Abstract
Pollen is an excellent source of actin for biochemical and physiological studies of the actomyosin system in higher plants. We have developed an efficient method to prepare relatively high levels of actin from the pollen of maize (Zea mays L.). The procedures of purification include acetone powder preparation, saturated ammonium sulfate fractionation, diethylaminoethyl-cellulose chromatography, a cycle of polymerization-depolymerization, and Sephacryl S-200 gel filtration. The average yield of actin is 19 milligrams per 100 grams of pollen grains extracted. This is comparable with those of Acanthamoeba castellanii and human platelets. The purified pollen actin is electrophoretically homogeneous and its molecular mass is 42 kilodaltons. The amino acid composition and circular dichroism spectrum of pollen actin are identical to those of muscle actin. The actin purified from pollen is able to polymerize to F-actin. The pollen F-actin activated the activity of the muscle myosin ATPase sevenfold.
Full text
PDF

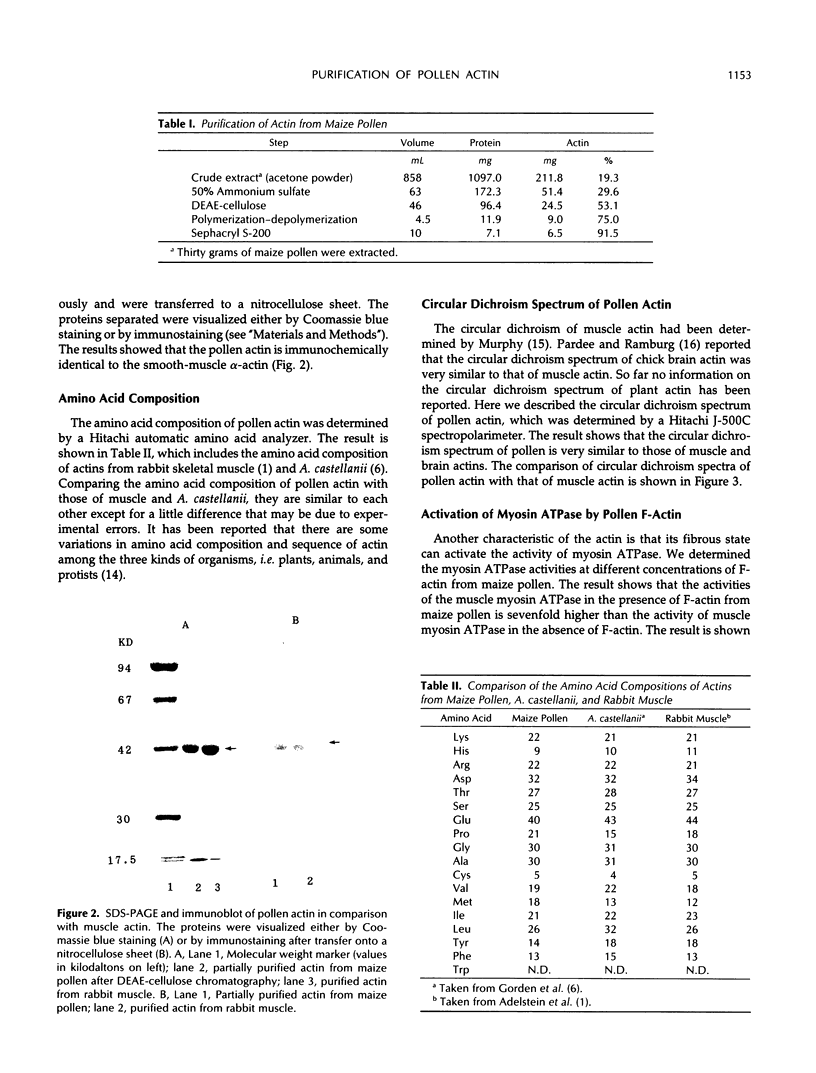

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelstein R. S., Kuehl W. M. Structural studies on rabbit skeletal actin. I. Isolation and characterization of the peptides produced by cyanogen bromide cleavage. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 17;9(6):1355–1364. doi: 10.1021/bi00808a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake M. S., Johnston K. H., Russell-Jones G. J., Gotschlich E. C. A rapid, sensitive method for detection of alkaline phosphatase-conjugated anti-antibody on Western blots. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):175–179. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90320-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Condeelis J. S. The identification of F actin of the pollen tube and protoplast of Amaryllis belladonna. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Oct;88(2):435–439. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon D. J., Eisenberg E., Korn E. D. Characterization of cytoplasmic actin isolated from Acanthamoeba castellanii by a new method. J Biol Chem. 1976 Aug 10;251(15):4778–4786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatano S., Oosawa F. Isolation and characterization of plasmodium actin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 31;127(2):488–498. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90402-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBel D., Poirier G. G., Beaudoin A. R. A convenient method for the ATPase assay. Anal Biochem. 1978 Mar;85(1):86–89. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90277-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma Y. Z., Yen L. F. Actin and Myosin in pea tendrils. Plant Physiol. 1989 Feb;89(2):586–589. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.2.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy A. J. Circular dichroism of the adenine and 6-mercaptopurine nucleotide complexes of actin. Biochemistry. 1971 Sep 28;10(20):3723–3728. doi: 10.1021/bi00796a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee J. D., Bamburg J. R. Actin from embryonic chick brain. Isolation in high yield and comparison of biochemical properties with chicken muscle actin. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2245–2252. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesacreta T. C., Carley W. W., Webb W. W., Parthasarathy M. V. F-actin in conifer roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2898–2901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S., Stracher A., Lucas R. C. Isolation and characterization of actin and actin-binding protein from human platelets. J Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;91(1):201–211. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tang X. J., Lancelle S. A., Hepler P. K. Fluorescence microscopic localization of actin in pollen tubes: comparison of actin antibody and phalloidin staining. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1989;12(4):216–224. doi: 10.1002/cm.970120404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva M. A., Ho S. C., Wang J. L. Isolation and characterization of one isoform of actin from cultured soybean cells. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1990 Feb 15;277(1):35–41. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(90)90546-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]