Abstract
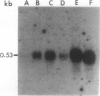
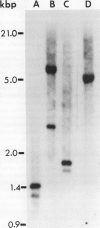
A uniquely regulated proteinase inhibitor I gene was isolated from the wild tomato species Lycopersicon peruvianum (L.) Mill. (LA 107) and characterized. The inhibitor gene is wound-inducible in leaves and is expressed in unripe fruit during development. The gene (λ clone 1) is present on a 15.5 kilobase pair Sal 1-SalI genomic DNA fragment. Southern blot analysis of L. peruvianum genomic DNA shows only one strongly hybridizing DNA fragment to probes derived from λ clone 1. S1 nuclease protection experiments and Northern analyses confirm that this gene is both wound-inducible in leaves and developmentally regulated in young unripe fruit. These observations are supported by comparisons of the 5′-flanking DNA sequences of the L. peruvianum inhibitor I gene with known elicitor responsive cis-acting sequences. The transcriptional regulation of the λ clone 1 inhibitor I gene in leaves of wounded plants and in developing unripe fruit indicates that the gene contains unique complex regulating elements. These elements respond to both environmental and developmental tissue-specific signals that can regulate proteinase inhibitor synthesis to protect the tissues of this wild species of tomato against predators and pathogens.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deikman J., Fischer R. L. Interaction of a DNA binding factor with the 5'-flanking region of an ethylene-responsive fruit ripening gene from tomato. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3315–3320. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03202.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham J. S., Pearce G., Merryweather J., Titani K., Ericsson L., Ryan C. A. Wound-induced proteinase inhibitors from tomato leaves. I. The cDNA-deduced primary structure of pre-inhibitor I and its post-translational processing. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 10;260(11):6555–6560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R., Narvaez J., An G., Ryan C. Expression of proteinase inhibitors I and II in transgenic tobacco plants: effects on natural defense against Manduca sexta larvae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9871–9875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawton M. A., Dixon R. A., Hahlbrock K., Lamb C. J. Elicitor induction of mRNA activity. Rapid effects of elicitor on phenylalanine ammonia-lyase and chalcone synthase mRNA activities in bean cells. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 17;130(1):131–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Brown W. E., Graham J. S., Pearce G., Fox E. A., Dreher T. W., Ahern K. G., Pearson G. D., Ryan C. A. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic studies of a wound-inducible proteinase inhibitor I gene in Lycopersicon species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7277–7281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lois R., Dietrich A., Hahlbrock K., Schulz W. A phenylalanine ammonia-lyase gene from parsley: structure, regulation and identification of elicitor and light responsive cis-acting elements. EMBO J. 1989 Jun;8(6):1641–1648. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03554.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margossian L. J., Federman A. D., Giovannoni J. J., Fischer R. L. Ethylene-regulated expression of a tomato fruit ripening gene encoding a proteinase inhibitor I with a glutamic residue at the reactive site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8012–8016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C. E., Ryan C. A. In vitro synthesis of pre-proteins of vacuolar compartmented proteinase inhibitors that accumulate in leaves of wounded tomato plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1975–1979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan C. A. Proteinase inhibitor gene families: strategies for transformation to improve plant defenses against herbivores. Bioessays. 1989 Jan;10(1):20–24. doi: 10.1002/bies.950100106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thornburg R. W., An G., Cleveland T. E., Johnson R., Ryan C. A. Wound-inducible expression of a potato inhibitor II-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene fusion in transgenic tobacco plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):744–748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingate V. P., Broadway R. M., Ryan C. A. Isolation and characterization of a novel, developmentally regulated proteinase inhibitor I protein and cDNA from the fruit of a wild species of tomato. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17734–17738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wingate V. P., Ryan C. A. A novel fruit-expressed trypsin inhibitor I gene from a wild species of tomato. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 25;266(9):5814–5818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]