Abstract
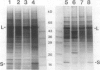
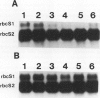
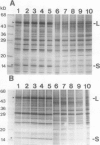
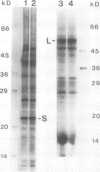
In conditions of limiting external inorganic carbon, the unicellular alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii induces a mechanism to actively transport and accumulate inorganic carbon within the cell. A high internal inorganic carbon concentration enables the cell to photosynthesize efficiently with little oxygen inhibition, even in conditions of limiting external inorganic carbon. A correlation between limiting inorganic carbon-induced induction of the CO2-concentrating mechanism and decreased synthesis of the large and small subunits of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase has been observed. Cells that had been transferred from elevated CO2 to limiting CO2 exhibit transient declines of label incorporation into both subunit polypeptides. We have found that this decrease in synthesis of large and small subunits results from specific and coordinated down-regulation of translation of both subunits possibly resulting, at least in part, from modification of large and small subunit transcripts.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailly J., Coleman J. R. Effect of CO(2) Concentration on Protein Biosynthesis and Carbonic Anhydrase Expression in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1988 Aug;87(4):833–840. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.4.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry J. O., Carr J. P., Klessig D. F. mRNAs encoding ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase remain bound to polysomes but are not translated in amaranth seedlings transferred to darkness. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4190–4194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry J. O., Nikolau B. J., Carr J. P., Klessig D. F. Translational regulation of light-induced ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase gene expression in amaranth. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2347–2353. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. R., Berry J. A., Togasaki R. K., Grossman A. R. Identification of Extracellular Carbonic Anhydrase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1984 Oct;76(2):472–477. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.2.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Gruissem W. Control of plastid gene expression during development: the limited role of transcriptional regulation. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):379–387. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90290-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz C. C., Herget T., Wolter F. P., Schell J., Schreier P. H. Reduced steady-state levels of rbcS mRNA in plants kept in the dark are due to differential degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4458–4462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraghty A. M., Anderson J. C., Spalding M. H. A 36 Kilodalton Limiting-CO(2) Induced Polypeptide of Chlamydomonas Is Distinct from the 37 Kilodalton Periplasmic Carbonic Anhydrase. Plant Physiol. 1990 May;93(1):116–121. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.1.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Rahire M. Sequence, evolution and differential expression of the two genes encoding variant small subunits of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 5;191(3):421–432. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanningmeier U. Possible control of transcript levels by chlorophyll precursors in Chlamydomonas. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Nov 1;177(2):417–424. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14391.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullet J. E., Klein R. R. Transcription and RNA stability are important determinants of higher plant chloroplast RNA levels. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1571–1579. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolau B. J., Klessig D. F. Coordinate, Organ-Specific and Developmental Regulation of Ribulose 1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase Gene Expression in Amaranthus hypochondriacus. Plant Physiol. 1987 Sep;85(1):167–173. doi: 10.1104/pp.85.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy H. Rubisco assembly: a model system for studying the mechanism of chaperonin action. Plant Cell. 1989 Nov;1(11):1035–1042. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.11.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt G. W., Mishkind M. L. Rapid degradation of unassembled ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunits in chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2632–2636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt G. W., Mishkind M. L. The transport of proteins into chloroplasts. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:879–912. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skadsen R. W., Scandalios J. G. Translational control of photo-induced expression of the Cat2 catalase gene during leaf development in maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2785–2789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. M., Ellis R. J. Light-stimulated accumulation of transcripts of nuclear and chloroplast genes for ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(2):127–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalding M. H., Jeffrey M. Membrane-Associated Polypeptides Induced in Chlamydomonas by Limiting CO(2) Concentrations. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):133–137. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalding M. H., Spreitzer R. J., Ogren W. L. Reduced Inorganic Carbon Transport in a CO(2)-Requiring Mutant of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Plant Physiol. 1983 Oct;73(2):273–276. doi: 10.1104/pp.73.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spreitzer R. J., Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Rahire M., Rochaix J. D. Nonsense mutations in the Chlamydomonas chloroplast gene that codes for the large subunit of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5460–5464. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spreitzer R. J., Mets L. Photosynthesis-deficient Mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardii with Associated Light-sensitive Phenotypes. Plant Physiol. 1981 Mar;67(3):565–569. doi: 10.1104/pp.67.3.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sültemeyer D. F., Miller A. G., Espie G. S., Fock H. P., Canvin D. T. Active CO(2) Transport by the Green Alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1989 Apr;89(4):1213–1219. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.4.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter U., Feierabend J. Multiple coordinate controls contribute to a balanced expression of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase subunits in rye leaves. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jan 26;187(2):445–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15324.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]