Figure 5. Autosomal H3K9me3 domains are enriched for late replicating long synaptic genes and replication stress-induced double strand breaks.
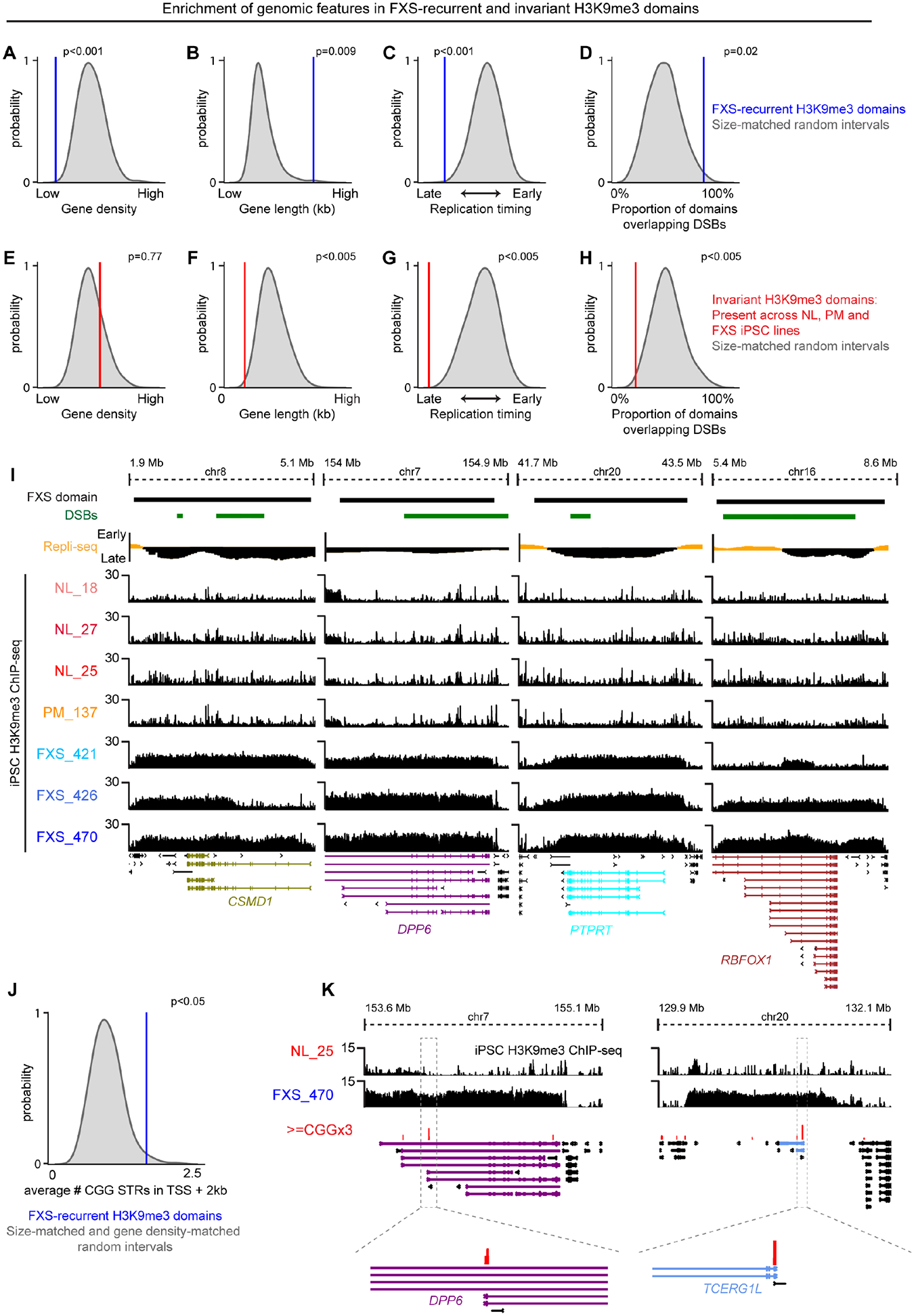
(A-H) Empirical randomization test assessing the enrichment of (A+E) gene density, (B+F) gene length, (C+G) replication timing, and (D+H) replication stress-induced double stranded breaks in (A-D) FXS-recurrent H3K9me3 domains or (E-H) genotype-invariant H3K9me3 domains compared to N=1000 draws of random genomic intervals matched by size. (I) FXS-recurrent H3K9me3 domains encompassing CSMD1 (gene length: ~2.10 Mb), DPP6 (gene length: ~1.15 Mb), PTPRT (gene length: ~1.16 Mb), and RBFOX1 (gene length: ~2.47 Mb). Replication stress-induced double strand breaks, dark green. Replication timing, yellow (early S phase) and black (late S phase). (J) Empirical randomization test assessing the enrichment of CGG tracts (>=CGGx3) in TSSs + 2kb within FXS-recurrent H3K9me3 domains compared to N=1000 draws of random genomic intervals matched by size. (K) Examples of CGG tracts in FXS-recurrent H3K9me3 domains encompassing DPP6 and TCERG1L.
