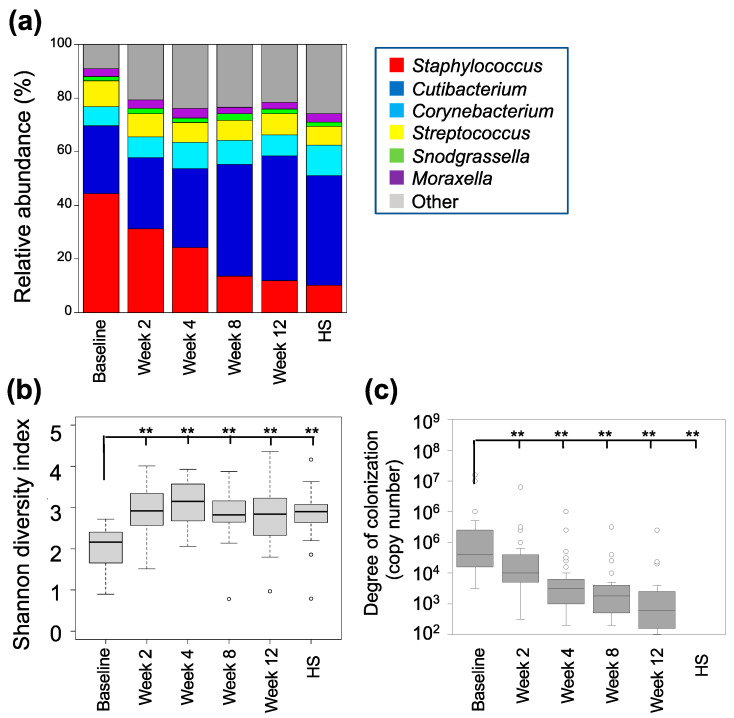
Figure 2.
Changes in the bacterial microbiome after dupilumab administration. Thirty lesion sites on the foreheads of patients were analyzed. (a) Abundant bacterial genera. Genera with a relative abundance of >2% are shown. The relative abundance of Staphylococcus decreased after dupilumab administration, whereas that of Cutibacterium increased. (b) Shannon diversity of the bacterial microbiome. Diversity increased 2 weeks after dupilumab administration. ** p < 0.01. (c) Changes in degree of skin colonization by Staphylococcus aureus revealed using qPCR. Experiments were performed in triplicate for each sample. The degree of skin colonization decreased compared to that at baseline. ** p < 0.01. HS, healthy subjects.