Abstract
Objective
To compare the efficacy and safety of the modified versus standard Valsalva maneuver in the treatment of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT).
Methods
The PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, CNKI, WanFang Data, and VIP electronic databases were searched to identify studies comparing the modified and standard Valsalva maneuvers in the treatment of PSVT from database inception to 1 May 2023. Two reviewers independently screened the literature, extracted the data, and assessed the risk of bias of all included studies.
Results
Nineteen randomized controlled trials involving 2527 patients with PSVT were included. The overall rate of cardioversion was higher in the modified than standard Valsalva group (risk ratio [RR] = 1.80, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 1.61–2.01), as was the success rate of cardioversion after a single Valsalva maneuver (RR = 2.05, 95% CI = 1.74–2.41). There was no statistically significant difference in adverse reactions between the two groups (RR = 1.07, 95% CI = 0.82–1.38).
Conclusion
Current evidence suggests that the modified Valsalva maneuver can significantly improve the success rate of cardioversion in patients with PSVT without increasing adverse reactions. The modified Valsalva maneuver is therefore worth promoting and should be considered as a routine first treatment.
INPLASY registration number: 2023100092
Keywords: Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia, modified Valsalva maneuver, meta-analysis, systematic review, randomized controlled trial, cardioversion
Introduction
Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is a common cardiac arrhythmia encountered in emergency departments, with a prevalence of approximately 2.25/1000 persons and incidence of 35/100,000 person-years.1,2 Paroxysmal SVT (PSVT) is characterized by sudden onset and termination, variable duration of episodes, and generally no impact on blood pressure. However, if not promptly terminated in patients of advanced age or those with underlying conditions such as coronary artery disease or severe infection, PSVT can lead to circulatory failure or even sudden death. 3
Common treatment methods for PSVT include vagal maneuvers, antiarrhythmic drug therapy, and radiofrequency ablation. Vagal maneuvers include the diving reflex, oculocardiac reflex, carotid sinus massage, bearing down, gag reflex, cough reflex, and Valsalva maneuver. The standard Valsalva maneuver was historically recommended by international guidelines for terminating PSVT, but the success rate for restoring regular heart rhythm was not ideal (5%–20%), limiting its widespread use in clinical practice. 1 The modified Valsalva maneuver involves assuming a semi-recumbent position and performing passive leg raising to a 45-degree angle immediately following the standard Valsalva maneuver. Elevating both legs immediately after the standard Valsalva maneuver can increase blood return to the heart, subsequently increasing jugular vein pressure. This in turn augments vagal tone, activates the vagus nerve, and reduces the heart rate.1,4,5
In recent years, several studies have shown that the modified Valsalva maneuver significantly improves the success rate of restoring normal rhythm in patients with PSVT and has high safety.6–8 Zhang et al. 7 indicated that the overall rates of cardioversion in the modified and standard Valsalva maneuver groups were 40.0% and 16.7%, respectively. However, because of differences in study designs and intervention methods as well as the use of small patient samples, the results vary among different studies, and the safety and overall efficacy of treatment are difficult to quantify. A recent meta-analysis showed that the modified Valsalva maneuver significantly increased the success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after a single Valsalva maneuver, multiple Valsalva maneuvers, and single and multiple Valsalva maneuvers with a risk ratio (RR) of 2.83, 3.83, and 2.85, respectively. 1 However, the meta-analysis did not include Chinese databases, which may have led to bias in the research results because numerous relevant studies have been published in Chinese. Therefore, the present meta-analysis was performed to collect and summarize all relevant studies assessing the modified Valsalva maneuver and thus provide the highest-level evidence to date for driving changes in practice.
Materials and methods
Ethics approval and patient consent were not applicable to this meta-analysis, which was based on published articles. This meta-analysis was carried out according to the 2020 Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement. 9
Search strategy
The electronic databases of PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure, WanFang, and China Science and Technology Journal Database were systematically searched for studies published from database inception to 1 May 2023 without language limits. We also manually searched the lists of included studies to identify additional potentially eligible studies. If two or more studies described the same participants, the study with the largest sample size was chosen for inclusion. The following keywords were used, both separately and in combination, as part of the search strategy in each database: “Valsalva,” “supraventricular tachycardias,” and “PSVT” (Box 1).
Box 1.
Search strings used for PubMed database.
| #1) Valsalva [Title/Abstract] |
| #2) Supraventricular tachycardias [Title/Abstract] |
| #3) Supraventricular tachycardias [MeSH Terms] |
| #4) PSVT [Title/Abstract] |
| #5) #2 OR #3 OR #4 |
| #6) Randomized controlled trial |
| #7) #1 AND #5 AND #6 |
Study selection
Studies were included in the meta-analysis if they were randomized controlled trials (RCTs), involved adult patients (aged >18 years) with PSVT and stable hemodynamics, treated the control group with the standard Valsalva maneuver and treated the experimental group with the modified Valsalva maneuver, set the primary outcome as the success rate of cardiac rhythm restoration and the secondary outcome as the occurrence of adverse reactions, and reported sufficient details regarding the success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after the Valsalva maneuver and the rate of adverse events. We only included studies with a sample size of >30 because of the limited representativeness of studies with small sample sizes.
Data extraction and quality assessment
Two reviewers independently selected the literature and extracted the data to an Excel database. Any disagreement was resolved by a third reviewer. When required, the authors were contacted directly to obtain further information and clarifications regarding their study. Data extraction included the first author’s surname, date of publication of the article, study design, sample size, participants’ age, outcome measurement data, and relevant elements of risk-of-bias assessment.
The quality of the included studies was independently evaluated by two reviewers based on the revised Cochrane risk-of-bias tool for randomized trials. 10 Any disagreement was resolved by a third reviewer.
Statistical analyses
All meta-analyses were performed using Stata 16 (StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA). The RR of binary variables between patient groups was calculated together with the associated 95% confidence interval (CI). The heterogeneity between studies was analyzed using the chi-square test (P < 0.10) and quantified using the I2 statistic. When no statistical heterogeneity was observed, a fixed-effects model was used; otherwise, a random-effects model was used. A sensitivity analysis was conducted to examine the impact of individual studies on the overall effect size. A funnel plot together with Begg’s test was used to evaluate publication bias. A two-tailed P value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Literature screening and characteristics of included studies
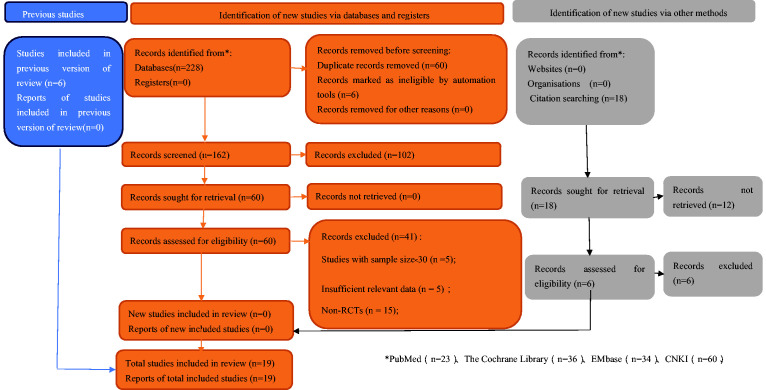
In total, 228 records were identified from the various databases examined, and 18 records were identified from citation searching. After a detailed assessment based on the inclusion criteria, 19 studies3,4,6–8,11–24 involving 2527 patients with PSVT were included in the meta-analysis (Figure 1). All studies were published from 2015 to 2022. Six were published in English and 13 in Chinese.
Figure 1.
Flowchart depicting literature screening process.
All studies3,4,6–8,11–24 reported the overall rate of cardioversion, including that associated with single and multiple Valsalva maneuvers, and 12 studies3,4,7,11–13,15–19,24 reported the rate of cardioversion after a single Valsalva maneuver. Eight studies4,7,11,13,15,20,22,24 repeated the standard or modified Valsalva maneuver up to two times if sinus rhythm was not restored after the first attempt, three studies6,16,21 repeated the maneuver up to three times, two studies17,18 repeated the maneuver up to five times, and six studies3,8,12,14,19,23 did not mention how many times the maneuver was repeated. The characteristics of all included studies are shown in Table 1.
Table 1.
Basic characteristics of included studies.
| Study | Country | Number of patients (Experimental/Control) | Mean age, years (Experimental/Control) | Intervention |
Outcomes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experimental group | Control group | |||||
| Li et al. (2017) 24 | China | 80/80 | 54.0 ± 8.9/52.0 ± 8.4 | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after single VM, repeated up to two times in unresponsive patientsRate of adverse events |
| Liu and Sun (2019) 11 | China | 67/67 | 50.0 ± 8.1/52.0 ± 7.8 | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after single VM, repeated up to two times in unresponsive patientsRate of adverse events |
| Wang et al. (2019) 12 | China | 120/120 | 50.0 ± 8.1/49.0 ± 7.5 | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after VM; no mention of how many times conductedRate of adverse events |
| Zhang et al. (2020) 7 | China | 50/48 | 46.3 ± 12.0/45.5 ± 10.3 | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after single VM, repeated up to two times in unresponsive patientsRate of adverse events |
| Long et al. (2020) 8 | China | 33/33 | 58.0 ± 1.8/55.1 ± 2.2 | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after VM; not mention of how many times conductedRate of adverse events |
| Wu et al. (2020) 13 | China | 45/43 | 66.9 ± 4.5/67.5 ± 5.3 | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after single VM, repeated up to two times in unresponsive patientsRate of adverse events |
| Song et al. (2020) 4 | China | 70/63 | 55 ± 7/56 ± 8 | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after single VM, repeated up to two times in unresponsive patientsRate of adverse events |
| Huang and Wang (2020) 14 | China | 34/34 | 56.0 ± 2.1/53.2 ± 1.9 | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after VM; no mention of how many times conductedRate of adverse events |
| Wei and Cen (2021) 15 | China | 32/31 | 52.6 ± 3.6/52.3 ± 3.3 | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after single VM, repeated up to two times in unresponsive patientsRate of adverse events |
| Chen and Xie (2021) 17 | China | 46/46 | 61 ± 12/60 ± 11 | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after single VM, repeated up to five times in unresponsive patientsRate of adverse events |
| Lin et al. (2021) 18 | China | 41/40 | 45.7 ± 11.6/43.2 ± 10.5 | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after single VM, repeated up to five times in unresponsive patientsRate of adverse events |
| Zhang et al. (2021) 3 | China | 18/18 | 40.7 ± 16.3/40.7 ± 16.9 | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after VM; no mention of how many times conductedRate of adverse events |
| Hu and Wu (2022) 19 | China | 30/30 | 42.1 ± 5.9/41.2 ± 6.3 | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after VM; no mention of how many times conductedRate of adverse events |
| Appelboam et al. (2015) 20 | Britain | 214/214 | 55.1 ± 16.3/54.5 ± 16.8 | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after single VM, repeated up to two times in unresponsive patientsRate of adverse events |
| Çorbacıoğlu et al. (2017) 21 | Turkey | 28/28 | 44.3 ± 4.9/48.4 ± 5.0 | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after single VM, repeated up to three times in unresponsive patientsRate of adverse events |
| Youssef et al. (2019) 22 | Egypt | 30/30 | NR | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after single VM, repeated up to two times in unresponsive patients |
| Ceylan et al. (2019) 23 | Turkey | 33/32 | 50.0 ± 6.25/61.0 ± 5.25 | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after VM; no mention of how many times conducted |
| Chen et al. (2020) 6 | China | 119/119 | NR | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after single VM, repeated up to three times in unresponsive patientsRate of adverse events |
| Wang et al. (2020) 16 | China | 180/181 | 51.0 ± 12.0/49.0 ± 13.6 | MVM | SVM | Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm after single VM, repeated up to three times in unresponsive patientsRate of adverse events |
VM, Valsalva maneuver; MVM, modified Valsalva maneuver; SVM, standard Valsalva maneuver; NR, not reported.
Risk-of-bias assessment
Two studies14,15 contained insufficient information regarding sequence generation. Furthermore, most included studies3,4,7,8,11–19,22–24 lacked information about allocation concealment. The majority of the evaluated trials3,4,7,8,11–15,17–19,21–24 had an unclear risk of bias in terms of participant, personnel, and outcome assessor blinding. However, all included trials had a low risk of bias in terms of selective outcome reporting and incomplete outcome data.
Meta-analysis results
Success rate of achieving sinus rhythm
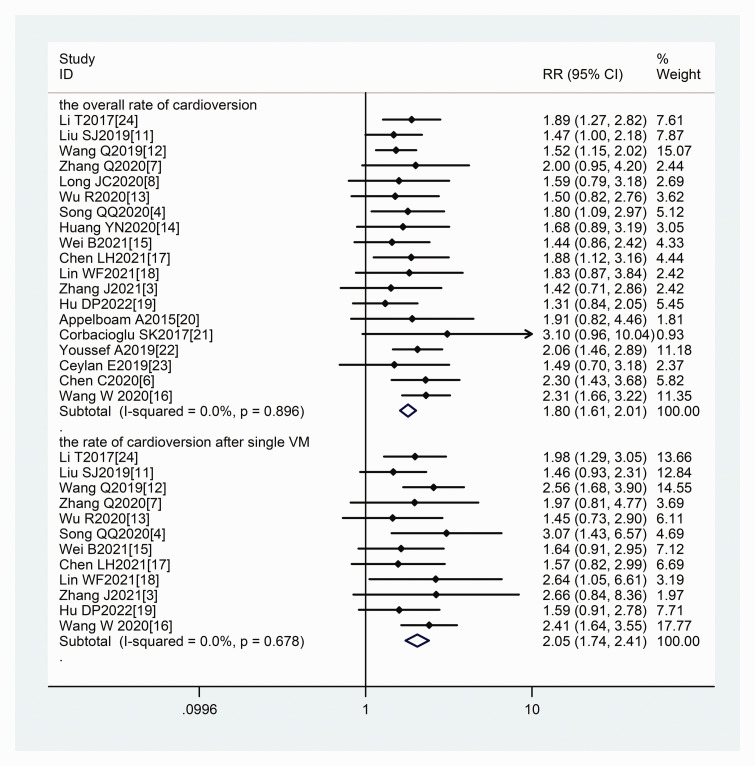
Nineteen studies3,4,6–8,11–24 reported the overall rate of cardioversion, and 12 studies3,4,7,11–13,15–19,24 reported the rate of cardioversion after a single Valsalva maneuver. No significant heterogeneity was observed among the studies; therefore, a fixed-effects model was used for the meta-analysis. The pooled results revealed that the success rate of cardioversion after a single maneuver (RR = 2.05, 95% CI = 1.74–2.41, P < 0.001) and the overall rate of cardioversion (RR = 1.80, 95% CI = 1.61–2.01, P < 0.001) were significantly higher in the modified than standard Valsalva maneuver group (Figure 2).
Figure 2.
Forest plots comparing success rates of two study groups.
Adverse reactions
Seventeen RCTs3,4,6–8,11–21,24 were included in the analysis of adverse reactions. The fixed-effect meta-analysis results showed no statistically significant difference in the occurrence of adverse reactions between the two groups (RR = 1.07, 95% CI = 0.82–1.38). Adverse reactions mainly included headache, dizziness, and palpitations, and no severe adverse reactions were reported in either group.
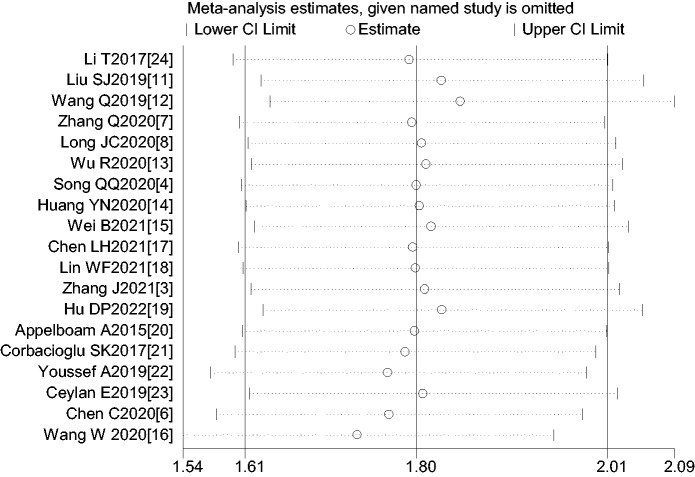
Sensitivity analysis
A sensitivity analysis was carried out by excluding one study at a time and reanalyzing the entire dataset. No significant changes were observed, indicating that the results were relatively stable (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
Sensitivity analysis of overall success rate of cardioversion.
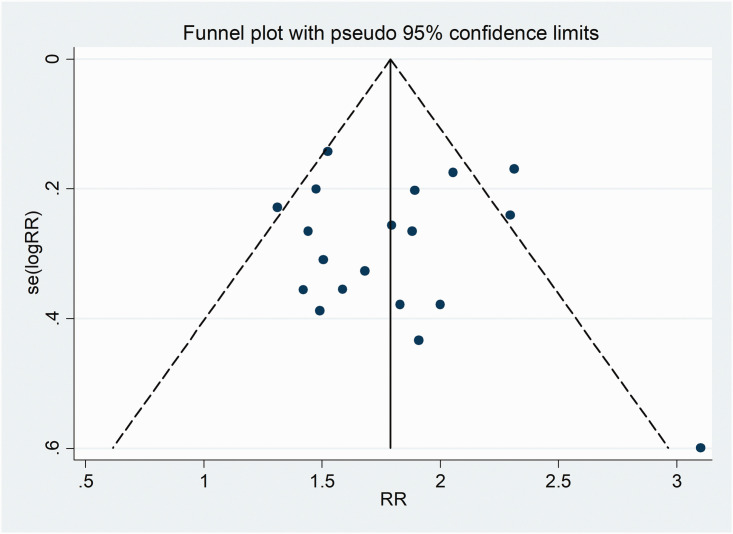
Publication bias
A funnel plot based on the overall rate of cardioversion showed that the P value of Begg’s test was 0.624, suggesting no significant risk of publication bias (Figure 4).
Figure 4.
Funnel plot of publication bias among all included studies.
Discussion
PSVT is a rapid, regular arrhythmia characterized by sudden onset and termination. Specifically, PSVT refers to atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) and atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia.1,25,26 During the acute phase of PSVT, the heart rate fluctuates between approximately 150 and 250 beats/minute. Patients with AVNRT typically do not exhibit any signs of structural heart disease, and the arrhythmia can occur at different ages and in both sexes. However, the proportion of patients with atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia decreases with age, whereas the proportion of those with AVNRT increases with age. AVNRT is the most common type of PSVT. Increasing evidence suggests that weaker vagal nerve stimulation significantly enhances the conduction differences in the atrioventricular junction, making it more prone to AVNRT, whereas high-intensity vagal nerve stimulation (such as carotid sinus massage and the Valsalva maneuver) significantly increases the effective refractory period of atrioventricular conduction, interrupting AVNRT and ultimately terminating SVT.4,27 Therefore, stimulation of the vagus nerve through techniques such as the Valsalva maneuver is a recommended first-line intervention to ensure stable blood pressure, respiration, and other vital signs in patients with PSVT.
The standard Valsalva maneuver is performed by placing the patient in a semi-recumbent position or sitting position at an angle of 45 to 90 degrees to the bed surface. The patient is then asked to blow into a 10-mL syringe to move the plunger until the recommended intrathoracic pressure of 40 mmHg is achieved. This state of exertion is maintained for 15 s. The patient then relaxes and resumes normal breathing before maintaining this posture for 1 minute. The standard Valsalva maneuver is not limited by the environment, and it has advantages such as simplicity, ease of operation, high safety, and low cost.16,20 However, cardioversion using the standard Valsalva maneuver is rarely successful in clinical practice, and its clinical application is limited. 5 Antiarrhythmic drugs (such as amiodarone and propafenone) and synchronized electrical cardioversion are also commonly used in the clinical treatment of PSVT, but these methods carry risks of hypotension, malignant arrhythmias, and even cardiac arrest. 24 The modified Valsalva maneuver involves placing the patient in the supine position with their legs elevated at a 45-degree angle immediately after application of the standard Valsalva maneuver; this position is maintained for 15 s by the researcher, and the patient is then returned to the semi-recumbent position for 45 s.1,6,20 Lying flat and passively elevating the legs can increase venous blood flow during the diastolic period, thus increasing the jugular vein pressure, enhancing parasympathetic nervous system tone, and improving the success rate of cardioversion.1,24
In recent years, several studies have shown that the modified Valsalva maneuver significantly improves the success rate of conversion in patients with PSVT compared with the standard Valsalva maneuver (43% vs. 17%, respectively), reducing the adverse reactions caused by drugs and electrical cardioversion.20,28–30 In 2021, Lan et al. 1 performed a meta-analysis of 6 RCTs involving 1208 patients with PSVT. The authors compared the efficacy of the modified versus standard Valsalva maneuver in the treatment of PSVT. The results showed that the modified Valsalva maneuver had a higher success rate in restoring sinus rhythm and reduced the use of antiarrhythmic drugs without increasing adverse reactions or the length of stay in the emergency department. The present meta-analysis included 19 RCTs involving 2527 patients with PSVT, and the results also showed that the modified Valsalva maneuver had significantly higher conversion efficiency than the standard Valsalva maneuver without a higher rate of adverse reactions. The results of these studies indicate that the modified Valsalva maneuver is an effective and safe treatment for PSVT.
The present meta-analysis included studies with large sample sizes from both Chinese databases and international sources. By including Chinese literature, we have provided a more representative systematic review than other recent meta-analyses and have gathered the most comprehensive evidence for the research question. The results of the meta-analysis showed no heterogeneity, also indicating that the research findings are reliable and representative. However, this study had certain limitations. First, although a large number of studies were included, most of them did not describe the specific randomization and blinding methods. This lack of information may have introduced selection and implementation biases. Second, the sample sizes of the included RCTs were small, which may have resulted in insufficient statistical power. Finally, variants of the standard and modified Valsalva maneuvers were used among the included studies, the patients’ disease durations and underlying comorbidities were not consistent, and the time from onset to treatment varied. These differences may have led to clinical heterogeneity.
Conclusion
There is currently sufficient evidence that the modified Valsalva maneuver can effectively improve the success rate of cardioversion in patients with PSVT, with high safety and ease of operation. The results are consistent with PSVT guidelines, indicating that the modified Valsalva maneuver is worth promoting and should be considered as a routine first treatment.
Supplemental Material
Supplemental material, sj-pdf-1-imr-10.1177_03000605231220871 for Efficacy and safety of modified Valsalva maneuver for treatment of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia: a meta-analysis by Zhao Lu, Jieyun Zhu, Min Gao, Qiuyun Song, Dongzan Pan, Chunli Huang, Liangfeng Zhu and Yin Shen in Journal of International Medical Research
Author contributions: Dongzan Pan, Liangfeng Zhu, and Chunli Huang collected and analyzed the data. Yin Shen acquired the funding. Zhao Lu and Jieyun Zhu designed the study and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Min Gao and Qiuyun Song designed and supervised the study and finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript. Zhao Lu and Jieyun Zhu are the first authors of this paper.
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Funding: This study was supported by the Guangxi Key Research and Development Plan (GuikeAB23026019).
ORCID iDs: Jieyun Zhu https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7718-9591
Data availability statement
Original data can be obtained by contacting the corresponding author.
References
- 1.Lan Q, Han B, Wu F, et al. Modified Valsalva maneuver for treatment of supraventricular tachycardias: a meta-analysis [J]. Am J Emerg Med 2021; 50: 507–512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Brugada J, Katritsis DG, Arbelo E, et al. 2019 ESC Guidelines for the management of patients with supraventricular tachycardia The Task Force for the management of patients with supraventricular tachycardia of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) [published correction appears in Eur Heart J. 2020 Nov 21; 41(44): 4258] [J]. Eur Heart J 2020; 41: 655–720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zhang J, Tang HM, Yang L, et al. Therapeutic effects of the modified simplified Valsalva maneuver in emergency treatment of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia [J]. Hebei Medicine 2021; 43: 2790–2792 + 2796. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Song QQ, Wang Y, Zhang XH, et al. Impact of modified Valsalva manoeuvre on patients with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia in emergency [J]. Practical Journal of Cardiac Cerebral Pneumal and Vascular Disease 2020; 28: 116–119. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Liu AL, Liu JY, Zhang F, et al. A retrospective analysis of cardioversion for paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia in emergency department [J]. Chin J Emerg Med 2018; 27: 200–203. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chen C, Tam TK, Sun S, et al. A multicenter randomized controlled trial of a modified Valsalva maneuver for cardioversion of supraventricular tachycardias [J]. Am J Emerg Med 2020; 38: 1077–1081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhang Q, Chen K, Lu JY, et al. Observation of the effect of Valsalva maneuver with modified body position in terminating paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia [J]. Chinese Primary Health Care 2020; 27: 306–308. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Long JC, Lai XY, Li XY, et al. Evaluation of application effect of modified Valsalva movement in patients with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia [J]. China Medicine and Pharmacy 2020; 10: 278–280. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021; 372: N71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Higgins JPT, Savović J, Page MJ, et al. Revised Cochrane risk of bias tool for randomized trials (RoB 2)(22 August 2019). Available at: https://www.riskofbias.info/welcome/rob-2-0-tool/currentversion-of-rob-2.
- 11.Liu SJ, Sun YB. Efficacy analysis of modified Valsalva maneuver in pre-hospital emergency treatment of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia [J]. Chinese Journal of Physicians 2019; 21: 737–739. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wang Q, Liu JY, Wu RJ, et al. Application of revised Valsalva in emergency patients with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia [J]. Chin J Emerg Resusc Disaster Med 2019; 14: 119–121. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wu R, Yan F, Han YQ, et al. Posture-modified Valsalva manoeuvre and standard Valsalva manoeuvre in elderly patients with PSVT conversion [J]. Chin J Geriatr Heart Brain Vessel Dis 2020; 22: 253–256. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Huang YN, Wang XQ. Efficacy study of modified Valsalva maneuver in patients with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia [J]. Jiangxi Medicine 2020; 55: 1653–1654. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wei B, Cen LZ. Clinical effect of modified Valsalva motility in emergency termination of supraventricular tachycardia [J]. Chinese and Foreign Medical Research 2021; 19: 134–136. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Wang W, Jiang TF, Han WZ, et al. Efficacy and economic benefits of a modified Valsalva maneuver in patients with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia [J]. World J Clin Cases 2020; 8: 5999–6008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chen LH, Xie YM. Application experience of improved Valsalva maneuver in patients with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia [J]. Journal of Practical Medical Technology 2021; 28: 1043–1045. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lin WF, Sun LQ, Zhang XH, et al. Application of modified Valsalva maneuver in emergency cardioversion in patients with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia [J]. Chin J Evid Based Cardiovasc Med 2021; 13: 1121–1123. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hu DP, Wu CF. Effect of modified Valsalva maneuver on patients with supraventricular tachycardia [J]. Acta Medicinae Sinica 2022; 35: 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Appelboam A, Reuben A, Mann C, et al. Postural modification to the standard Valsalva manoeuvre for emergency treatment of supraventricular tachycardias (REVERT): a randomised controlled trial [J]. Lancet 2015; 386: 1747–1753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Çorbacıoğlu ŞK, Akıncı E, Çevik Y, et al. Comparing the success rates of standard and modified Valsalva maneuvers to terminate PSVT: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Am J Emerg Med 2017; 35: 1662–1665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Youssef A, Omar M, Nasr G, et al. Evaluation of modified Valsalva maneuver in treatment of supraventricular tachycardia among adult patients presenting to ER [J]. Europace 2019; 21: ii153–ii154. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ceylan E, Ozpolat C, Onur O, et al. Initial and sustained response effects of 3 vagal maneuvers in supraventricular tachycardia: a randomized, clinical trial [J]. J Emerg Med 2019; 57: 299–305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Li T, Liu CC, Wang P, et al. Application effect of modified Valsalva maneuver in patients with paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia [J]. Practical Journal of Cardiac Cerebral Pneumal and Vascular Disease 2017; 25: 77–79. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hou CX, Huang SX, Tao ZY. Curative effect of intravenous injections of amiodarone and verapamil on paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of New Clinical Medicine 2017; 10: 325–329. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dong HM, Mei X, Gao ZZ, et al. Efficacy and influencing factors of modified Valsalva maneuver for the cardioversion of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia [J]. Chin J Crit Care 2021; 41: 661–664. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Michaud A, Lang E. Leg lift Valsalva maneuver for treatment of supraventricular tachycardias [J]. CJEM 2017; 19: 235–237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Smith GD. A modified Valsalva manoeuvre results in greater termination of supraventricular tachycardia than standard Valsalva manoeuvre [J]. Evid Based Med 2016; 21: 61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Li YH, Huang CX. Treatment of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia with modified Valsalva maneuver [J]. Adv Cardiovasc Dis 2020; 41: 1177–1179. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Chinese Society of Electrocardiology and Pacing, Professional Committee of Cardiology of Chinese Medical Doctor Association. Chinese Expert Consensus on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Supraventricular Tachycardia (2021) [J]. Chinese Journal of Arrhythmias 2022; 26: 202–262. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental material, sj-pdf-1-imr-10.1177_03000605231220871 for Efficacy and safety of modified Valsalva maneuver for treatment of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia: a meta-analysis by Zhao Lu, Jieyun Zhu, Min Gao, Qiuyun Song, Dongzan Pan, Chunli Huang, Liangfeng Zhu and Yin Shen in Journal of International Medical Research
Data Availability Statement
Original data can be obtained by contacting the corresponding author.