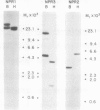
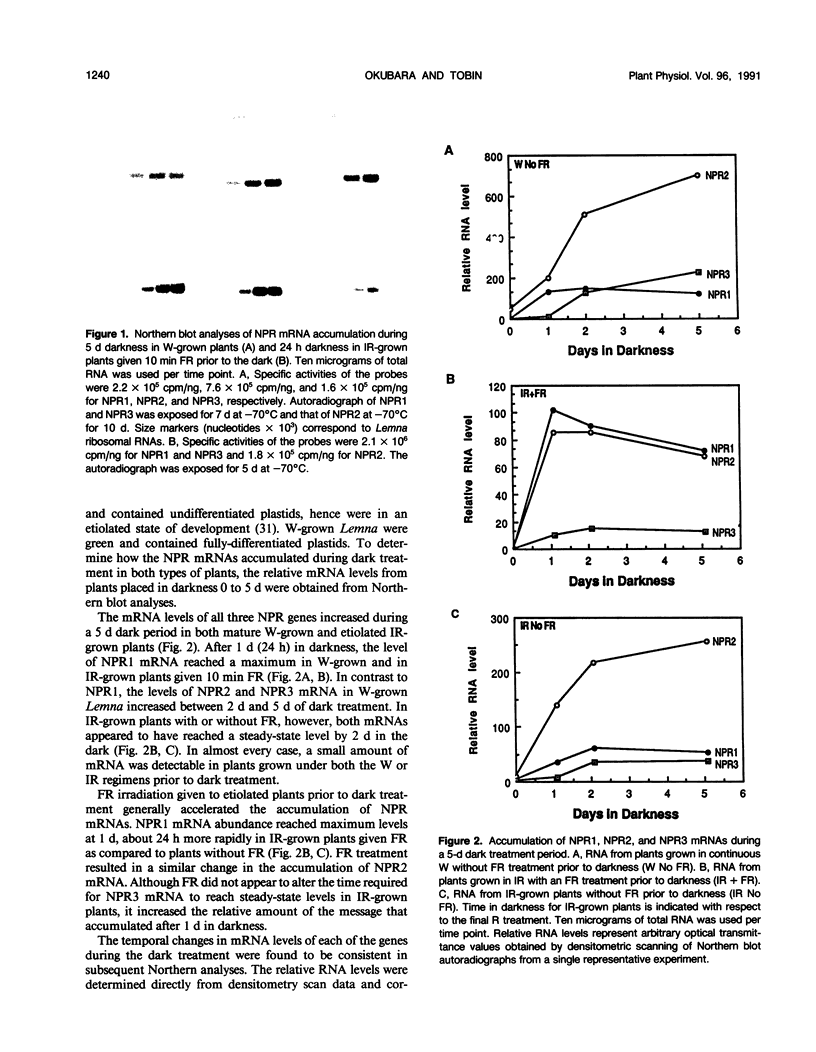
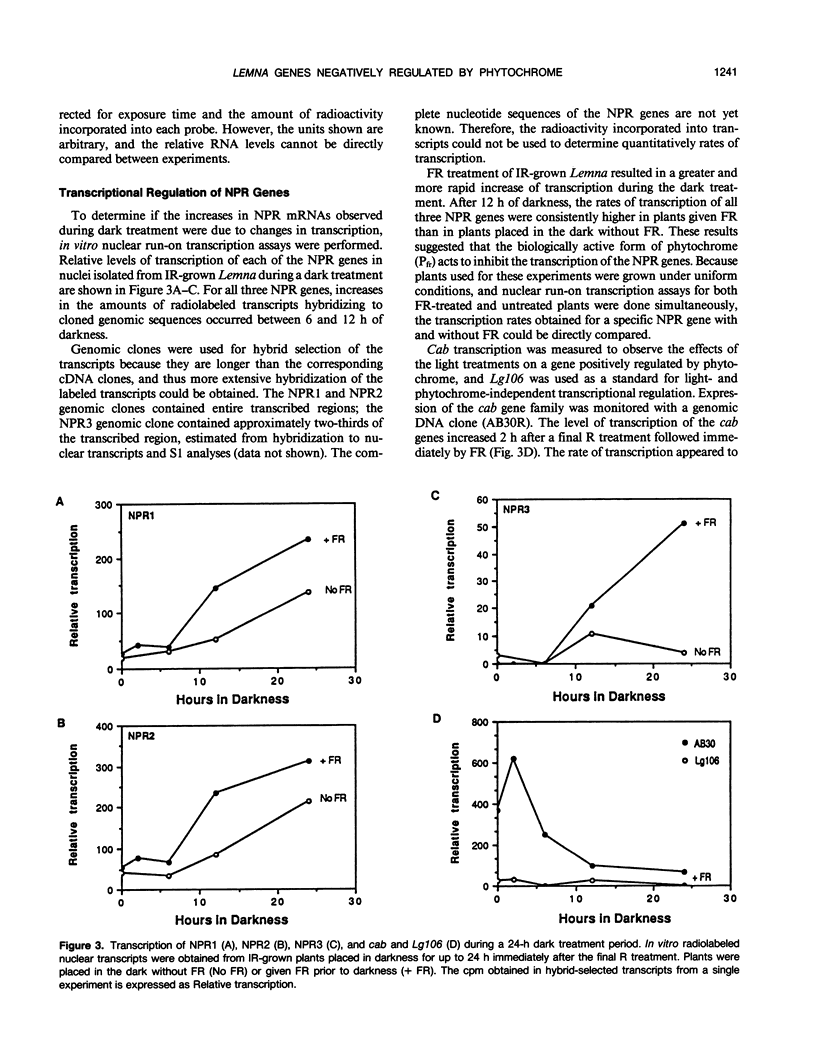
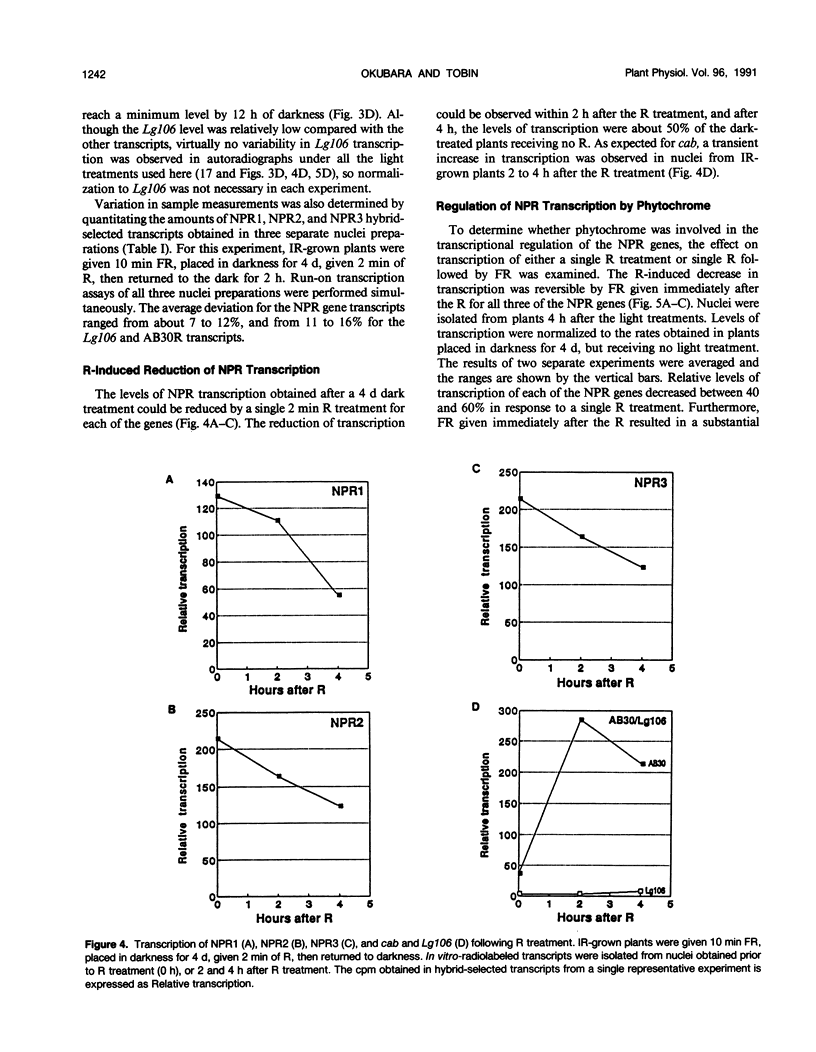
Abstract
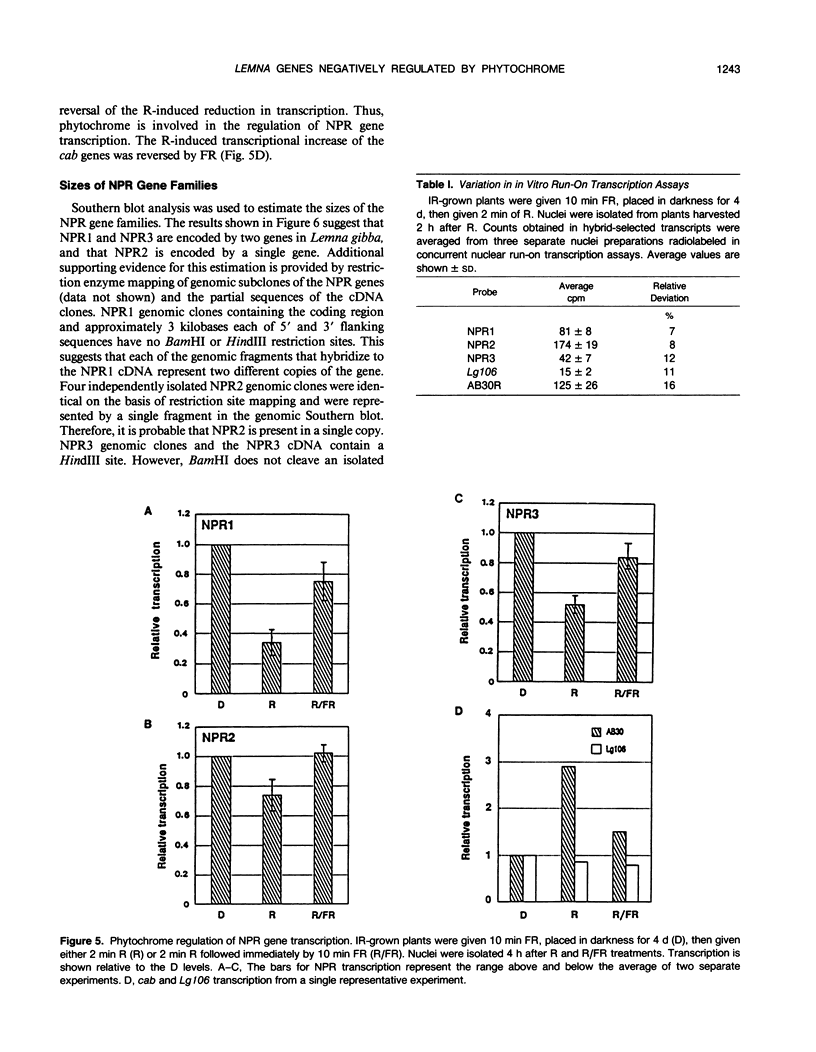
We have isolated three distinct cDNA clones from Lemna gibba representing mRNAs that increase in abundance during dark treatment. All three mRNAs showed reduced expression in response to red or white light. These mRNAs range from approximately 680 to 800 nucleotides in length and thus encode relatively small proteins (maximum relative molecular weight 17,000 to 19,000). The genes corresponding to these dark-abundant mRNAs are designated NPR (negatively phytochrome regulated) 1, 2, and 3. Differences in the rapidity of mRNA accumulation during dark treatment were observed for each of the genes in both mature green plants and in etiolated plants. Differences in accumulation pattern were also observed in etiolated plants, depending on whether the plants received a far-red light treatment prior to darkness. Transcription of all three genes, assayed in nuclei isolated from either green or etiolated plants, increased during dark treatment. In etiolated plants, a single 2 minute red light treatment caused a detectable decrease in the transcription of the genes after the dark treatment, and 10 minutes of far-red light given immediately after the red light resulted in a reversal of the effect of red light. Additionally, treatment of the plants with far-red light prior to darkness resulted in greater rates of transcription of the NPR genes. Therefore, we conclude that phytochrome action results in decreased transcription of these NPR genes. Each of the NPR mRNAs are encoded by one to two genes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bustos M. M., Guiltinan M. J., Cyr R. J., Ahdoot D., Fosket D. E. Light Regulation of beta-Tubulin Gene Expression during Internode Development in Soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr.). Plant Physiol. 1989 Nov;91(3):1157–1161. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.3.1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castresana C., Garcia-Luque I., Alonso E., Malik V. S., Cashmore A. R. Both positive and negative regulatory elements mediate expression of a photoregulated CAB gene from Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):1929–1936. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03030.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbert J. T., Costigan S. A., Zhao Z. Photoregulation of beta-Tubulin mRNA Abundance in Etiolated Oat and Barley Seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1990 Jul;93(3):1196–1202. doi: 10.1104/pp.93.3.1196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotton J. L., Ross C. W., Byrne D. H., Colbert J. T. Down-regulation of phytochrome mRNA abundance by red light and benzyladenine in etiolated cucumber cotyledons. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 May;14(5):707–714. doi: 10.1007/BF00016503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond M. I., Miner J. N., Yoshinaga S. K., Yamamoto K. R. Transcription factor interactions: selectors of positive or negative regulation from a single DNA element. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1266–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.2119054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Clouse S. D., Dixon R. A., Lawton M. A., Lamb C. J. Glutathione and fungal elicitor regulation of a plant defense gene promoter in electroporated protoplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6738–6742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluhr R., Chua N. H. Developmental regulation of two genes encoding ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit in pea and transgenic petunia plants: Phytochrome response and blue-light induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2358–2362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin P. M., Sarokin L., Memelink J., Chua N. H. Molecular light switches for plant genes. Plant Cell. 1990 May;2(5):369–378. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.5.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohorn B. D., Harel E., Chitnis P. R., Thornber J. P., Tobin E. M. Functional and mutational analysis of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein of thylakoid membranes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):972–981. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlemeier C., Fluhr R., Green P. J., Chua N. H. Sequences in the pea rbcS-3A gene have homology to constitutive mammalian enhancers but function as negative regulatory elements. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):247–255. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Manley J. L. Transcriptional repression of eukaryotic promoters. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):405–408. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman I. A. Rapid electric responses of oats to phytochrome show membrane processes unrelated to pelletability. Plant Physiol. 1981 Dec;68(6):1494–1499. doi: 10.1104/pp.68.6.1494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohl S., Hedrick S. A., Chory J., Lamb C. J. Functional properties of a phenylalanine ammonia-lyase promoter from Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 1990 Sep;2(9):837–848. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.9.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajasekhar V. K., Gowri G., Campbell W. H. Phytochrome-mediated light regulation of nitrate reductase expression in squash cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1988 Oct;88(2):242–244. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.2.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reimann-Philipp U., Behnke S., Batschauer A., Schäfer E., Apel K. The effect of light on the biosynthesis of leaf-specific thionins in barley, Hordeum vulgare. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jun 15;182(2):283–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14828.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R. Transcriptional repression in eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 1990 Jun;6(6):192–197. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90176-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs C. D., Voelker T. A., Chrispeels M. J. Cotyledon nuclear proteins bind to DNA fragments harboring regulatory elements of phytohemagglutinin genes. Plant Cell. 1989 Jun;1(6):609–621. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.6.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux S. J., Wayne R. O., Datta N. Role of calcium ions in phytochrome responses: an update. Physiol Plant. 1986;66:344–348. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3054.1986.tb02430.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto A., Takeba G., Shibata D., Tanaka K. Phytochrome-mediated activation of the gene for cytosolic glutamine-synthetase (GS1) during imbibition of photosensitive lettuce seeds. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Aug;15(2):317–323. doi: 10.1007/BF00036917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharrock R. A., Quail P. H. Novel phytochrome sequences in Arabidopsis thaliana: structure, evolution, and differential expression of a plant regulatory photoreceptor family. Genes Dev. 1989 Nov;3(11):1745–1757. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.11.1745. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Nasmyth K. Purification and cloning of a DNA binding protein from yeast that binds to both silencer and activator elements. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90095-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tingey S. V., Tsai F. Y., Edwards J. W., Walker E. L., Coruzzi G. M. Chloroplast and cytosolic glutamine synthetase are encoded by homologous nuclear genes which are differentially expressed in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9651–9657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda T., Pichersky E., Malik V. S., Cashmore A. R. Level of expression of the tomato rbcS-3A gene is modulated by a far upstream promoter element in a developmentally regulated manner. Plant Cell. 1989 Feb;1(2):217–227. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.2.217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]