Abstract
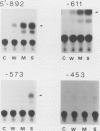
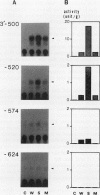
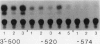
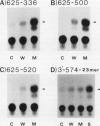
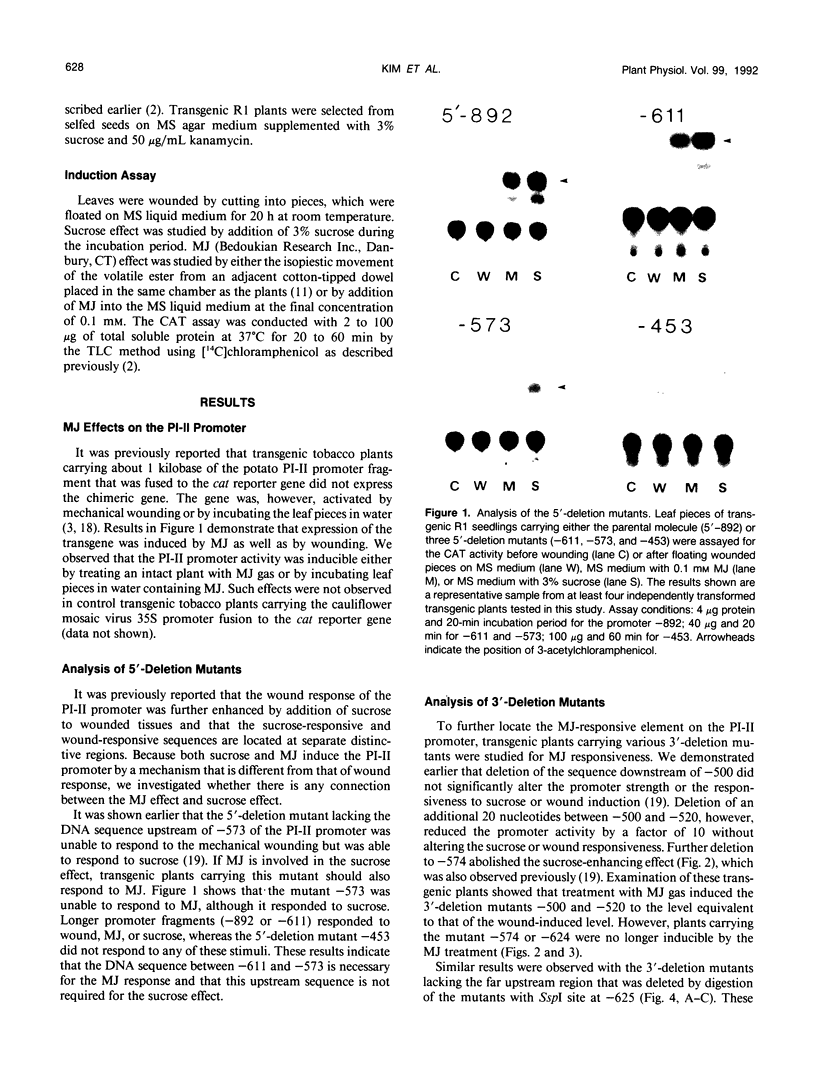
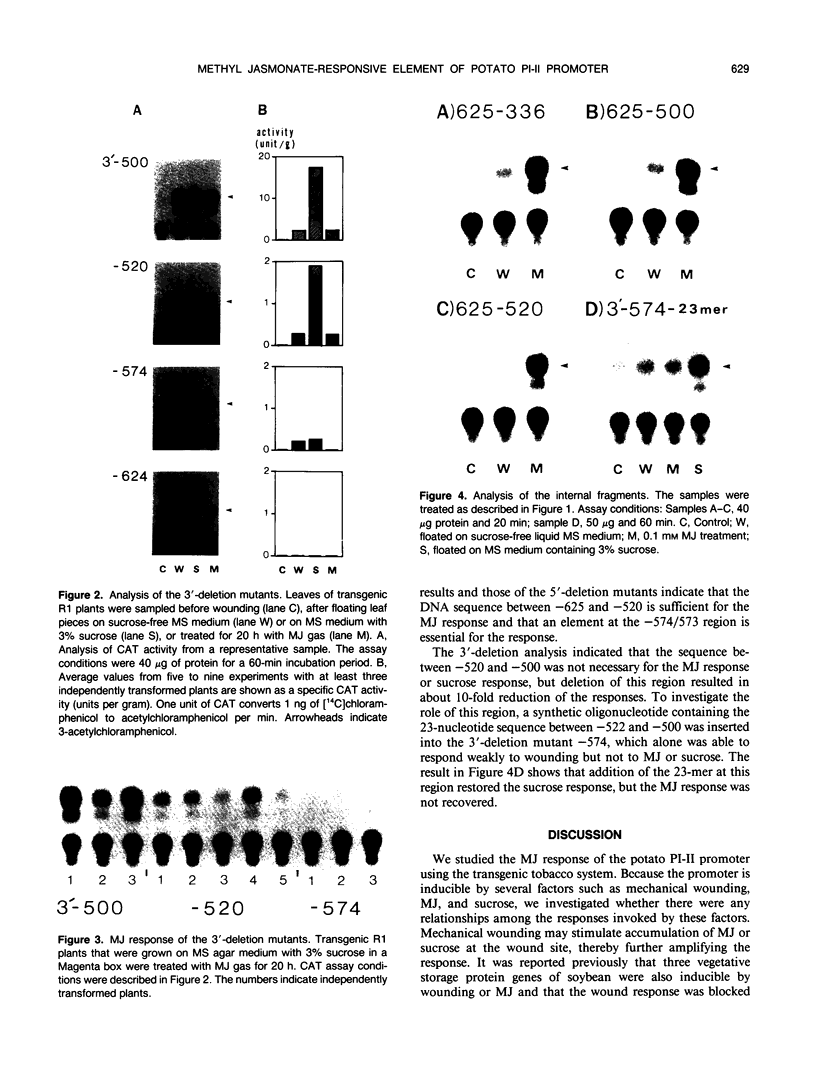
The potato proteinase inhibitor II promoter was studied to identify cis-acting regulatory sequences involved in methyl jasmonate (MJ) response using transgenic tobacco plants carrying various lengths of the promoter fused to a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter gene. An internal fragment between −625 and −520 was sufficient to confer a response to MJ, wounding, or sucrose when it was placed upstream of the nos promoter −101, which contains the CAAT-TATA region. Deletion of the proteinase inhibitor II promoter sequence upstream of −611 did not affect the MJ response, but a further deletion to −573 eliminated the response. The 3′-deletion study showed that the DNA sequence downstream from −520 is dispensable. However, 3′-deletion mutant −574 did not respond to the MJ treatment. These results indicated that an element essential for the MJ response is located at the −574/−573 region where the G-box sequence (CACGTGG) is located. The G-box sequence was not required for the sucrose enhancer effect, suggesting that the MJ response mechanism is different from that of sucrose.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- An G., Costa M. A., Ha S. B. Nopaline synthase promoter is wound inducible and auxin inducible. Plant Cell. 1990 Mar;2(3):225–233. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.3.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- An G., Mitra A., Choi H. K., Costa M. A., An K., Thornburg R. W., Ryan C. A. Functional analysis of the 3' control region of the potato wound-inducible proteinase inhibitor II gene. Plant Cell. 1989 Jan;1(1):115–122. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Morgan J. G., Crabtree G. R., Sharp P. A. The adenovirus major late transcription factor activates the rat gamma-fibrinogen promoter. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):684–688. doi: 10.1126/science.3672119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisle A. J., Ferl R. J. Characterization of the Arabidopsis Adh G-box binding factor. Plant Cell. 1990 Jun;2(6):547–557. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.6.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiRita V. J., Gelvin S. B. Deletion analysis of the mannopine synthase gene promoter in sunflower crown gall tumors and Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 May;207(2-3):233–241. doi: 10.1007/BF00331583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald R. G., Cashmore A. R. Mutation of either G box or I box sequences profoundly affects expression from the Arabidopsis rbcS-1A promoter. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1717–1726. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08295.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donald R. G., Schindler U., Batschauer A., Cashmore A. R. The plant G box promoter sequence activates transcription in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and is bound in vitro by a yeast activity similar to GBF, the plant G box binding factor. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1727–1735. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08296.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer E. E., Ryan C. A. Interplant communication: airborne methyl jasmonate induces synthesis of proteinase inhibitors in plant leaves. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7713–7716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franceschi V. R., Grimes H. D. Induction of soybean vegetative storage proteins and anthocyanins by low-level atmospheric methyl jasmonate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6745–6749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiltinan M. J., Marcotte W. R., Jr, Quatrano R. S. A plant leucine zipper protein that recognizes an abscisic acid response element. Science. 1990 Oct 12;250(4978):267–271. doi: 10.1126/science.2145628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R., Ryan C. A. Wound-inducible potato inhibitor II genes: enhancement of expression by sucrose. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Apr;14(4):527–536. doi: 10.1007/BF00027498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri F., Lam E., Chua N. H. Two tobacco DNA-binding proteins with homology to the nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1989 Aug 31;340(6236):727–730. doi: 10.1038/340727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keil M., Sanchez-Serrano J., Schell J., Willmitzer L. Localization of Elements Important for the Wound-Inducible Expression of a Chimeric Potato Proteinase Inhibitor II-CAT Gene in Transgenic Tobacco Plants. Plant Cell. 1990 Jan;2(1):61–70. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. R., Costa M. A., An G. H. Sugar response element enhances wound response of potato proteinase inhibitor II promoter in transgenic tobacco. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Nov;17(5):973–983. doi: 10.1007/BF00037137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E., Benfey P. N., Gilmartin P. M., Fang R. X., Chua N. H. Site-specific mutations alter in vitro factor binding and change promoter expression pattern in transgenic plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7890–7894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oeda K., Salinas J., Chua N. H. A tobacco bZip transcription activator (TAF-1) binds to a G-box-like motif conserved in plant genes. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1793–1802. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07704.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pēna-Cortés H., Sánchez-Serrano J. J., Mertens R., Willmitzer L., Prat S. Abscisic acid is involved in the wound-induced expression of the proteinase inhibitor II gene in potato and tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9851–9855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan C. A. Oligosaccharide signalling in plants. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:295–317. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler U., Cashmore A. R. Photoregulated gene expression may involve ubiquitous DNA binding proteins. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3415–3427. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07549.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulze-Lefert P., Dangl J. L., Becker-André M., Hahlbrock K., Schulz W. Inducible in vivo DNA footprints define sequences necessary for UV light activation of the parsley chalcone synthase gene. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):651–656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh K., Dennis E. S., Ellis J. G., Llewellyn D. J., Tokuhisa J. G., Wahleithner J. A., Peacock W. J. OCSBF-1, a maize ocs enhancer binding factor: isolation and expression during development. Plant Cell. 1990 Sep;2(9):891–903. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.9.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staswick P. E., Huang J. F., Rhee Y. Nitrogen and methyl jasmonate induction of soybean vegetative storage protein genes. Plant Physiol. 1991 May;96(1):130–136. doi: 10.1104/pp.96.1.130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabata T., Takase H., Takayama S., Mikami K., Nakatsuka A., Kawata T., Nakayama T., Iwabuchi M. A protein that binds to a cis-acting element of wheat histone genes has a leucine zipper motif. Science. 1989 Sep 1;245(4921):965–967. doi: 10.1126/science.2772648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda J., Kato J. Isolation and Identification of a Senescence-promoting Substance from Wormwood (Artemisia absinthium L.). Plant Physiol. 1980 Aug;66(2):246–249. doi: 10.1104/pp.66.2.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]