Abstract
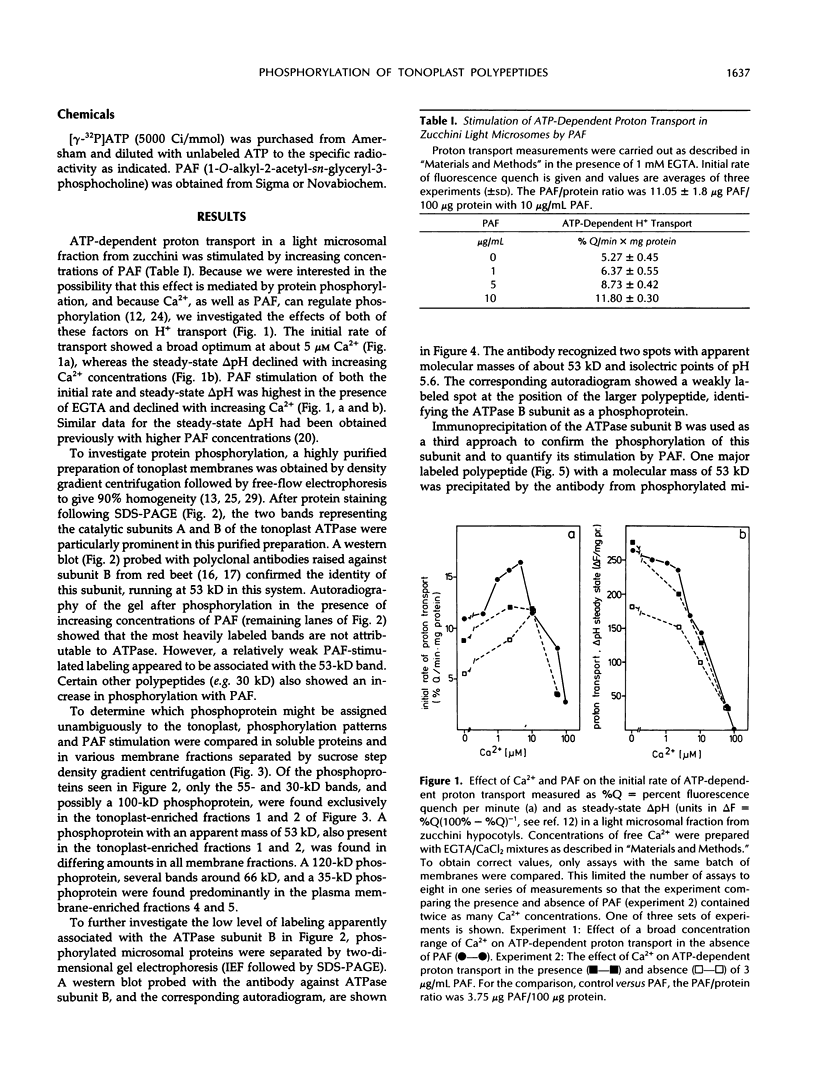
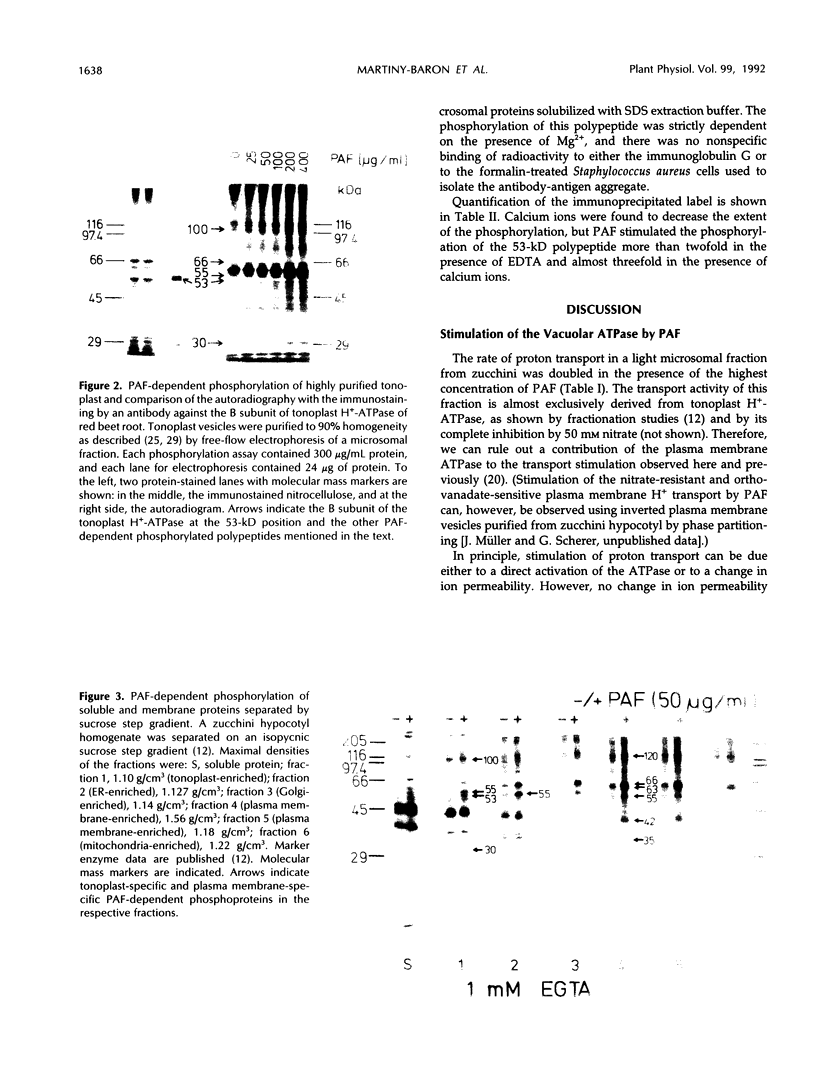
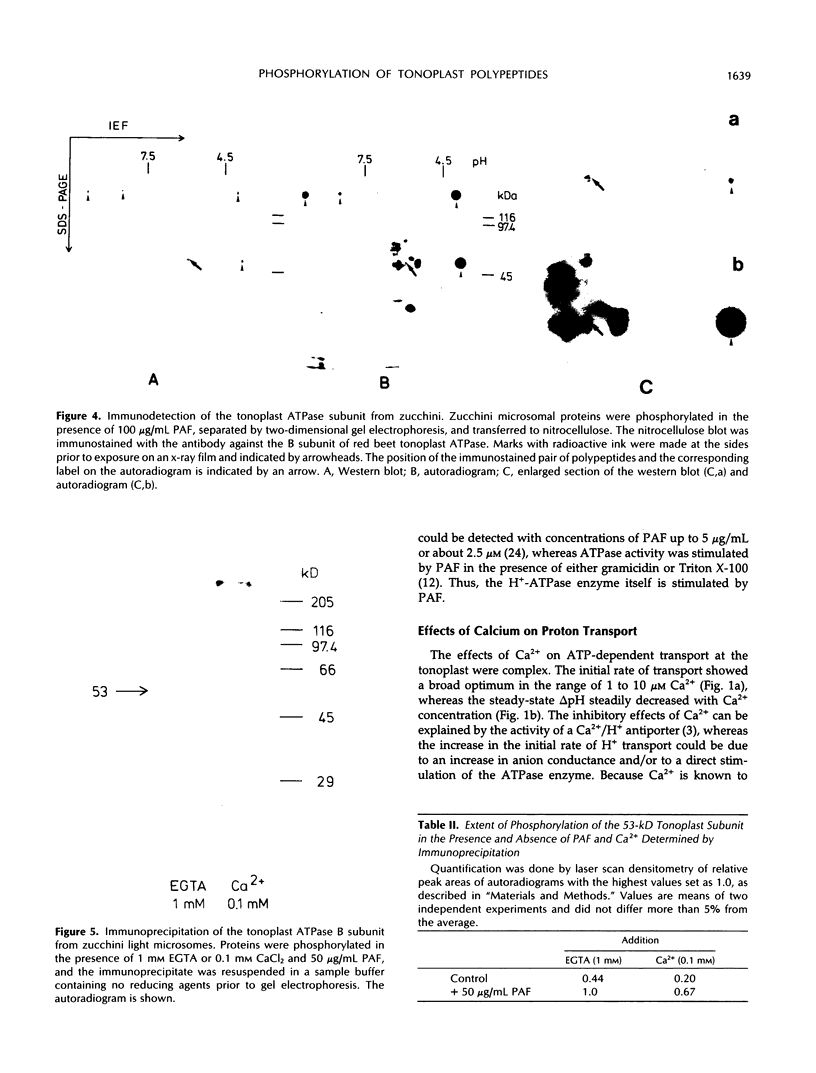
The ether phospholipid platelet-activating factor and certain similar phospholipids, including lysophosphatidylcholine, are known to stimulate both H+ transport and protein phosphorylation in plant microsomal membranes. In the present work, several polypeptides in highly purified tonoplast membranes from zucchini (Cucurbita pepo L.) showed platelet-activating factor-dependent phosphorylation. Comparison of protein phosphorylation in different membrane fractions separated by sucrose step density gradient centrifugation indicated that some of the phosphoproteins were contaminants or were common to several membrane fractions, but platelet-activating factor-dependent phosphorylation of peptides at 30, 53, and perhaps 100 kilodaltons was tonoplast specific. The phosphoprotein of 53 kilodaltons was shown by three different approaches (one- and two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, western blots, and immunoprecipitation) to cross-react with antibody raised against the B subunit of the tonoplast ATPase from red beet (Beta vulgaris L.).
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckhout T. J. Characterization of Ca Transport in Purified Endoplasmic Reticulum Membrane Vesicles from Lepidium sativum L. Roots. Plant Physiol. 1984 Dec;76(4):962–967. doi: 10.1104/pp.76.4.962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bush D. R., Sze H. Calcium transport in tonoplast and endoplasmic reticulum vesicles isolated from cultured carrot cells. Plant Physiol. 1986 Feb;80(2):549–555. doi: 10.1104/pp.80.2.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont F. M., Tanaka C. K., Hurkman W. J. separation and Immunological Characterization of Membrane Fractions from Barley Roots. Plant Physiol. 1988 Mar;86(3):717–724. doi: 10.1104/pp.86.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. J. Platelet activating factor: a biologically active phosphoglyceride. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:483–509. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladror U. S., Zielinski R. E. Protein kinase activities in tonoplast and plasmalemma membranes from corn roots. Plant Physiol. 1989 Jan;89(1):151–158. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manolson M. F., Ouellette B. F., Filion M., Poole R. J. cDNA sequence and homologies of the "57-kDa" nucleotide-binding subunit of the vacuolar ATPase from Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):17987–17994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manolson M. F., Rea P. A., Poole R. J. Identification of 3-O-(4-benzoyl)benzoyladenosine 5'-triphosphate- and N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide-binding subunits of a higher plant H+-translocating tonoplast ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12273–12279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martiny-Baron G., Scherer G. F. Phospholipid-stimulated protein kinase in plants. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):18052–18059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson N. Structure, molecular genetics, and evolution of vacuolar H+-ATPases. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1989 Oct;21(5):553–571. doi: 10.1007/BF00808113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall S. K., Sze H. Probing the catalytic subunit of the tonoplast H+-ATPase from oat roots. Binding of 7-chloro-4-nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1,3,-diazole to the 72-kilodalton polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7135–7141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuveni M., Bennett A. B., Bressan R. A., Hasegawa P. M. Enhanced H Transport Capacity and ATP Hydrolysis Activity of the Tonoplast H-ATPase after NaCl Adaptation. Plant Physiol. 1990 Oct;94(2):524–530. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.2.524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G. F. 1-Alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (platelet activating factor) stimulates plant H+ transport in vitro and growth. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Dec 31;133(3):1160–1167. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91258-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer G. F., André B. A rapid response to a plant hormone: auxin stimulates phospholipase A2 in vivo and in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92106-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soderling T. R. Protein kinases. Regulation by autoinhibitory domains. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):1823–1826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






