Abstract
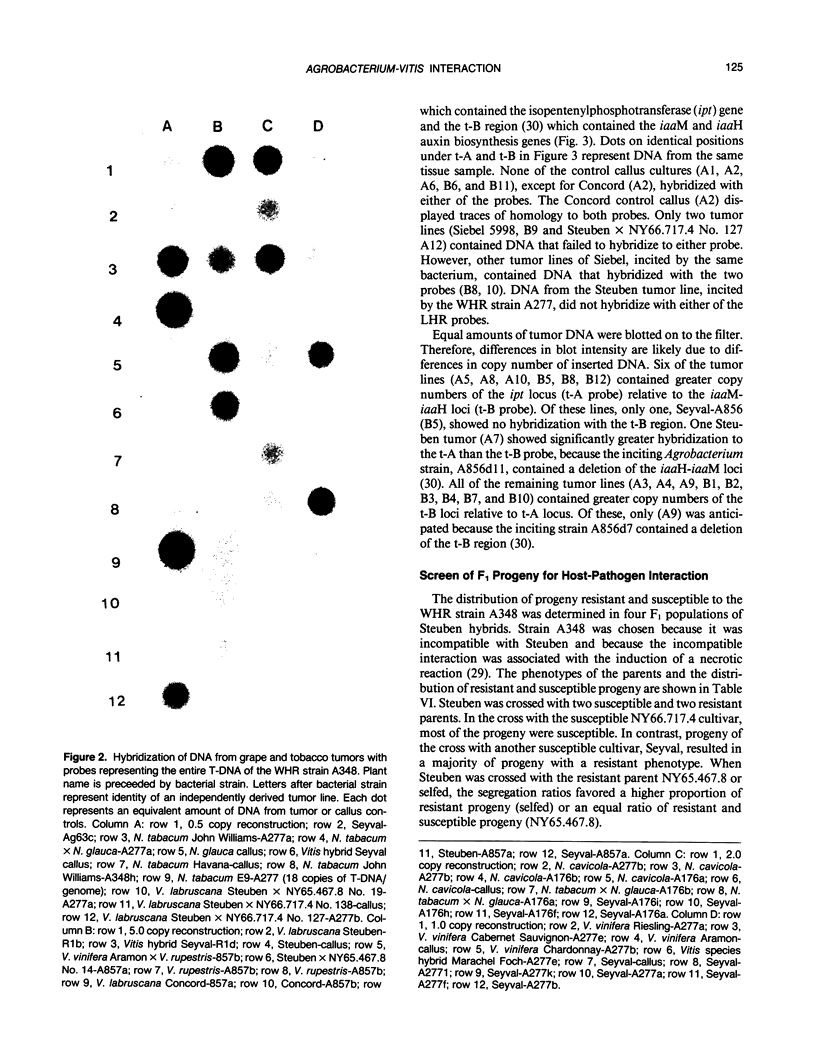
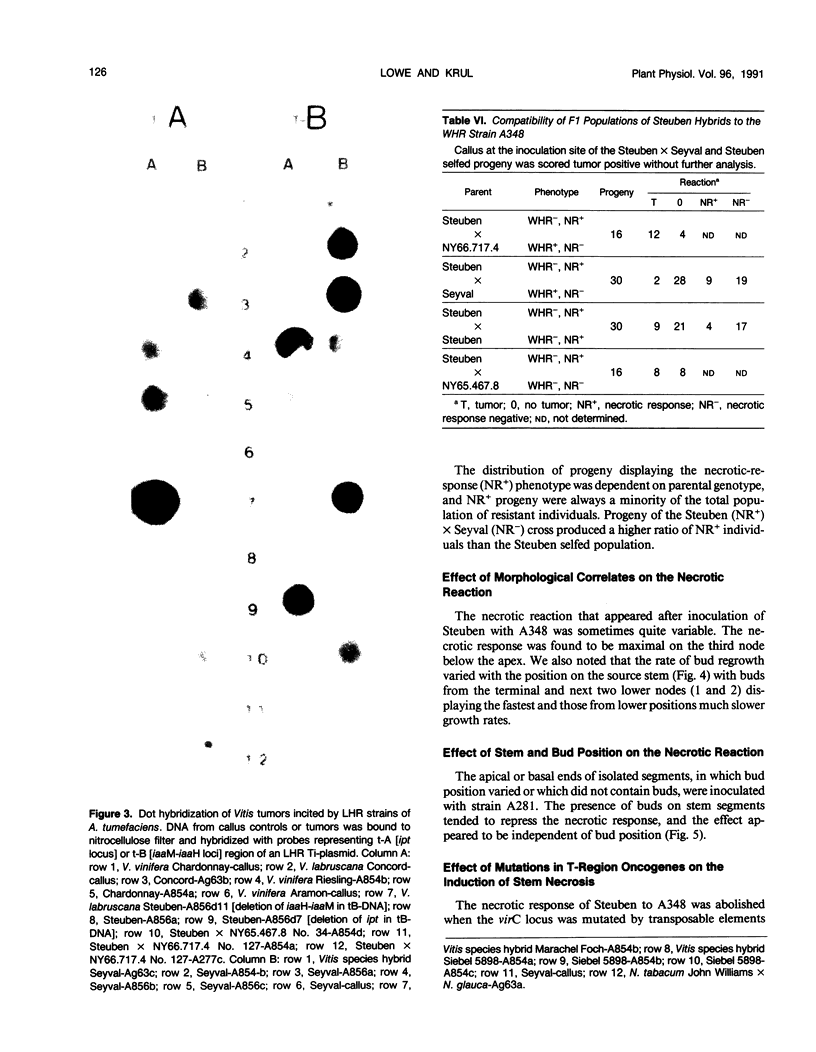
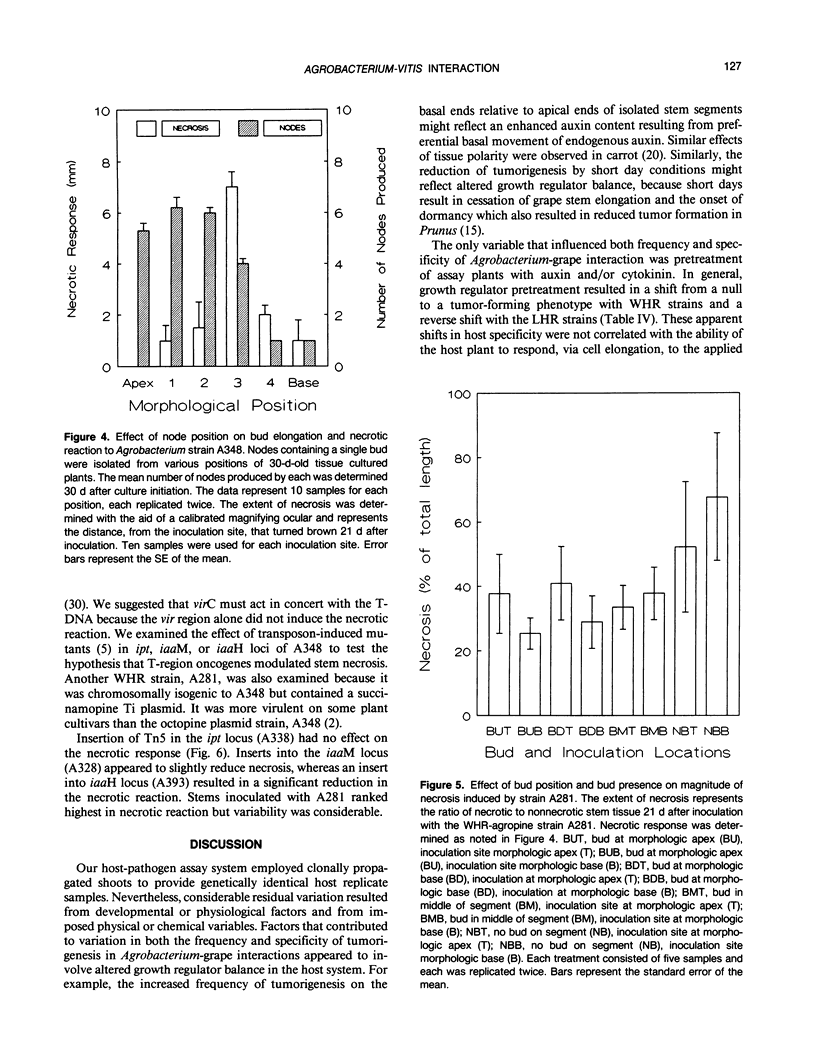
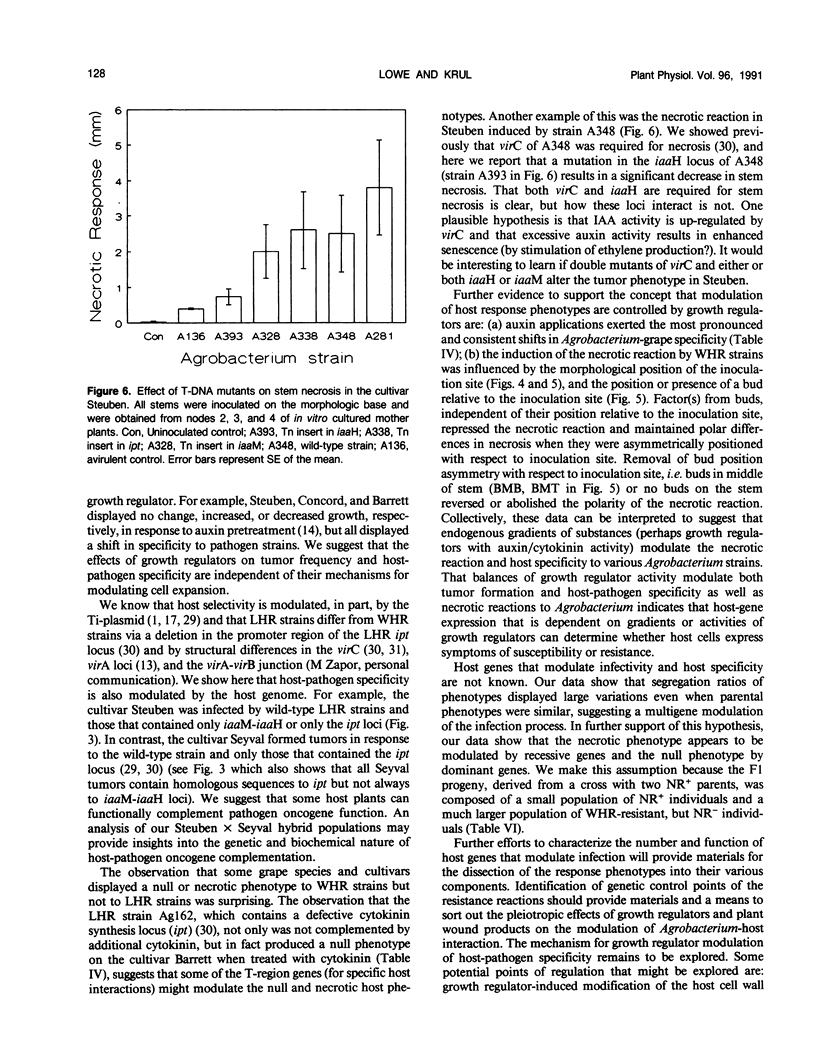
Tumor formation in Vitis species and hybrids, incited by Agrobacterium tumefaciens, was altered by chemical, physical, developmental, and genetic variables. Knowledge of the effect of these variables was used to develop a stringent in vitro assay system to select parents for a study of genetic factors that modulate tumor formation. Tumor formation was reduced by short day preconditioning of assay plants and by inoculation of the morphological apex of isolated stem segments. Pretreatment of plants with auxin or cytokinin altered specificity in various combinations of strains and host genotypes. All Vitis species and hybrids formed tumors in response to strains designated as limited host range, but some displayed a necrotic reaction (cell death at and below site of inoculation) or a null response (same as the response to inoculation with an avirulent strain) to strains designated as wide host range (VC Knauf, CG Panagopoulos, EW Nester [1982] Phytopathology 72: 1545-1549). Screens of F1 progeny, derived from crosses of null, necrotic, and tumor-producing phenotypes, demonstrated that the null and the necrotic phenotypes were modulated by dominant and recessive host genes. The extent of cellular necrosis in the necrotic phenotype was modified by the morphological location of the inoculation site, by the presence of buds on the host stem, and by deletion of the tryptophane monooxygenase locus gene of the Ti-plasmid.
Full text
PDF


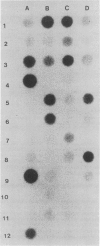
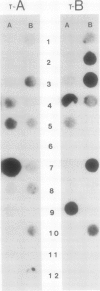
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buchholz W. G., Thomashow M. F. Host range encoded by the Agrobacterium tumefaciens tumor-inducing plasmid pTiAg63 can be expanded by modification of its T-DNA oncogene complement. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):327–332. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.327-332.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfinkel D. J., Simpson R. B., Ream L. W., White F. F., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Genetic analysis of crown gall: fine structure map of the T-DNA by site-directed mutagenesis. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90368-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman T. C., Montoya A. L., Williams S., Chilton M. D. Sustained ethylene production in Agrobacterium-transformed carrot disks caused by expression of the T-DNA tms gene products. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):387–388. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.387-388.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawes M. C., Robbs S. L., Pueppke S. G. Use of a Root Tumorigenesis Assay to Detect Genotypic Variation in Susceptibility of Thirty-four Cultivars of Pisum sativum to Crown Gall. Plant Physiol. 1989 May;90(1):180–184. doi: 10.1104/pp.90.1.180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood E. E., Fraley R. T., Chilton M. D. Virulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens Strain A281 on Legumes. Plant Physiol. 1987 Mar;83(3):529–534. doi: 10.1104/pp.83.3.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroux B., Yanofsky M. F., Winans S. C., Ward J. E., Ziegler S. F., Nester E. W. Characterization of the virA locus of Agrobacterium tumefaciens: a transcriptional regulator and host range determinant. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):849–856. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04830.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otten L. A., Schilperoort R. A. A rapid micro scale method for the detection of lysopine and nopaline dehydrogenase activities. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 8;527(2):497–500. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90363-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens L. D., Cress D. E. Genotypic variability of soybean response to agrobacterium strains harboring the ti or ri plasmids. Plant Physiol. 1985 Jan;77(1):87–94. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryder M. H., Tate M. E., Kerr A. Virulence properties of strains of agrobacterium on the apical and Basal surfaces of carrot root discs. Plant Physiol. 1985 Jan;77(1):215–221. doi: 10.1104/pp.77.1.215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sciaky D., Montoya A. L., Chilton M. D. Fingerprints of Agrobacterium Ti plasmids. Plasmid. 1978 Feb;1(2):238–253. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90042-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stachel S. E., Nester E. W., Zambryski P. C. A plant cell factor induces Agrobacterium tumefaciens vir gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):379–383. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Karlinsey J. E., Marks J. R., Hurlbert R. E. Identification of a new virulence locus in Agrobacterium tumefaciens that affects polysaccharide composition and plant cell attachment. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3209–3216. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3209-3216.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomashow M. F., Knauf V. C., Nester E. W. Relationship between the limited and wide host range octopine-type Ti plasmids of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):484–493. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.484-493.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger L., Ziegler S. F., Huffman G. A., Knauf V. C., Peet R., Moore L. W., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. New class of limited-host-range Agrobacterium mega-tumor-inducing plasmids lacking homology to the transferred DNA of a wide-host-range, tumor-inducing plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):723–730. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.723-730.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson B., Currier T. C., Gordon M. P., Chilton M. D., Nester E. W. Plasmid required for virulence of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):255–264. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.255-264.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky M. F., Nester E. W. Molecular characterization of a host-range-determining locus from Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):244–250. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.244-250.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky M., Montoya A., Knauf V., Lowe B., Gordon M., Nester E. Limited-host-range plasmid of Agrobacterium tumefaciens: molecular and genetic analyses of transferred DNA. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):341–348. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.341-348.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]