Abstract
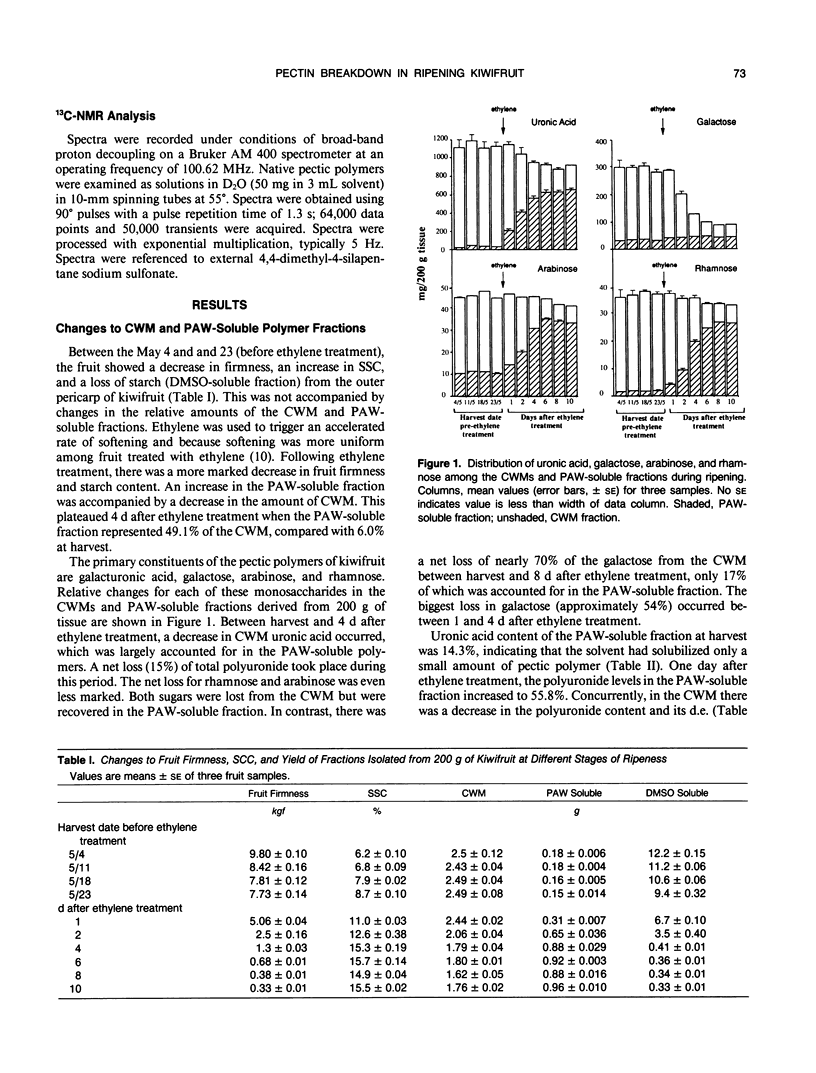
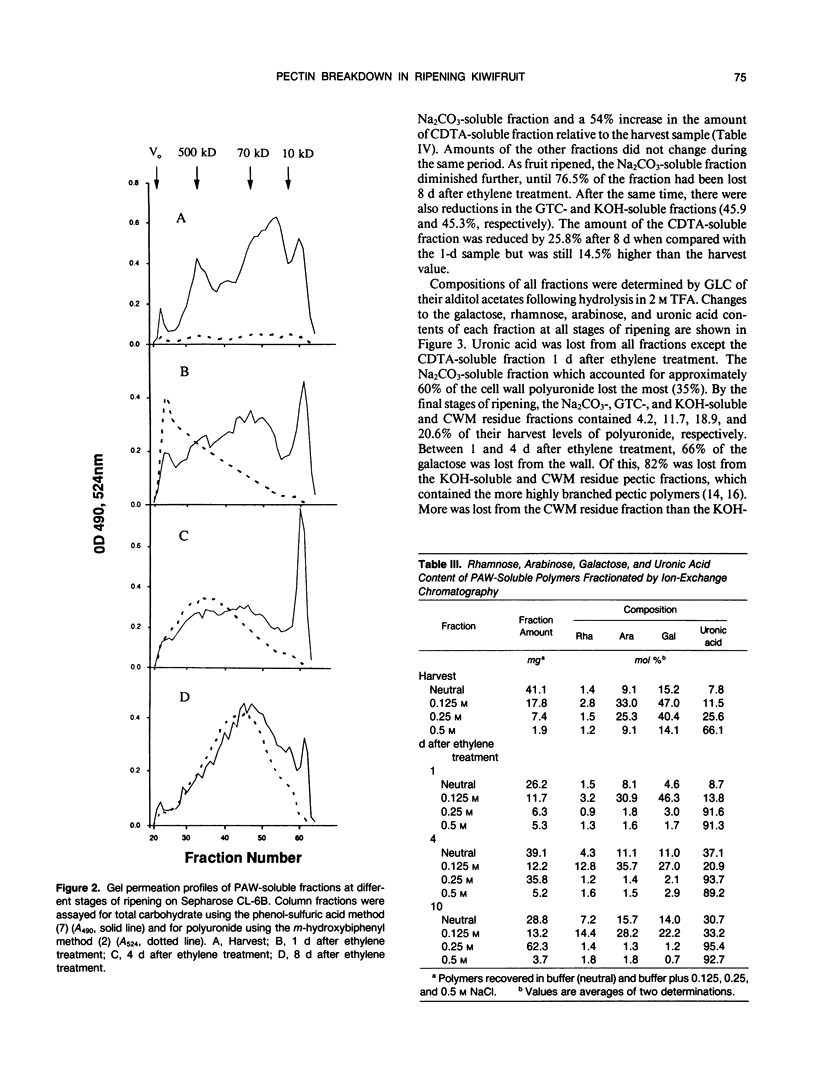
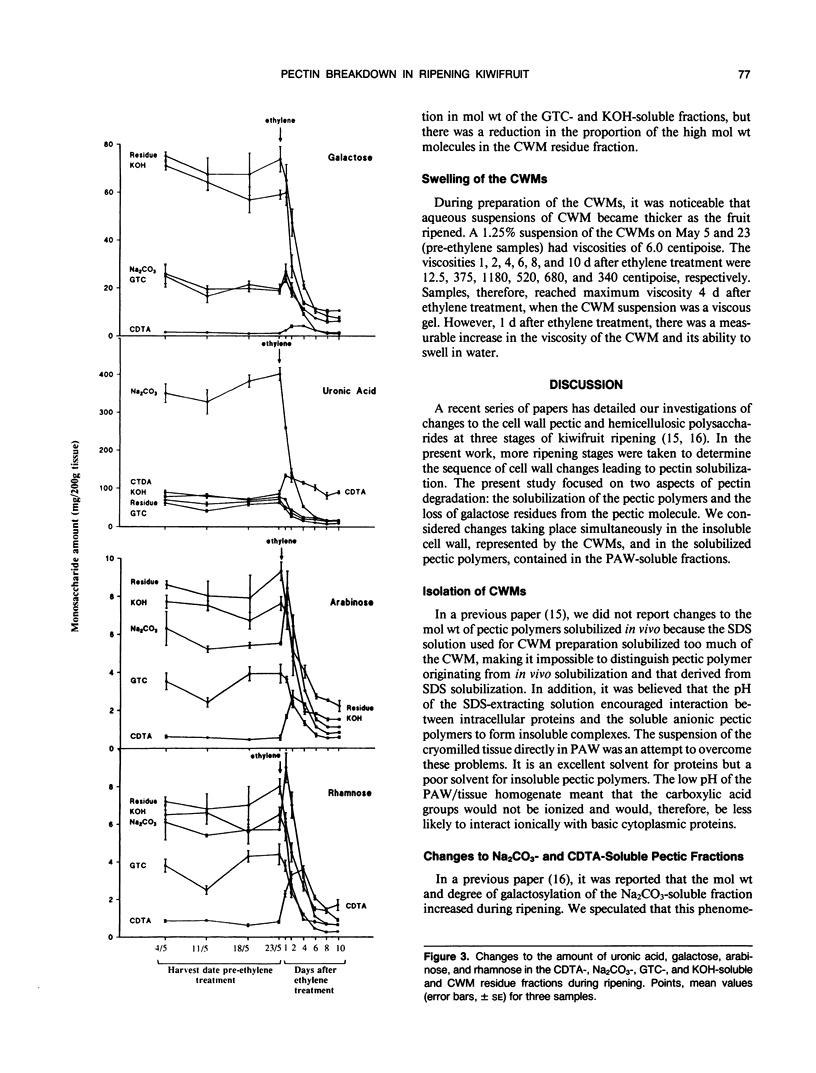
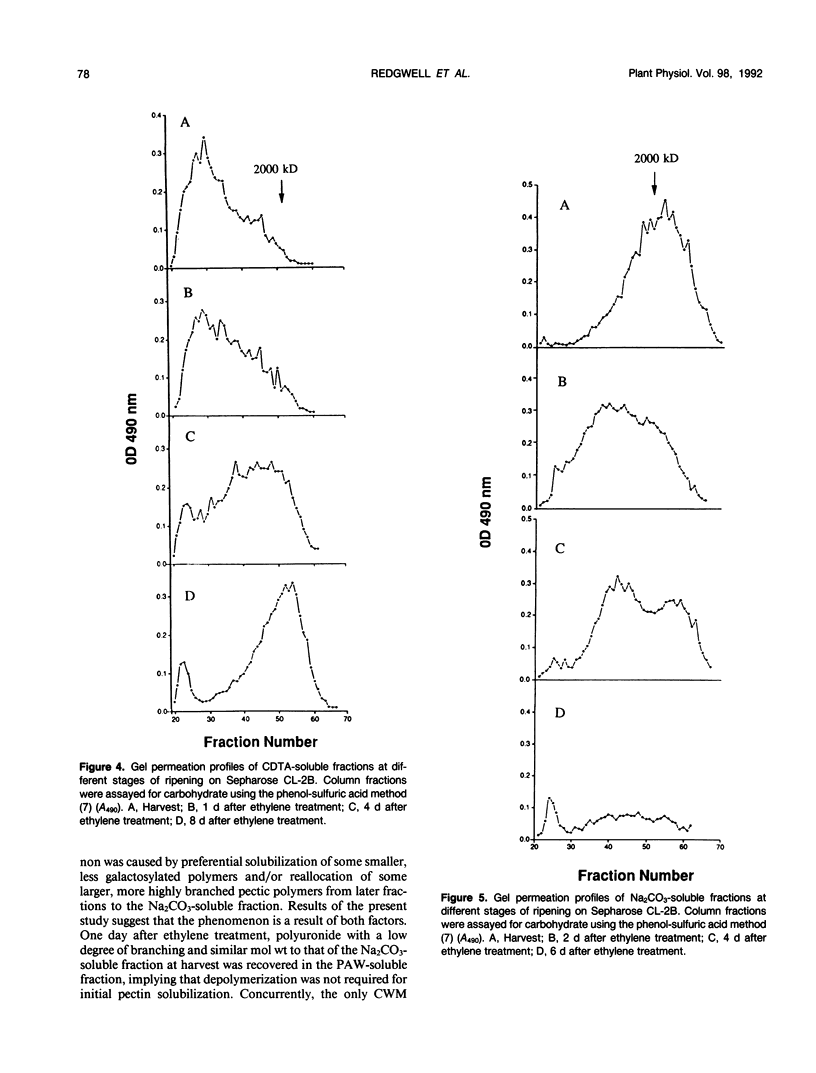
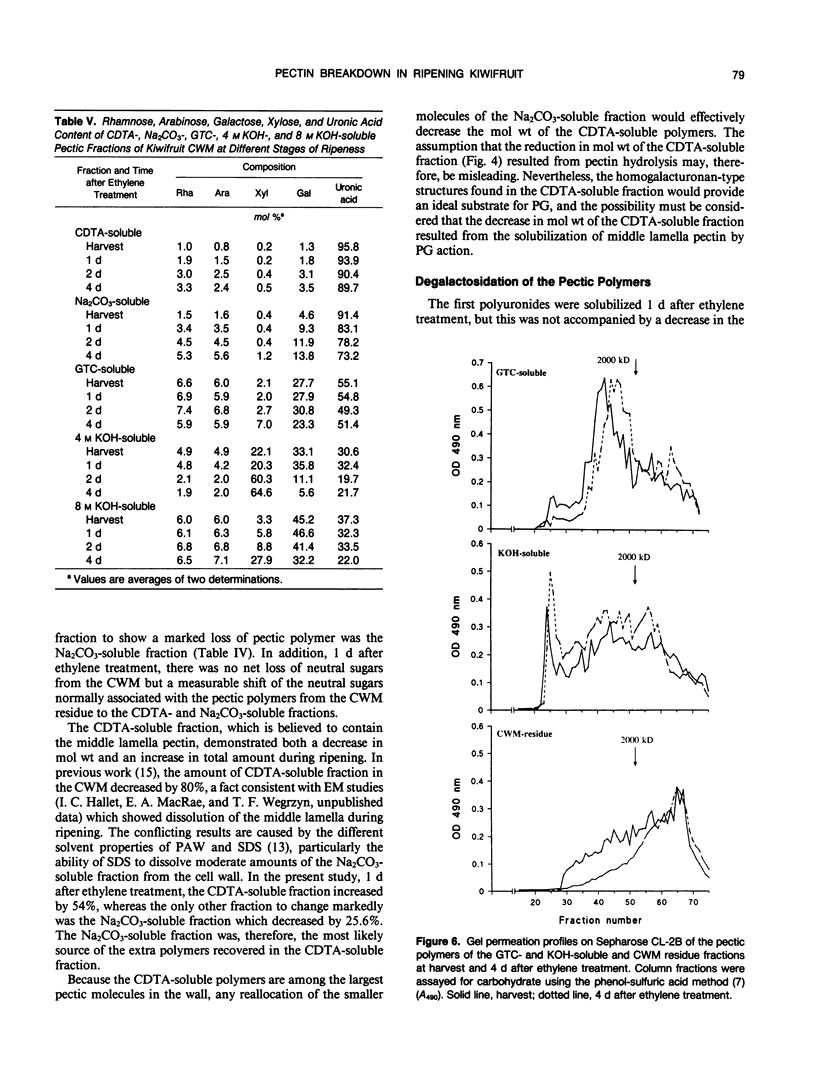
Pectic polysaccharides solubilized in vivo during ripening, were isolated using phenol, acetic acid, and water (PAW) from the outer pericarp of kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa [A. Chev.] C.F. Liang and A.R. Ferguson var deliciosa `Hayward') before and after postharvest ethylene treatment. Insoluble polysaccharides of the cell wall materials (CWMs) were solubilized in vitro by chemical extraction with 0.05 molar cyclohexane-trans-1,2-diamine tetraacetate (CDTA), 0.05 molar Na2CO3, 6 molar guanidinium thiocyanate, and 4 molar KOH. The Na2CO3-soluble fraction decreased by 26%, and the CDTA-soluble fraction increased by 54% 1 day after ethylene treatment. Concomitantly, an increase in the pectic polymer content of the PAW-soluble fraction occurred without loss of galactose from the cell wall. The molecular weight of the PAW-soluble pectic fraction 1 day after ethylene treatment was similar to that of the Na2CO3-soluble fraction before ethylene treatment. Four days after ethylene treatment, 60% of cell wall polyuronide was solubilized, and 50% of the galactose was lost from the CWM, but the degree of galactosylation and molecular weight of pectic polymers remaining in the CWMs did not decrease. The exception was the CDTA-soluble fraction which showed an apparent decrease in molecular weight during ripening. Concurrently, the PAW-soluble pectic fraction showed a 20-fold reduction in molecular weight. The results suggest that considerable solubilization of the pectic polymers occurred during ripening without changes to their primary structure or degree of polymerization. Following solubilization, the polymers then became susceptible to depolymerization and degalactosidation. Pectolytic enzymes such as endopolygalacturonase and β-galactosidase were therefore implicated in the degradation of solubilized cell wall pectic polymers but not the initial solubilization of the bulk of the pectic polymers in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bieleski R. L., Turner N. A. Separation and estimation of amino acids in crude plant extracts by thin-layer electrophoresis and chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1966 Nov;17(2):278–293. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90206-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenkrantz N., Asboe-Hansen G. New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem. 1973 Aug;54(2):484–489. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90377-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellapenna D., Alexander D. C., Bennett A. B. Molecular cloning of tomato fruit polygalacturonase: Analysis of polygalacturonase mRNA levels during ripening. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6420–6424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dellapenna D., Lashbrook C. C., Toenjes K., Giovannoni J. J., Fischer R. L., Bennett A. B. Polygalacturonase Isozymes and Pectin Depolymerization in Transgenic rin Tomato Fruit. Plant Physiol. 1990 Dec;94(4):1882–1886. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.4.1882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni J. J., DellaPenna D., Bennett A. B., Fischer R. L. Expression of a chimeric polygalacturonase gene in transgenic rin (ripening inhibitor) tomato fruit results in polyuronide degradation but not fruit softening. Plant Cell. 1989 Jan;1(1):53–63. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. J., Watson C. F., Morris P. C., Bird C. R., Seymour G. B., Gray J. E., Arnold C., Tucker G. A., Schuch W., Harding S. Inheritance and effect on ripening of antisense polygalacturonase genes in transgenic tomatoes. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Mar;14(3):369–379. doi: 10.1007/BF00028773. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


