Abstract
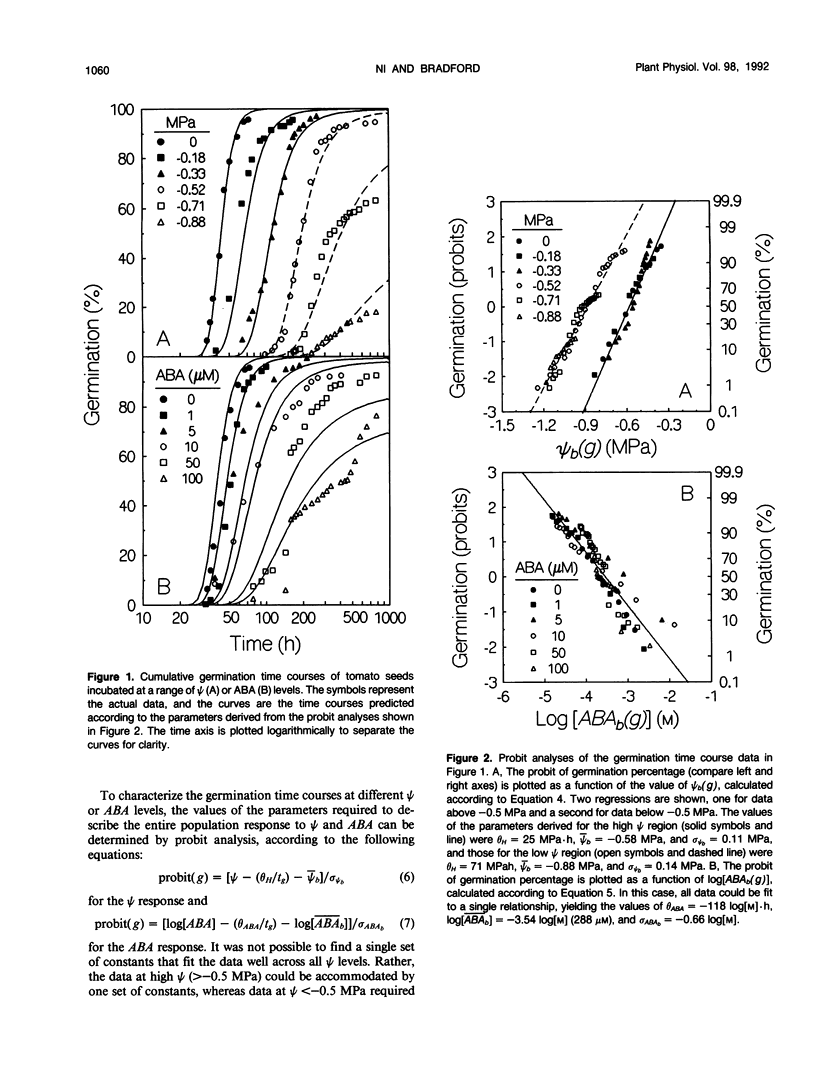
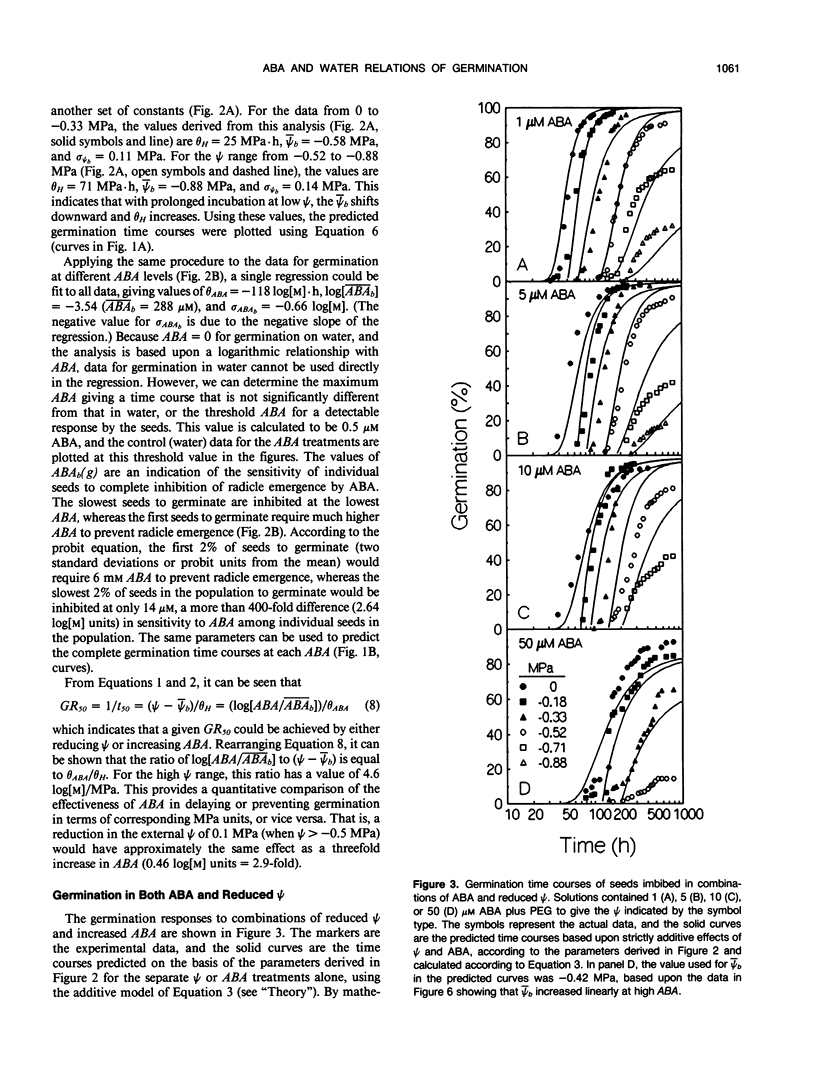
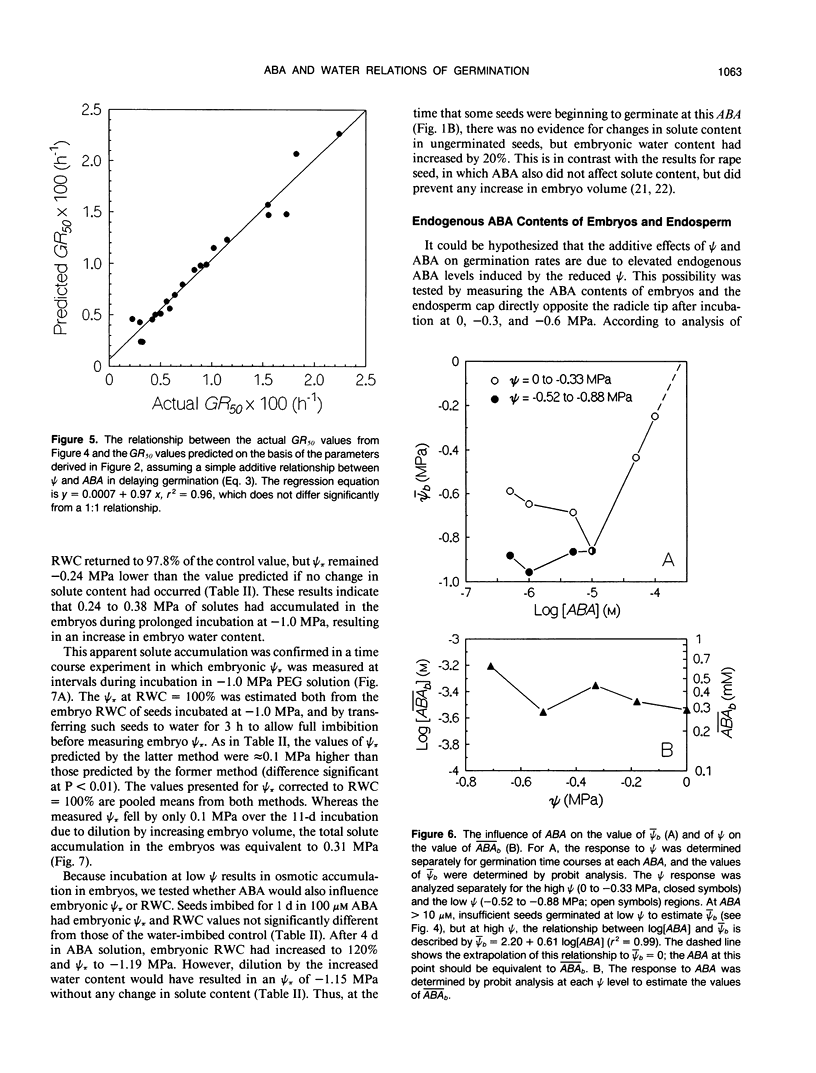
Mathematical models were developed to characterize the physiological bases of the responses of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. cv T5) seed germination to water potential (ψ) and abscisic acid (ABA). Using probit analysis, three parameters were derived that can describe the germination time courses of a seed population at different ψ or ABA levels. For the response of seed germination to reduced ψ, these parameters are the mean base water potential (¯ψb, MPa), the standard deviation of the base water potential among seeds in the population (σψb, MPa), and the “hydrotime constant” (θH, MPa·h). For the response to ABA, they are the log of the mean base ABA concentration ([unk]ABAb, m), the standard deviation of the base ABA concentration among seeds in the population (σABAb, log[m]), and the “ABA-time constant” (θABA, log[m]·h). The values of ¯ψb and [unk]ABAb provide quantitative estimates of the mean sensitivity of germination rate to ψ or ABA, whereas σψb and σABAb account for the variation in sensitivity among seeds in the population. The time constants, θH and θABA, indicate the extent to which germination rate will be affected by a given change in ψ or ABA. Using only these parameters, germination time courses can be predicted with reasonable accuracy at any medium ψ according to the equation probit(g) = [ψ - (θH/tg) - ¯ψb]/σψb, or at any ABA concentration according to the equation probit(g) = [log[ABA] - (θABA/tg) - log[[unk]ABAb]]/σABAb, where tg is the time to radicle emergence of percentage g, and ABA is the ABA concentration (m) in the incubation solution. In the presence of both ABA and reduced ψ, the same parameters can be used to predict seed germination time courses based upon strictly additive effects of ψ and ABA in delaying the time of radicle emergence. Further analysis indicates that ABA and ψ can act both independently and interactively to influence physiological processes preparatory for radicle growth, such as the accumulation of osmotic solutes in the embryo. The models provide quantitative values for the sensitivity of germination to ABA or ψ, allow evaluation of independent and interactive effects of the two factors, and have implications for understanding how ABA and ψ may regulate growth and development.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford K. J. A water relations analysis of seed germination rates. Plant Physiol. 1990 Oct;94(2):840–849. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.2.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creelman R. A., Mason H. S., Bensen R. J., Boyer J. S., Mullet J. E. Water Deficit and Abscisic Acid Cause Differential Inhibition of Shoot versus Root Growth in Soybean Seedlings : Analysis of Growth, Sugar Accumulation, and Gene Expression. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jan;92(1):205–214. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.1.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koornneef M., Hanhart C. J., Hilhorst H. W., Karssen C. M. In Vivo Inhibition of Seed Development and Reserve Protein Accumulation in Recombinants of Abscisic Acid Biosynthesis and Responsiveness Mutants in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jun;90(2):463–469. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.2.463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liptay A., Schopfer P. Effect of Water Stress, Seed Coat Restraint, and Abscisic Acid upon Different Germination Capabilities of Two Tomato Lines at Low Temperature. Plant Physiol. 1983 Dec;73(4):935–938. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.4.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel B. E. Evaluation of the water potentials of solutions of polyethylene glycol 8000 both in the absence and presence of other solutes. Plant Physiol. 1983 May;72(1):66–70. doi: 10.1104/pp.72.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schopfer P., Plachy C. Control of Seed Germination by Abscisic Acid : II. Effect on Embryo Water Uptake in Brassica napus L. Plant Physiol. 1984 Sep;76(1):155–160. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schopfer P., Plachy C. Control of Seed Germination by Abscisic Acid : III. Effect on Embryo Growth Potential (Minimum Turgor Pressure) and Growth Coefficient (Cell Wall Extensibility) in Brassica napus L. Plant Physiol. 1985 Mar;77(3):676–686. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.3.676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skriver K., Mundy J. Gene expression in response to abscisic acid and osmotic stress. Plant Cell. 1990 Jun;2(6):503–512. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.6.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker-Simmons M. ABA Levels and Sensitivity in Developing Wheat Embryos of Sprouting Resistant and Susceptible Cultivars. Plant Physiol. 1987 May;84(1):61–66. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welbaum G. E., Tissaoui T., Bradford K. J. Water Relations of Seed Development and Germination in Muskmelon (Cucumis melo L.) : III. Sensitivity of Germination to Water Potential and Abscisic Acid during Development. Plant Physiol. 1990 Apr;92(4):1029–1037. doi: 10.1104/pp.92.4.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]