RRs, we would have followed the methods proposed by Rücker et al (Rücker 2008).
Data synthesis
For statistical analysis of the study results, we would have followed the statistical guidance in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011). If there were studies of similar comparisons reporting the same outcomes, we would have used random‐effects models to pool the results in a meta‐analysis, providing that there were four or more studies. If there were less than four studies, the fixed‐effect model would have been used.
Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity
We would have performed subgroup analysis according to age, sex, occupation and socioeconomic condition, severity of the relapse of the lower front teeth and type of treatment.
Sensitivity analysis
If there were sufficient included studies, sensitivity analysis would have been undertaken excluding studies at high or unclear risk of bias.
Presentation of main results
A summary of findings table would have been developed for the primary outcomes of this review using GRADEPro software. The quality of the body of evidence would have been assessed with reference to the overall risk of bias of the included studies, the directness of the evidence, the inconsistency of the results, the precision of the estimates, the risk of publication bias and the magnitude of the effect. The quality of the body of evidence for each of the primary outcomes would have been categorised as high, moderate, low or very low.
Results
Description of studies
After deduplication, the electronic searching identified 527 publications. Although, after reviewing the titles and abstracts, none focused on interventions to correct the relapse of the lower front teeth, nor comparing such interventions against each other. The handsearching found several descriptive publications, some of which were mentioned in background, but there were no randomised controlled trials (RCTs) or ongoing trials. The process of study identification is presented in Figure 8.
8.
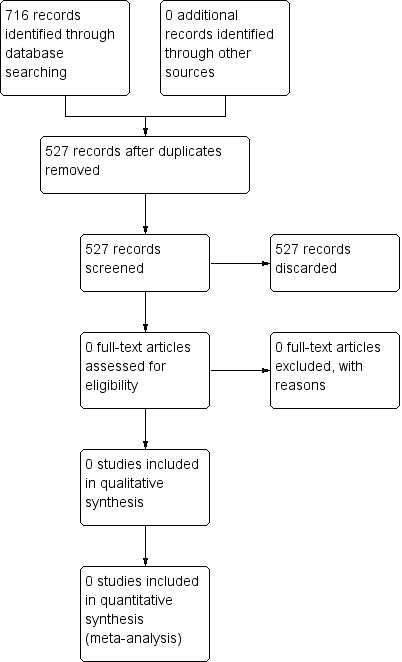
Study flow diagram
Risk of bias in included studies
No RCTs met the inclusion criteria for this review.
Effects of interventions
No RCTs met the inclusion criteria for this review.
Discussion
Summary of main results
Despite undertaking an extensive search of the literature (electronic searching, handsearching and identifying ongoing trials), there were no studies meeting the inclusion criteria for this review.
Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews
Only one publication was identified that addressed re‐treatment of relapsed front teeth. Liou et al conducted a small uncontrolled study of 18 patients treated for relapse of the lower front teeth using the 0.018 inch nickel‐titanium lingual retainer (Liou 2001). During the period of relapse, the irregularity index of the lower front teeth increased from 1.3 mm to 3.5 mm. After re‐treatment, the irregularity index decreased from 3.5 mm to 1 mm. This simple technique effectively solved relapse of the lower front teeth over a period of 4 months. This mandibular‐bonded lingual 3‐3 retainer could be used both actively, to re‐treat the crowding of the lower front teeth without the use of lingual brackets, and passively for maintenance as a bonded lingual retainer (Liou 2001).
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
There is no evidence from randomised controlled trials (RCTs) to guide orthodontists in selecting an effective method to treat relapse of alignment of lower front teeth following initial orthodontic treatment. The experience of the orthodontist will ultimately prove to be the deciding factor for selecting the best and most suitable form of intervention for treating the relapse of the lower anterior dentition.
Implications for research.
There is a need for rigorously conducted, and reported, RCTs to be undertaken to assess the effects of different approaches to orthodontic re‐treatment following relapse of lower front teeth alignment.
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 11 March 2014 | Review declared as stable | This empty review will not be updated until a substantial body of evidence on the topic becomes available. If trials are conducted and found eligible for inclusion in the future, the review would then be updated accordingly. |
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Anne Littlewood (Cochrane Oral Health Group) for her assistance with literature searching, Luisa Fernandez Mauleffinch and Philip Riley (Cochrane Oral Health Group) for their administrative support and Jayne Harrison for help with the preparation of this review.
Appendices
Appendix 1. Cochrane Oral Health Group Trials Register Search Strategy
((orthodontic* and (brace* or band* or wire* or appliance* or extract* or remov*)) AND (relaps* or recur* or retain* or retreat*))
Appendix 2. Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) Search Strategy
#1. MeSH descriptor Orthodontics explode all trees #2. MeSH descriptor Malocclusion this term only #3. (orthodontic* in All Text and (brace* in All Text or band* in All Text or wire* in All Text or device* in All Text)) #4. ("growth modif*" in All Text and (jaw* in All Text or maxilla* in All Text or mandible in All Text)) #5. (("fixed appliance*" in All Text and orthodontic* in All Text) or "activator* appliance*" in All Text) #6. ((extraoral in All Text or extra‐oral in All Text or "extra oral" in All Text) and traction in All Text) #7. ("chin cap*" in All Text or chin‐cap* in All Text or chincap* in All Text or "chin cup*" in All Text or chincup* in All Text or chin‐cup* in All Text) #8. (("face mask*" in All Text or facemask* in All Text or "reverse head‐gear" in All Text or "reverse head gear" in All Text) and orthodontic* in All Text) #9. ((orthopedic* in All Text or orthopaedic* in All Text) and (dental in All Text or orthodontic* in All Text or facial in All Text)) #10. MeSH descriptor TOOTH EXTRACTION explode all trees #11. ("lip bumper*" in All Text or lip‐bumper* in All Text) #12. "leeway space*" in All Text #13. ("arch develop*" in All Text and (jaw in All Text or mandib* in All Text)) #14. (extract* in All Text and (dental in All Text or teeth in All Text or tooth in All Text) and orthodontic* in All Text) #15. (remov* in All Text and (dental in All Text or teeth in All Text or tooth in All Text) and orthodontic* in All Text) #16. ((space* in All Text near/3 maintain* in All Text) and orthodontic* in All Text) #17. ((space* in All Text near/3 mainten* in All Text) and orthodontic* in All Text) #18. ((interceptive in All Text or correct* in All Text or prevent* in All Text) and orthodontic* in All Text) #19. (orthodontic* in All Text and (functional in All Text or removable in All Text) and appliance* in All Text) #20. MeSH descriptor TOOTH MIGRATION this term only #21. (postorthodontic* in All Text or post‐orthodontic* in All Text or "post orthodontic*" in All Text) #22. (relaps* in All Text or recurr* in All Text or retain* in All Text or reten* in All Text or retreat* in All Text) #23. (#1 or #2 or #3 or #4 or #5 or #6 or #7 or #8 or #9 or #10 or #11 or #12 or #13 or #14 or #15 or #16 or #17 or #18 or #19) #24. (#20 or #21 or #22) #25. (#23 and #24)
Appendix 3. MEDLINE (OVID) Search Strategy
exp ORTHODONTICS/
Malocclusion/
(orthodontic$ and (brace$ or band$ or wire$ or device$)).mp.
("growth modif$" and (jaw$ or maxilla$ or mandible)).mp.
(("fixed appliance$" and orthodontic$) or "activator$ appliance$").mp.
((extraoral or extra‐oral or "extra oral") and traction).mp.
("chin cap$" or chin‐cap$ or chincap$ or "chin cup$" or chincup$ or chin‐cup$).mp.
(("face mask" or facemask or "reverse head‐gear" or "reverse headgear") and orthodontic$).mp.
((orthopedic$ or orthopaedic$) and (dental or orthodontic$ or facial)).mp.
exp TOOTH EXTRACTION/
("lip bumper$" or lip‐bumper$).mp.
"leeway space$".mp.
("arch develop$" and (jaw or mandib$)).mp.
(extract$ and (dental or teeth or tooth) and orthodontic$).mp.
((space adj3 mainten$) and orthodontic$).mp.
((space adj3 maintain$) and orthodontic$).mp.
((interceptive or correct$ or prevent$) and orthodontic$).mp.
(orthodontic$ and (functional or removable) and appliance$).mp.
or/1‐18
INCISOR/
"lower anterior teeth".mp.
("mandibular anterior teeth" or "mandibular incisor$").mp.
"lower front teeth".mp.
or/20‐23
TOOTH MIGRATION/
(postorthodontic$ or post‐orthodontic$ or "post orthodontic$").mp.
(relaps$ or recurr$ or retain$ or retent$ or retreat$).mp.
or/25‐27
24 and 19 and 28
The above subject search was linked to the Cochrane Highly Sensitive Search Strategy (CHSSS) for identifying randomised trials in MEDLINE: sensitivity maximising version (2008 revision) as referenced in Chapter 6.4.11.1 and detailed in box 6.4.c of The Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011] (Higgins 2011)
1. randomized controlled trial.pt. 2. controlled clinical trial.pt. 3. randomized.ab. 4. placebo.ab. 5. drug therapy.fs. 6. randomly.ab. 7. trial.ab. 8. groups.ab. 9. or/1‐8 10. exp animals/ not humans.sh. 11. 9 not 10
Appendix 4. EMBASE (OVID) Search Strategy
exp ORTHODONTICS/
Malocclusion/
(orthodontic$ and (brace$ or band$ or wire$ or device$)).mp.
("growth modif$" and (jaw$ or maxilla$ or mandible)).mp.
(("fixed appliance$" and orthodontic$) or "activator$ appliance$").mp.
((extraoral or extra‐oral or "extra oral") and traction).mp.
("chin cap$" or chin‐cap$ or chincap$ or "chin cup$" or chincup$ or chin‐cup$).mp.
(("face mask" or facemask or "reverse head‐gear" or "reverse headgear") and orthodontic$).mp.
((orthopedic$ or orthopaedic$) and (dental or orthodontic$ or facial)).mp.
exp TOOTH EXTRACTION/
("lip bumper$" or lip‐bumper$).mp.
"leeway space$".mp.
("arch develop$" and (jaw or mandib$)).mp.
(extract$ and (dental or teeth or tooth) and orthodontic$).mp.
((space adj3 mainten$) and orthodontic$).mp.
((space adj3 maintain$) and orthodontic$).mp.
((interceptive or correct$ or prevent$) and orthodontic$).mp. [mp=title, original title, abstract, name of substance word, subject heading word]
(orthodontic$ and (functional or removable) and appliance$).mp.
or/1‐18
INCISOR/
"lower anterior teeth".mp.
("mandibular anterior teeth" or "mandibular incisor$").mp. [mp=title, original title, abstract, name of substance word, subject heading word]
"lower front teeth".mp.
or/20‐23
TOOTH MIGRATION/
(postorthodontic$ or post‐orthodontic$ or "post orthodontic$").mp.
(relaps$ or recurr$ or retain$ or retent$ or retreat$).mp.
or/25‐27
24 and 19 and 28
The above subject search was linked to the Cochrane Oral Health Group filter for EMBASE via OVID:
1. random$.ti,ab. 2. factorial$.ti,ab. 3. (crossover$ or cross over$ or cross‐over$).ti,ab. 4. placebo$.ti,ab. 5. (doubl$ adj blind$).ti,ab. 6. (singl$ adj blind$).ti,ab. 7. assign$.ti,ab. 8. allocat$.ti,ab. 9. volunteer$.ti,ab. 10. CROSSOVER PROCEDURE.sh. 11. DOUBLE‐BLIND PROCEDURE.sh. 12. RANDOMIZED CONTROLLED TRIAL.sh. 13. SINGLE BLIND PROCEDURE.sh. 14. or/1‐13 15. ANIMAL/ or NONHUMAN/ or ANIMAL EXPERIMENT/ 16. HUMAN/ 17. 16 and 15 18. 15 not 17 19. 14 not 18
Contributions of authors
Sun Jie and Yu Yongchun conceived the review and were responsible for designing the review, designing the search strategy and undertaking the searches with the help of Anne Littlewood from the Cochrane Oral Health Group, and for data extraction.
Wenli Lai co‐ordinated the review.
Taixiang Wu would have analysed the data. Zongdao Shi was the third assessor.
Sun Jie was responsible for writing to the authors of papers for additional information and obtaining and screening data on unpublished studies.
Stephen Koshy was our English‐speaking co‐author.
All review authors wrote the protocol and wrote the review.
Sources of support
Internal sources
West China College of Stomatology, Sichuan University, China.
Chinese EBM/Cochrane Center, China.
External sources
-
Cochrane Oral Health Group Global Alliance, UK.
All reviews in the Cochrane Oral Health Group are supported by Global Alliance member organisations (British Orthodontic Society, UK; British Society of Paediatric Dentistry, UK; British Society of Periodontology, UK; Canadian Dental Hygienists Association, Canada; National Center for Dental Hygiene Research & Practice, USA and New York University College of Dentistry, USA; Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh, UK) providing funding for the editorial process (http://ohg.cochrane.org/)
-
National Institute for Health Research (NIHR), UK.
CRG funding acknowledgement: The NIHR is the largest single funder of the Cochrane Oral Health Group
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed therein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NIHR, NHS or the Department of Health
Declarations of interest
None known.
Stable (no update expected for reasons given in 'What's new')
References
Additional references
Al‐Balkhi 2004
- Al‐Balkhi KM. The effect of different lower third molar conditions on the re‐crowding of lower anterior teeth in the absence of tight interproximal contacts one‐year post orthodontic treatment: a pilot study. Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice 2004;5(3):66‐73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Artun 1996
- Artun J, Garol JD, Little RM. Long‐term stability of mandibular incisors following successful treatment of Class II, Division 1, malocclusions. Angle Orthodontist 1996;66(3):229‐38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bloore 1998
- Bloore JA, Bloore GE. Correction of adult incisor crowding with a new removable appliance. Journal of Clinical Orthodontics 1998;32(2):111‐6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Boese 1980
- Boese LR. Fiberotomy and reproximation without lower retention, nine years in retrospect. Angle Orthodontist 1980;50(2):88‐97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Caniklioglu 2005
- Caniklioglu C, Oztürk Y. Patient discomfort: a comparison between lingual and labial fixed appliances. Angle Orthodontist 2005;75(1):86‐91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Canut 1999
- Canut JA, Arias S. A long‐term evaluation of treated Class II division 2 malocclusions: a retrospective study model analysis. European Journal of Orthodontics 1999;21(4):377‐86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Carano 2001
- Carano A, Ciocia C, Farronato G. Use of lingual brackets for deep‐bite correction. Journal of Clinical Orthodontics 2001;35(7):449‐50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chaushu 2008
- Chaushu S, Becker A, Chaushu G. Lingual orthodontic treatment and absolute anchorage to correct an impacted maxillary canine in an adult. American Journal of Othodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 2008;134(6):811‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cureton 1996
- Cureton SL. Correcting Malaligned Mandibular Incisors with Removable Retainers. Journal of Clinical Orthodontics 1996;1996(7):390‐5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Egger 1997
- Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder CE. Bias in meta‐analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997;315(7109):629‐34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Fillion 1997
- Fillion D. The correction of open‐bite in adults using lingual orthodontics. Orthodontie Francaise 1997;68(1):307‐10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gorman 1991
- Gorman JC, Smith RJ. Comparison of treatment effects with labial and lingual fixed appliances. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 1991;99(3):202‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Grauer 2011
- Grauer D, Proffit WR. Accuracy in tooth positioning with a fully customized lingual orthodontic appliance. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 2011;140(3):433‐43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hansen 1997
- Hansen K, Koutsonas TG, Pancherz H. Long‐term effects of Herbst treatment on the mandibular incisor segment: a cephalometric and biometric investigation. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 1997;112(1):92‐103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2011
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hohoff 2003
- Hohoff A, Fillion D, Stamm T, Goder G, Sauerland C, Ehmer U. Oral comfort, function and hygiene in patients with lingual brackets. A prospective longitudinal study. Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics 2003;64(5):359‐71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Invisalign 2006
- Introducing Invisalign. The invisible way to straighten your teeth without braces. Available from www.invisalign.co.uk/.
Joffe 2003
- Joffe L. Invisalign: early experiences. Journal of Orthodontics 2003;30(4):348‐52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Joondeph 1994
- Joondeph DR, Reidel RA. Retention and relapse. In: Vanarsdall RL Jr editor(s). Orthodontics: Current Principles and Techniques. St Louis: Mosby‐Year Book, 1994:908‐50. [Google Scholar]
Kahl‐Nieke 1995
- Kahl‐Nieke B, Fischbach H, Schwarze CW. Post‐retention crowding and incisor irregularity: a long‐term follow‐up evaluation of stability and relapse. British Journal of Orthodontics 1995;22(3):249‐57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kawakami 2004
- Kawakami M, Miyawaki S, Noguchi H, Kirita T. Screw‐type implants used as anchorage for lingual orthodontic mechanics: a case of bimaxillary protrusion with second premolar extraction. Angle Orthodontist 2004;74(5):715‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kurz 1998
- Kurz C, Romano R. Lingual orthodontics: historical perspective. In: Romano R editor(s). Lingual Orthodontics. Hamilton (ON): BC Decker, 1998:3‐20. [Google Scholar]
Liou 2001
- Liou EJ, Chen LI, Huang CS. Nickel‐titanium mandibular bonded lingual 3‐3 retainer: for permanent retention and solving relapse of mandibular anterior crowding. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 2001;119(4):443‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Little 1975
- Little RM. The irregularity index: a quantitative score of mandibular anterior alignment. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 1975;68(5):554‐63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Little 1981
- Little RM, Wallen TR, Riedel RA. Stability and relapse of mandibular anterior alignment ‐ first premolar extraction cases treated by traditional edgewise orthodontics. American Journal of Orthodontics 1981;80(4):349‐65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Little 1988
- Little RM, Riedel RA, Artun J. An evaluation of changes in mandibular anterior alignment from 10 to 20 years postretention. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 1988;93(3):423‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Moss 1980a
- Moss JP. The soft tissue environment of teeth and jaws. An experimental and clinical study: part 1. British Journal of Orthodontics 1980;7(3):127‐37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Moss 1980b
- Moss JP. The soft tissue environment of teeth and jaws. Experimental malocclusion: parts 2 and 3. British Journal of Orthodontics 1980;7(4):205‐16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pauls 2008
- Pauls HJ. Lingual orthodontics with orthognathic surgery in a severe class II, division 2 case. Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics 2008;69(2):449‐50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pauls 2010
- Pauls AH. Therapeutic accuracy of individualized brackets in lingual orthodontics. Journal of Orofacial Orthopedics 2010;71(5):348‐61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Perera 1987
- Perera PS. Rotational growth and incisor compensation. Angle Orthodontist 1987;57(1):39‐49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Poon 1998
- Poon KC, Taverne AA. Lingual orthodontics: a review of its history. Australian Orthodontic Journal 1998;15(2):101‐4,9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Richardson 1994
- Richardson ME. Late lower arch crowding: the role of differential horizontal growth. British Journal of Orthodontics 1994;21(4):379‐85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rossouw 1993
- Rossouw PE, Preston CB, Lombard CJ, Truter JW. A longitudinal evaluation of the anterior border of the dentition. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 1993;104(2):146‐52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rygh 1988
- Rygh P, Moyer RE. Force systems and tissue responses to forces in orthodontics and facial orthopedics. In: Moyers RE editor(s). Handbook of Orthodontics. 4th Edition. Chicago: Year Book Medical Publishers, 1988:306‐11. [Google Scholar]
Rücker 2008
- Rücker G, Schwarzer G, Carpenter J. Arcsine test for publication bias in meta‐analyses with binary outcomes. Statistics in Medicine 2008;27(5):746‐63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Shah 2003
- Shah AA. Postretention changes in mandibular crowding: a review of the literature. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 2003;124(4):298‐308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sharpe 1987
- Sharpe W, Reed B, Subtelny JD, Polson A. Orthodontic relapse, apical root resorption, and crestal alveolar bone levels. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 1987;91(3):252‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sinclair 1986
- Sinclair PM, Cannito MF, Goates LJ, Solomos LF, Alexander CM. Patient responses to lingual appliances. Journal of Clinical Orthodontics 1986;20(6):396‐404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Southard 1992
- Southard TE, Southard KA, Tolley EA. Periodontal force: a potential cause of relapse. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 1992;101(3):221‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
van der Veen 2010
- Veen MH, Attin R, Schwestka‐Polly R, Wiechmann D. Caries outcomes after orthodontic treatment with fixed appliances: do lingual brackets make a difference?. European Journal of Oral Sciences 2010;118(3):298‐303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Vlaskalic 2001
- Vlaskalic V, Boyd R. Orthodontic treatment of a mildly crowded malocclusion using the Invisalign System. Australian Orthodontic Journal 2001;17(1):41‐6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wu 2011
- Wu A, McGrath C, Wong RW, Wiechmann D, Rabie AB. Comparison of oral impacts experienced by patients treated with labial or customized lingual fixed orthodontic appliances. American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics 2011;139(6):784‐90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


