Abstract
The acidic, extracellular, glucan endo-1,3-β-glucosidases (EC 3.2.1.39; β-1,3-glucanases), pathogenesis-related proteins-2, -N, and -O (i.e. PR-2, PR-N, and PR-O) were purified from Nicotiana tabacum (tobacco) and their partial amino acid sequences determined. Based on these data, complementary DNA (cDNA) clones encoding the proteins were isolated. Additional cDNAs were isolated that encoded proteins approximately 90% identical with PR-2, PR-N, and PR-O. Although the proteins encoded by these cDNAs have not been identified, their deduced amino acid sequences have slightly basic or neutral calculated isoelectric points, as well as carboxy-terminal extensions. These physical characteristics are shared by the vacuolar form of β-1,3-glucanase and other vacuolar localized analogs of PR proteins, suggesting that the unidentified proteins may be similarly localized. A preliminary evolutionary model that separates the β-1,3-glucanase gene family from tobacco into at least five distinct subfamilies is proposed. The expression of β-1,3-glucanase messenger RNAs (mRNAs) in response to infection by tobacco mosaic virus was examined. Messages for the acidic glucanases were induced similarly to the mRNAs for other PR proteins. However, the basic glucanase showed a different response, suggesting that different isoforms are differentially regulated by tobacco mosaic virus infection at the mRNA level.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abeles F. B., Bosshart R. P., Forrence L. E., Habig W. H. Preparation and purification of glucanase and chitinase from bean leaves. Plant Physiol. 1971 Jan;47(1):129–134. doi: 10.1104/pp.47.1.129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulcke M. V., Bauw G., Castresana C., Van Montagu M., Vandekerckhove J. Characterization of vacuolar and extracellular beta(1,3)-glucanases of tobacco: Evidence for a strictly compartmentalized plant defense system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2673–2677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffmann S., Legrand M., Geoffroy P., Fritig B. Biological function of ;pathogenesis-related' proteins: four PR proteins of tobacco have 1,3-beta-glucanase activity. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3209–3212. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02637.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keen N. T., Yoshikawa M. beta-1,3-Endoglucanase from Soybean Releases Elicitor-Active Carbohydrates from Fungus Cell Walls. Plant Physiol. 1983 Mar;71(3):460–465. doi: 10.1104/pp.71.3.460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrimini L. M., Rothstein S. Tissue specificity of tobacco peroxidase isozymes and their induction by wounding and tobacco mosaic virus infection. Plant Physiol. 1987 Jun;84(2):438–442. doi: 10.1104/pp.84.2.438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb C. J., Lawton M. A., Dron M., Dixon R. A. Signals and transduction mechanisms for activation of plant defenses against microbial attack. Cell. 1989 Jan 27;56(2):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90894-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linthorst H. J., Melchers L. S., Mayer A., van Roekel J. S., Cornelissen B. J., Bol J. F. Analysis of gene families encoding acidic and basic beta-1,3-glucanases of tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8756–8760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan T., Ori N., Fluhr R. Pathogenesis-related proteins are developmentally regulated in tobacco flowers. Plant Cell. 1989 Sep;1(9):881–887. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.9.881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauch F., Mauch-Mani B., Boller T. Antifungal Hydrolases in Pea Tissue : II. Inhibition of Fungal Growth by Combinations of Chitinase and beta-1,3-Glucanase. Plant Physiol. 1988 Nov;88(3):936–942. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.3.936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohnen D., Shinshi H., Felix G., Meins F. Hormonal regulation of beta1,3-glucanase messenger RNA levels in cultured tobacco tissues. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1631–1635. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03830.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne G., Ahl P., Moyer M., Harper A., Beck J., Meins F., Jr, Ryals J. Isolation of complementary DNA clones encoding pathogenesis-related proteins P and Q, two acidic chitinases from tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(1):98–102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
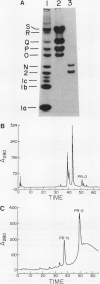
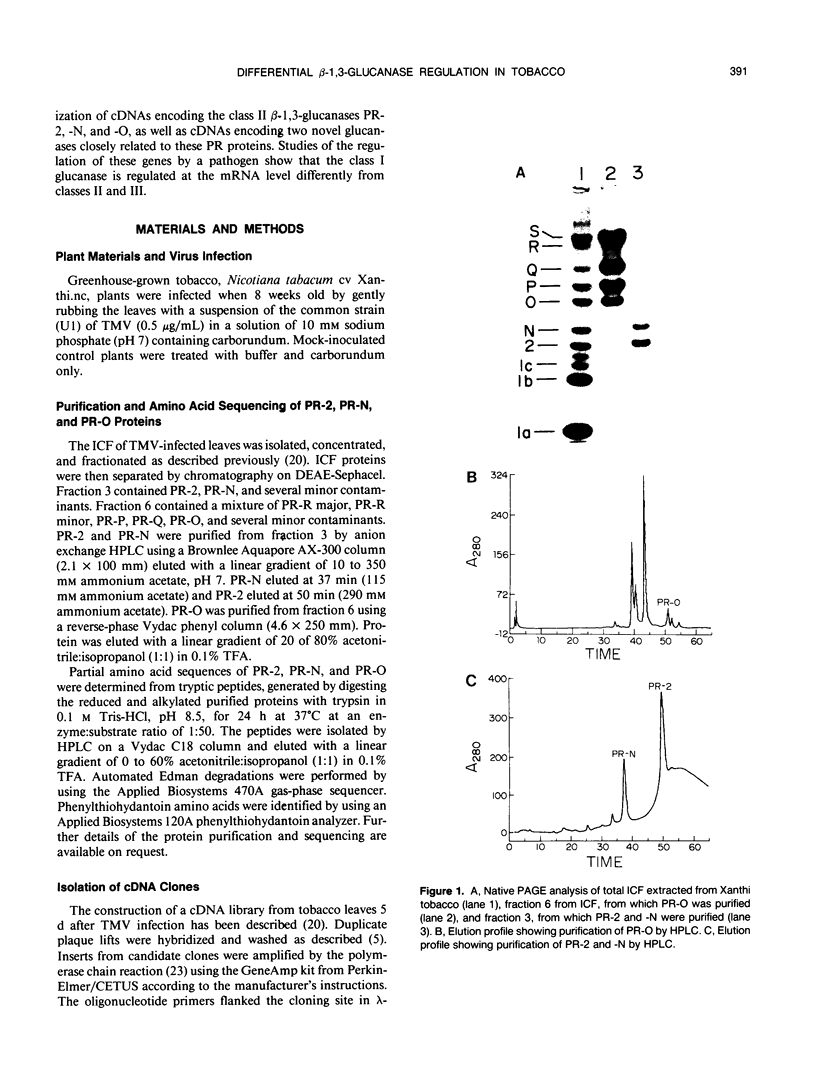
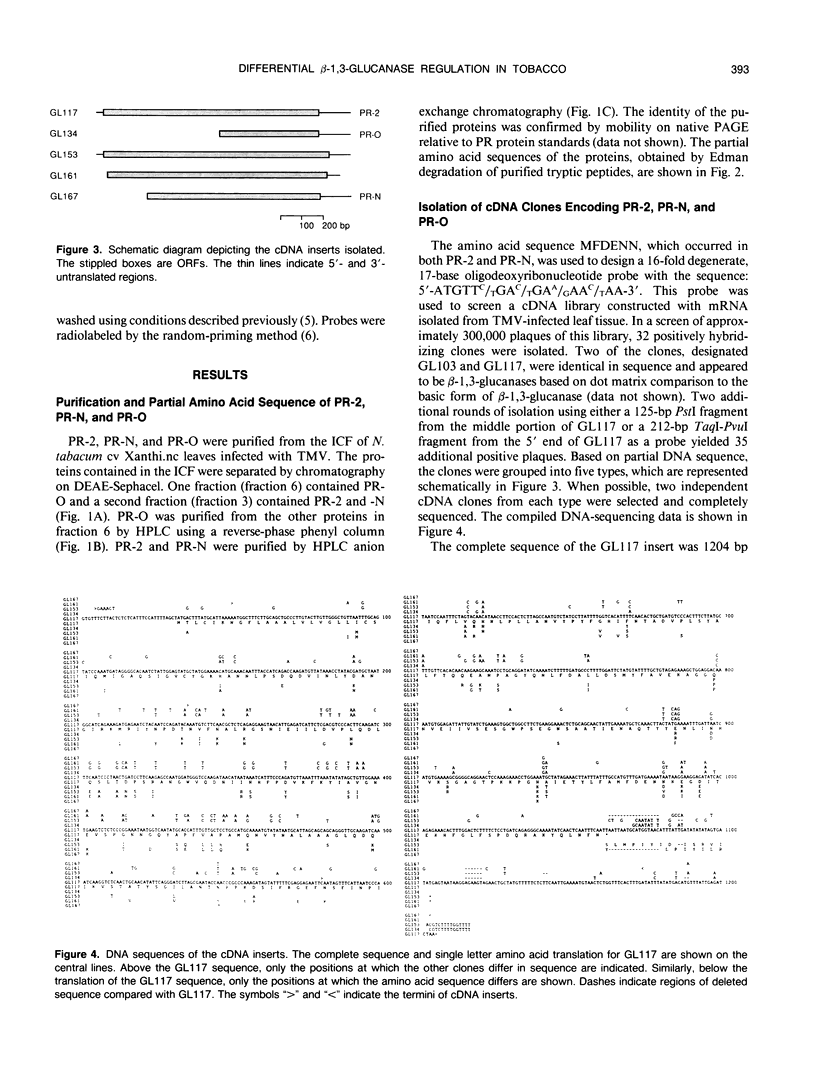
- Payne G., Ward E., Gaffney T., Goy P. A., Moyer M., Harper A., Meins F., Jr, Ryals J. Evidence for a third structural class of beta-1,3-glucanase in tobacco. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Dec;15(6):797–808. doi: 10.1007/BF00039420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinshi H., Wenzler H., Neuhaus J. M., Felix G., Hofsteenge J., Meins F. Evidence for N- and C-terminal processing of a plant defense-related enzyme: Primary structure of tobacco prepro-beta-1,3-glucanase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5541–5545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showalter A. M., Bell J. N., Cramer C. L., Bailey J. A., Varner J. E., Lamb C. J. Accumulation of hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein mRNAs in response to fungal elicitor and infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6551–6555. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeuchi Y., Yoshikawa M., Takeba G., Tanaka K., Shibata D., Horino O. Molecular Cloning and Ethylene Induction of mRNA Encoding a Phytoalexin Elicitor-Releasing Factor, beta-1,3-Endoglucanase, in Soybean. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jun;93(2):673–682. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.2.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]