Abstract
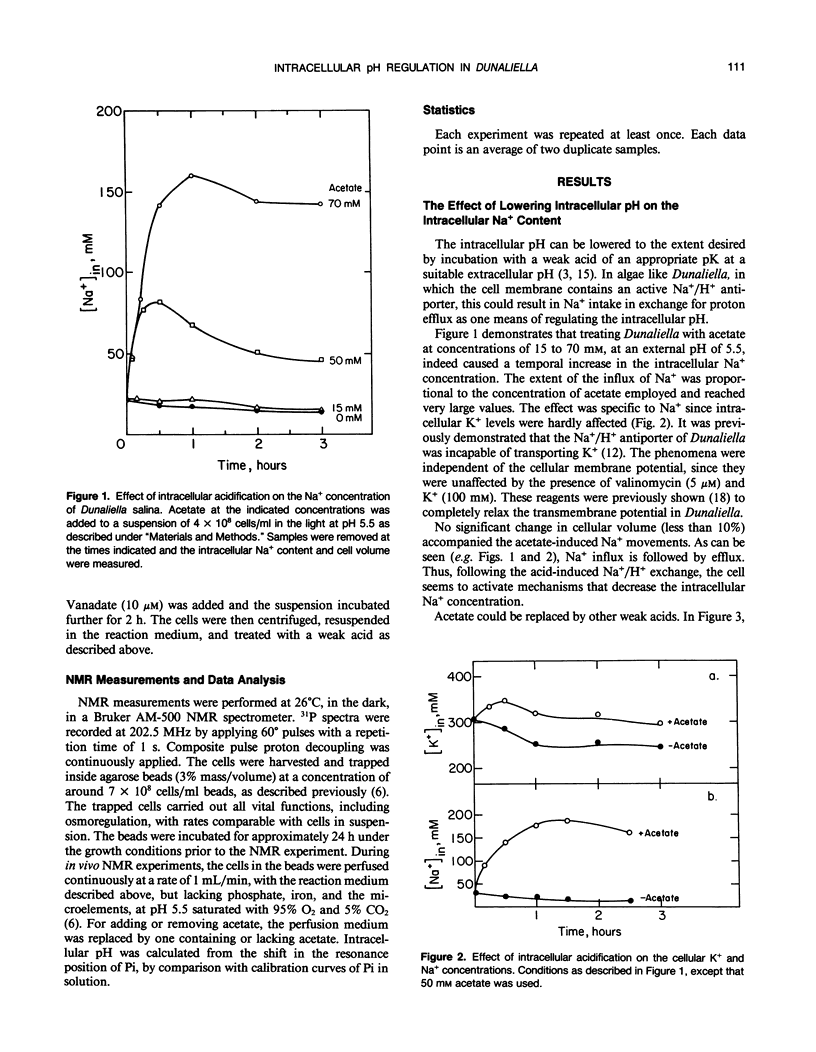
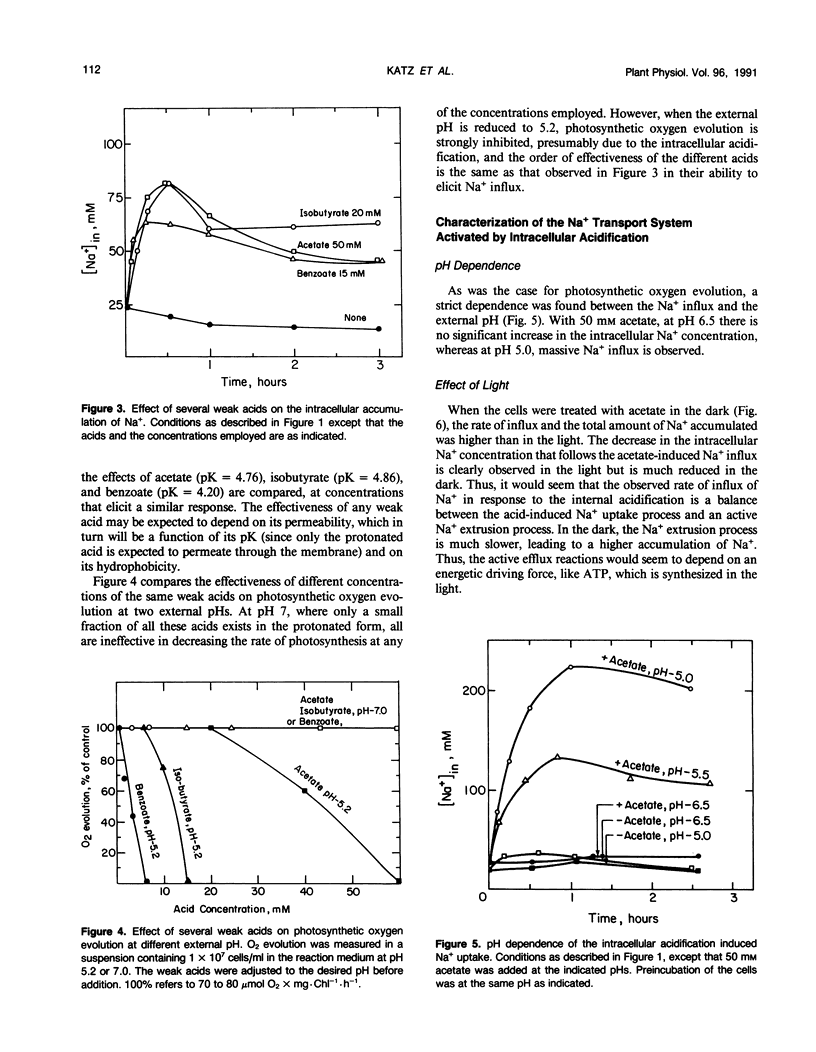
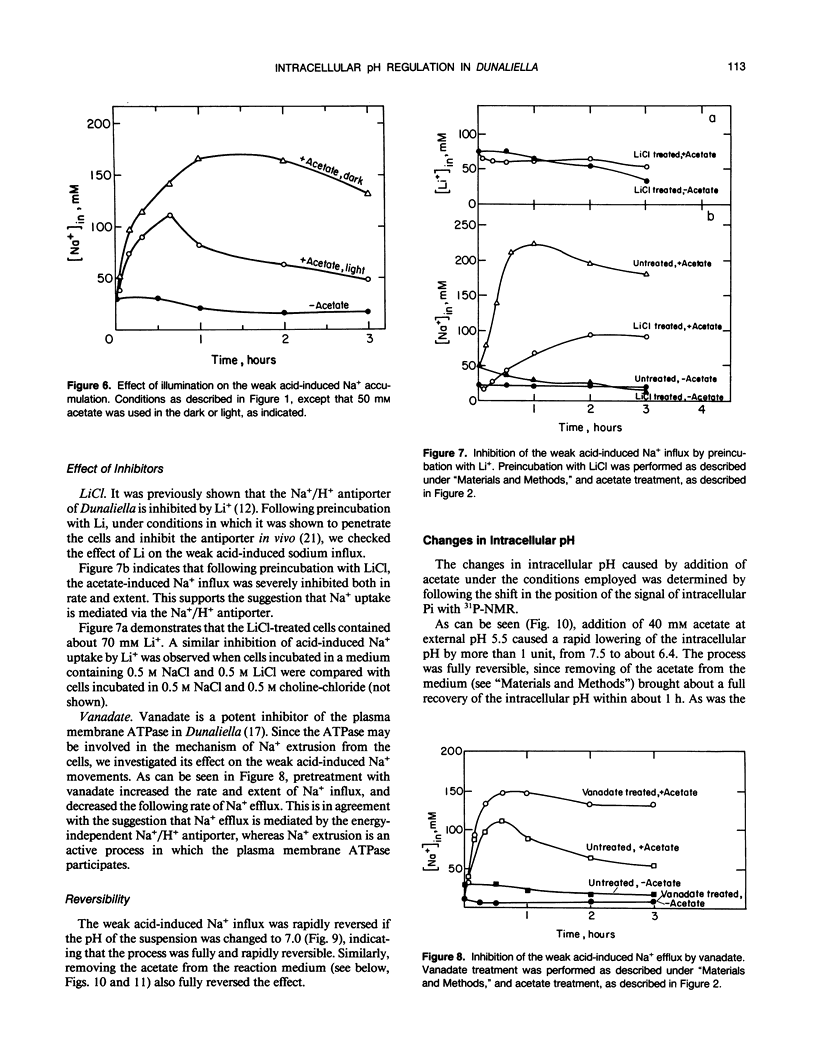
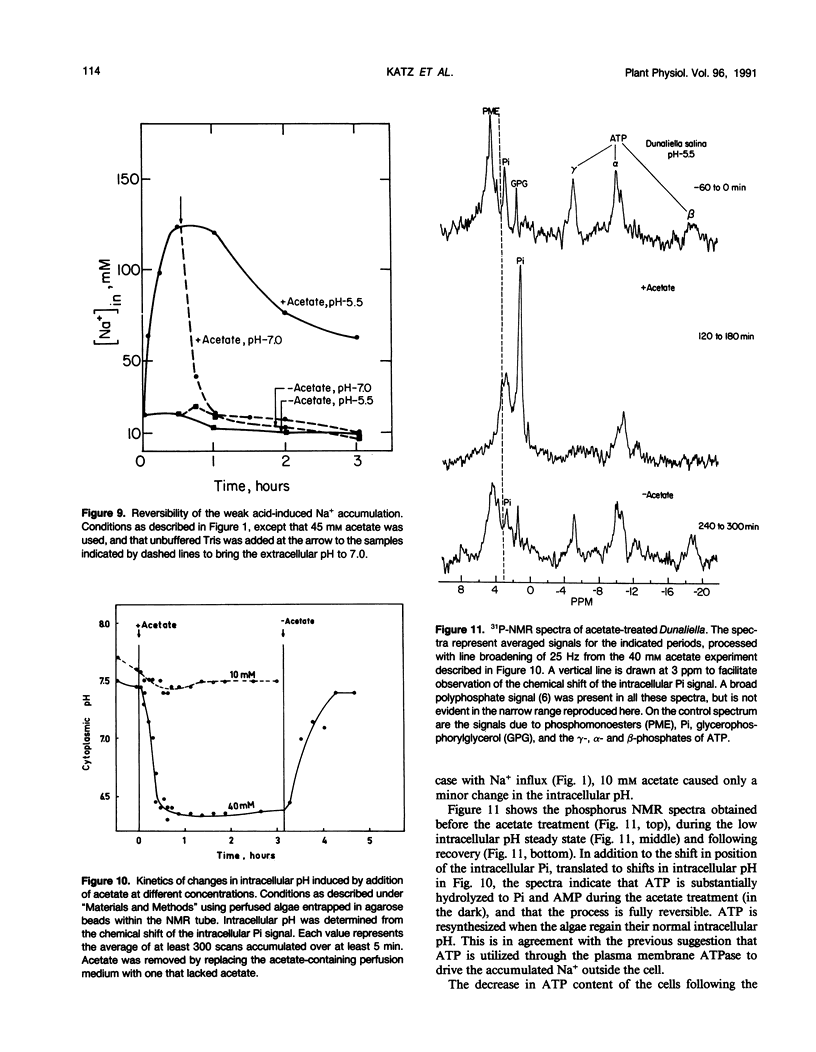
Na+/H+ exchange activity in whole cells of the halotolerant alga Dunaliella salina can be elicited by intracellular acidification due to addition of weak acids at appropriate external pH. The changes in both intracellular pH and Na+ were followed. Following a mild intracellular acidification, intracellular Na+ content increased dramatically and then decreased. We interpret the phase of Na+ influx as due to the activation of the plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter and the phase of Na+ efflux as due to an active Na+ extrusion process. The following observations are in agreement with this interpretation: (a) the Na+ influx phase was sensitive to Li+, which is an inhibitor of the Na+/H+ antiporter, did not require energy, and was insensitive to vanadate; (b) the Na+ efflux phase is energy-dependent and sensitive to the plasma membrane ATPase inhibitor, vanadate. Following intracellular acidification, a drastic decrease in the intracellular ATP content is observed that is reversed when the cells regain their neutral pH value. We suggest that the intracellular acidification-induced change in the internal Na+ concentration is due to a combination of Na+ uptake via the Na+/H+ antiporter and an active, ATPase-dependent, Na+ extrusion. The Na+/H+ antiporter seems, therefore, to play a principal role in internal pH regulation in Dunaliella.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aronson P. S. Kinetic properties of the plasma membrane Na+-H+ exchanger. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:545–560. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Amotz A., Shaish A., Avron M. Mode of Action of the Massively Accumulated beta-Carotene of Dunaliella bardawil in Protecting the Alga against Damage by Excess Irradiation. Plant Physiol. 1989 Nov;91(3):1040–1043. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.3.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bental M., Degani H., Avron M. Na-NMR Studies of the Intracellular Sodium Ion Concentration in the Halotolerant Alga Dunaliella salina. Plant Physiol. 1988 Aug;87(4):813–817. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.4.813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bental M., Pick U., Avron M., Degani H. Metabolic studies with NMR spectroscopy of the alga Dunaliella salina trapped within agarose beads. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Feb 22;188(1):111–116. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15377.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guern J., Mathieu Y., Pean M., Pasquier C., Beloeil J. C., Lallemand J. Y. Cytoplasmic pH Regulation in Acer pseudoplatanus Cells: I. A P NMR Description of Acid-Load Effects. Plant Physiol. 1986 Nov;82(3):840–845. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.3.840. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Pick U., Avron M. Characterization and reconstitution of the Na+/H+ antiporter from the plasma membrane of the halotolerant alga Dunaliella. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jul 24;983(1):9–14. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90373-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krulwich T. A. Na+/H+ antiporters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Dec 30;726(4):245–264. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(83)90011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathieu Y., Guern J., Pean M., Pasquier C., Beloeil J. C., Lallemand J. Y. Cytoplasmic pH Regulation in Acer pseudoplatanus Cells: II. Possible Mechanisms Involved in pH Regulation during Acid-Load. Plant Physiol. 1986 Nov;82(3):846–852. doi: 10.1104/pp.82.3.846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren-Shamir M., Pick U., Avron M. Involvement of the Plasma Membrane ATPase in the Osmoregulatory Mechanism of the Alga Dunaliella salina. Plant Physiol. 1989 Apr;89(4):1258–1263. doi: 10.1104/pp.89.4.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren-Shamir M., Pick U., Avron M. Plasma membrane potential of the alga dunaliella, and its relation to osmoregulation. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jun;93(2):403–408. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.2.403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padan E., Schuldiner S. Intracellular pH and membrane potential as regulators in the prokaryotic cell. J Membr Biol. 1987;95(3):189–198. doi: 10.1007/BF01869481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pick U., Karni L., Avron M. Determination of Ion Content and Ion Fluxes in the Halotolerant Alga Dunaliella salina. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):92–96. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.92. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


