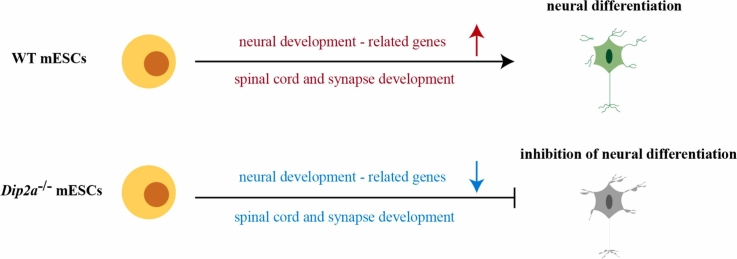
Abstract
Introduction
The disconnected-interacting protein 2 homolog A (DIP2A), a member of disconnected-interacting 2 protein family, has been shown to be involved in human nervous system-related mental illness. This protein is highly expressed in the nervous system of mouse. Mutation of mouse DIP2A causes defects in spine morphology and synaptic transmission, autism-like behaviors, and defective social novelty [5], [27], indicating that DIP2A is critical to the maintenance of neural development. However, the role of DIP2A in neural differentiation has yet to be investigated.
Objective
To determine the role of DIP2A in neural differentiation, a neural differentiation model was established using mouse embryonic stem cells (mESCs) and studied by using gene-knockout technology and RNA-sequencing-based transcriptome analysis.
Results
We found that DIP2A is not required for mESCs pluripotency maintenance, but loss of DIP2A causes the neural differentiation abnormalities in both N2B27 and KSR medium. Functional knockout of Dip2a gene also decreased proliferation of mESCs by perturbation of the cell cycle and profoundly inhibited the expression of a large number of neural development-associated genes which mainly enriched in spinal cord development and postsynapse assembly.
Conclusions
The results of this report demonstrate that DIP2A plays an essential role in regulating differentiation of mESCs towards the neural fate.
Keywords: Dip2a, Neural differentiation, Mouse embryonic stem cell, RNA-sequencing
Graphical Abstract
The model shows the important role of Dip2a gene in the neural differentiation.
1. Introduction
The disconnected-interacting protein 2 (DIP2) is a highly conserved protein present in multiple organisms including Caenorhabditis elegans, Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly), mouse, and human [1], [2], [3], [4]. This protein contains two tandem Adenylate-forming domains (AFD-1 and AFD-2) and one DNA methyltransferase 1-associated protein (DMAP1)-binding domain [5].
In Caenorhabditis elegans, DIP2 is responsible for the maintenance of neuron morphology and axon regrowth. Functional loss of DIP2 lead to a progressive increase in ectopic neurite sprouting and branching during development [6]. The Drosophila melanogaster homolog of DIP2 [1] is required for acyl-CoA metabolism [7]. Mutation of DIP2 reduced acyl-CoA expression and consequently disturbed the precise axonal bifurcation in Drosophila mushroom body neurons [7]. Moreover, the direction of axon projection of Drosophila can be modulated by c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and basket (Bsk)-mediated DIP2 expression [8].
In mouse and human, three members of Dip2 protein family have been reported, including DIP2A, DIP2B, and DIP2C, which were encoded by different genes. These three proteins seem to be associated with different human diseases. DIP2A is involved in nervous system-related mental illness [9], [10], [11], [12], [13], [14]. DIP2B appears to be associated with human intellectual disability [15] and can influence salivary gland maturation [16]. DIP2C participates in DNA methylation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition [17], and also plays a role in breast cancer [18] or in neuronal disease [19]. DIP2A, as a type I receptor molecule [20], may exert a variety of signaling roles [1] and other biological processes including acetylcoenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) synthesis [5]. DIP2A seems responsible for the development of normal neural system as the mutation in DIP2A gene is associated with developmental retardation [21]. Mutations in DIP2A also make human at a substantial risk to other neurodevelopmental disorders including developmental dyslexia [10], [22] and autism spectrum disorder (ASD)[11], [13], [23], [24]. As a membrane receptor protein with intracellular domain, DIP2A can bind to Follistatin-related protein (FRP) and is associated with other members of TGF-superfamily to regulate the expression of FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog (FOS) [20]. DIP2A can cooperate with the HDAC2 (histone deacetylase 2)-DMAP1 (DNA methyltransferase 1-associated protein 1) complex to enhance H3K9Ac deacetylation, decrease the transcription of methylguanine-DNA-methyltransferase (MGMT) [25].
The functions of DIP2A were also investigated in mouse model. The expression of murine homolog DIP2A was initially identified in brain lobes and the ventral cord during early embryonic stages [1]. In adult mice, DIP2A can be found in multiple brain regions including the neocortex, hippocampus, amygdala, and cerebellum [26]. Murine DIP2A can interact with the postsynaptic actin-binding protein, cortactin [27]. Deletion of Dip2a in mice change the postsynaptic density (PSD) construction and reduce either miniature excitatory postsynaptic current (mEPSC) amplitude or cortactin acetylation. The mutant mice have defects in spine morphology and synaptic transmission, and autism-like behaviors such as excessive repetitive self-grooming and defective social novelty [5], [27]. Those results indicate that DIP2A is required for the maintenance of neural development of mice [28]. Since the neural differentiation is a decisive step in normal neural development, we hypothesized that DIP2A may play a role in the neural differentiation. Herein, in this report, the in vitro neural differentiation model was established using mouse embryotic stem cells (mESCs), and the role of Dip2a in neural differentiation was systemically examined by using gene-knockout technology and RNA-sequencing-based transcriptome analysis. We found that DIP2A is not required for the maintenance of mESC pluripotency, but is essential for the neural differentiation by modulating a number of neural development-related gene expression. The report provides important data informative for further decoding the molecular mechanism of neural differentiation.
2. Results
2.1. Dip2a is not required for mESCs pluripotency maintenance
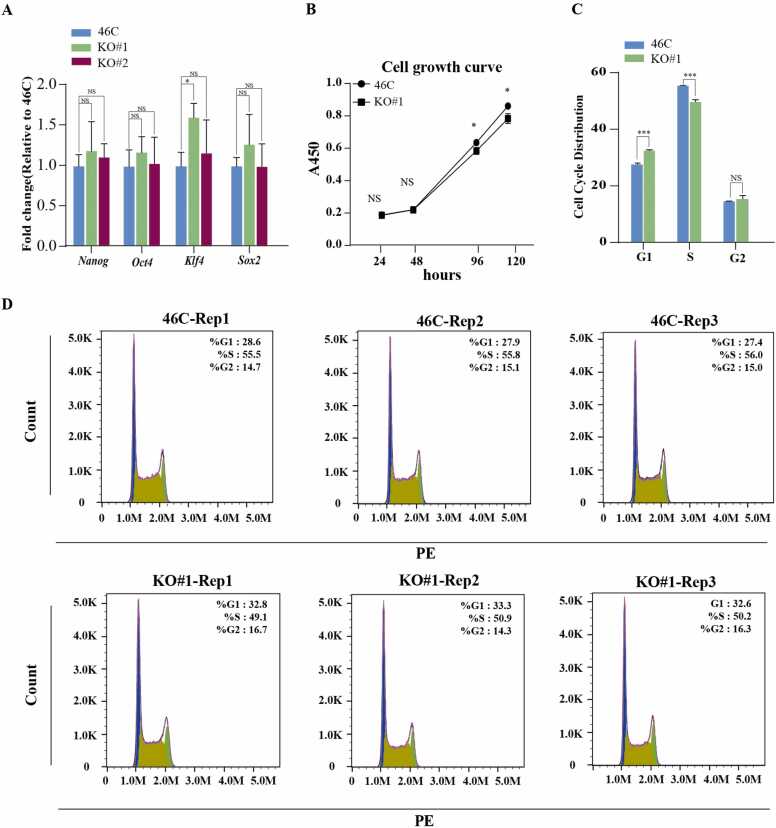
To examine if DIP2A is involved in the maintenance of mESCs, we established two Dip2a-/- mESCs stable cell lines (KO#1 and KO#2) using the CRISPR/Cas9 technology as previously described [29], and then evaluated the alterations in mESCs pluripotency through multiple passages. The RT-qPCR analysis of pluripotent marker genes (Sox2, Nanog, Oct4, Klf4) showed that there was no significant difference in gene expression between Dip2a-/- and wild type (46 C with SOX1-GFP knock-in reporter [30]) mESCs (Fig. 1A). Similar results were obtained by immunofluorescence staining, where there was no significant difference in the expression level of NANOG and OCT4 between 46 C and Dip2a-/- mESCs (Fig. S1A), indicating that Dip2a may be not required for mESCs pluripotency maintenance. Next, cell proliferation assay showed a lower proliferation of Dip2a-/- mESCs compared to 46 C (Fig. 1B). The propidium Iodide (PI) staining assay was performed to analyze the cell cycle. As shown in Fig. 1C and Fig. 1D, Dip2a-/- mESCs displayed a longer cell cycle G1 phase and shorter S phase. The proportions of 46 C and Dip2a-/- cells in the G1 phase were 28.0%, and 32.9%, respectively, and in the S phase were 55.8%, and 50.1%, respectively, while there was no significant difference in G2 phase. Our results are consistent with the previous observation that prolongation of G1 phase induced cell proliferation arrest [31], [32]. We selected six differentially expressed genes (Mapk12, Casp3, Ube2e2, Myb, Rb1, Snd1) related to cell cycle and G1/S transition, and the differential expression of these six genes between 46 C and Dip2a-/- cell line detected by RT-qPCR also confirmed our findings (Fig. S4). Collectively, our results show that Dip2a is not required for mESCs pluripotency maintenance while knockout of Dip2a caused a decreased proliferation rate and increased G1 phase.
Fig. 1.
Dip2a is not required for mESCs to maintain pluripotency, but is associated with proliferation and cell cycle. (A) The mRNA expression levels of pluripotent markers (Sox2, Klf4, Nanog, Oct4) in 46 C and Dip2a-/- mESCs were detected by RT-qPCR (n = 3). (B) Cell proliferation assay was performed at four time points (24 h, 48 h, 96 h, 120 h) (n = 3). (C-D) Cell cycle analysis for 46 C and Dip2a-/- mESCs (n = 3), count: cell numbers, PE: fluorescent relative intensity. (NS means not statistically significant,* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001).
2.2. Dip2a knockout affects neural differentiation in N2B27 medium
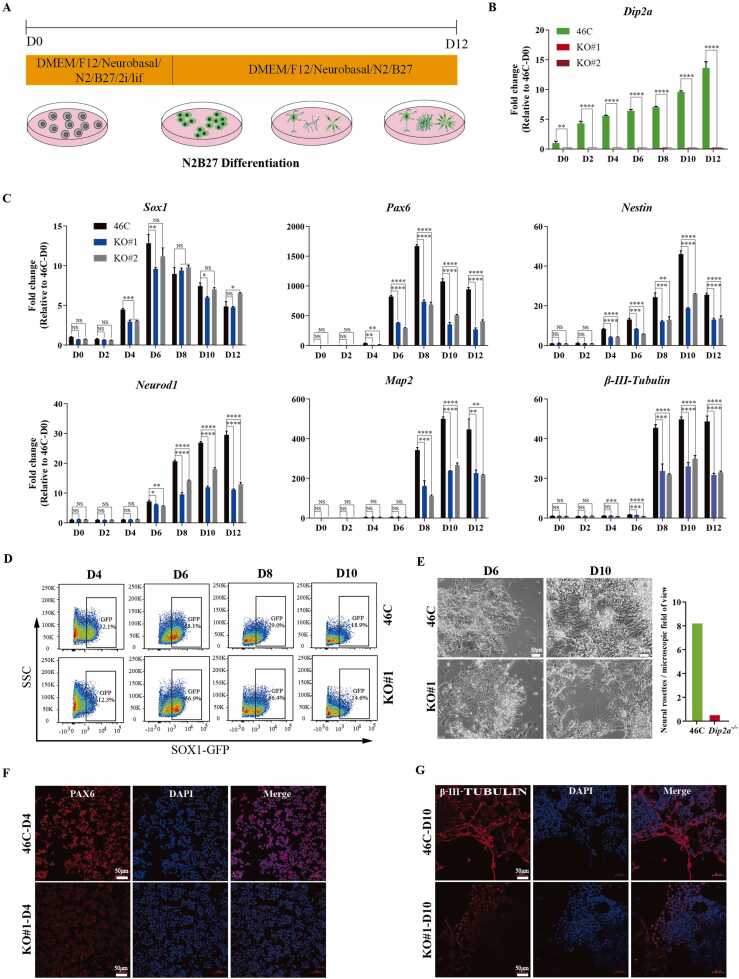
To explore the role of DIP2A in neural differentiation, both Dip2a-/- and 46 C mESCs were subjected to differentiation toward neural lineage in N2B27 medium (Fig. 2A) [33]. We observed that the expression of Dip2a gene was gradually increased during the neural differentiation in 46 C cells, indicating that DIP2A may play an important role during neural differentiation (Fig. 2B). RT-qPCR analysis showed that the loss of Dip2a significantly inhibited the expression of neural stem cell marker genes including Sox1, Pax6 and Nestin (Fig. 2C). Moreover, neuronal markers (β-III-Tubulin, Neurod1, Map2) were significantly down-regulated in Dip2a-/- cells compared with that in 46 C post differentiation. Flow cytometry (FCM) analysis showed that the number of SOX1-GFP expressing cells in Dip2a-/- cell line was significantly lower than that in 46 C at day4 (D4), but it caught up at D6 (Fig. 2D, data of KO#2 was displayed in Fig. S2A.). The number of neural rosettes of Dip2a-/- cell line (0.5 / field of view) was less than that of 46 C (8.2 / field of view) at D6. In addition, fiber-formed neuronal related cells were obviously decreased at D10 post differentiation of Dip2a-/- cell line compared with 46 C (Fig. 2E). Immunofluorescence results showed that expression level of PAX6 in 46 C was stronger than that in Dip2a-/- cell line at D4, and the amount of nerve fibers marked by β-III-TUBULIN was significantly reduced (Fig. 2F-G, data of KO#2 was displayed in Fig. S2B-C). These results demonstrate that depletion of Dip2a can interfere with neural differentiation in N2B27 medium.
Fig. 2.
Dip2a is required for neural differentiation in N2B27 medium. (A) Schematic showing the procedure for mESC differentiation in N2B27 medium. (B) RT-qPCR analysis of Dip2a expression at D0-D12 post differentiation. (C) Expression of neural marker genes (Sox1, Pax6, Nestin, Neurod1, Map2, β-III-Tubulin) detected by RT-qPCR (n = 3). (D) FCM analysis of SOX1-GFP+ cells in 46 C and KO#1 cell line during differentiation (NC gate was displayed in Fig. S2A). (E) Left, representative morphology of neural rosettes and nerve fibers of 46 C and KO#1 cell line during differentiation; Right, average number of neural rosette per field of view (ten fields of view were counted). (F-G) Immunofluorescence staining of 46 C and KO#1 at D4 (F) and D10 (G). ((NS means not statistically significant,* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001).
2.3. Loss of Dip2a causes the neural differentiation abnormalities in KSR medium
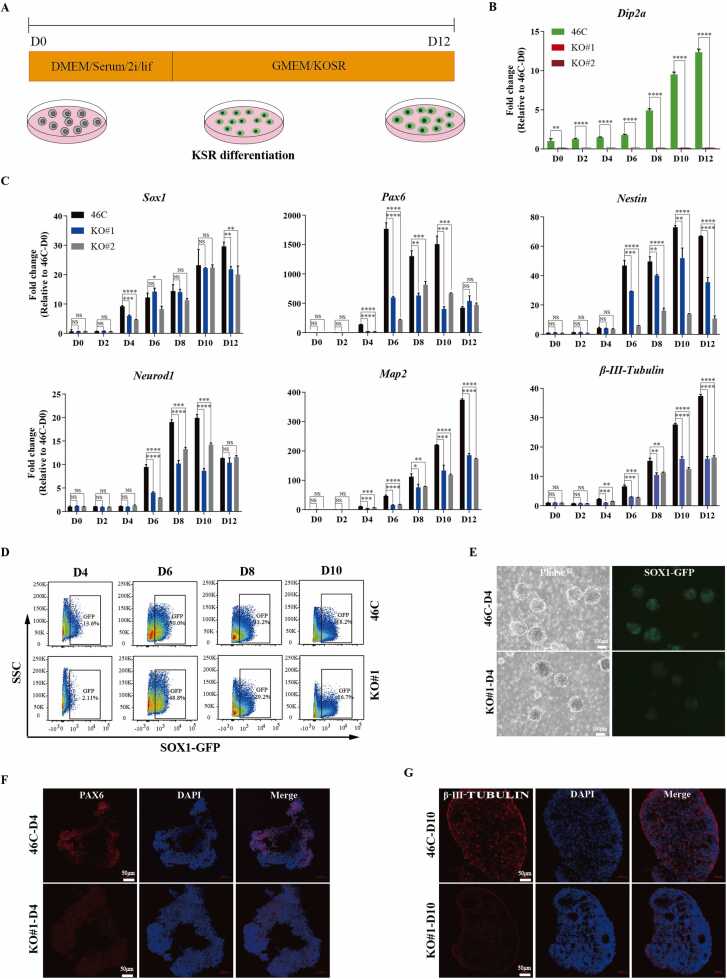
To further confirm our findings, we induced 46 C and Dip2a-/- mESCs to perform neural differentiation in KSR (Knockout Serum Replacement) medium (Fig. 3A). This protocol was used to differentiate mESCs into large and round neurospheres, which is a model for studying the directed neural differentiation of mESCs [34], [35]. As expected, the expression level of Dip2a was gradually increased during the directed differentiation of 46 C cell line in the KSR medium (Fig. 3B). RT-qPCR analysis showed that the expression of marker genes associated with neural differentiation (Sox1, Pax6, Nestin, β-III-Tubulin, Neurod1, Map2) were significantly decreased in Dip2a-/- cells compared with that in 46 C cells (Fig. 3C). FCM analysis showed similar results to neural differentiation in N2B27 medium, the amount of SOX1-GFP+ cells in Dip2a-/- cell line was obviously fewer than that of 46 C at D4, and then no significant differences were observed during subsequent differentiation (Fig. 3D, data of KO#2 was displayed in Fig. S3A). The Data of Fig. 3E also displayed consistent results that neurospheres of Dip2a-/- cell line presented only a limited number of cells expressing SOX1-GFP at D4. Additionally, immunofluorescence staining was performed. 46 C cells showed stronger fluorescence intensity of PAX6 and β-III-TUBULIN than Dip2a-/- cells during differentiation (Fig. 3F-G, data of KO#2 was displayed in Fig. S3B-C). Together, these results confirm that knockout of Dip2a can disrupt the neural differentiation in KSR medium.
Fig. 3.
Dip2a is required for neural differentiation in KSR medium. (A) Schematic showing the KSR medium procedure for mESCs differentiation toward neural cells. (B) RT-qPCR analysis of the of Dip2a expression at D0-D12 post differentiation (n = 3). (C) Gene expression analysis of the Sox1, Pax6, Nestin, Neurod1, β-III-Tubulin, Map2 in 46 C and Dip2a-/- cells at D0-D12 post differentiation (n = 3). (D).The percentage of SOX1-GFP+ cells detected by FCM during the differentiation of 46 C and KO#1 cell line (NC gate was displayed in Fig. S3A). (E) Representative cellular morphologies of neurosphere derived from 46 C and KO#1 cell line at day 4 post differentiation. (F-G) Immunofluorescence staining of 46 C and KO#1 neurosphere at D4 (F) and D10 (G) post differentiation. (NS means not statistically significant,* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001).
2.4. Transcriptomic profiling reveals the role of Dip2a during neural differentiation in N2B27 medium
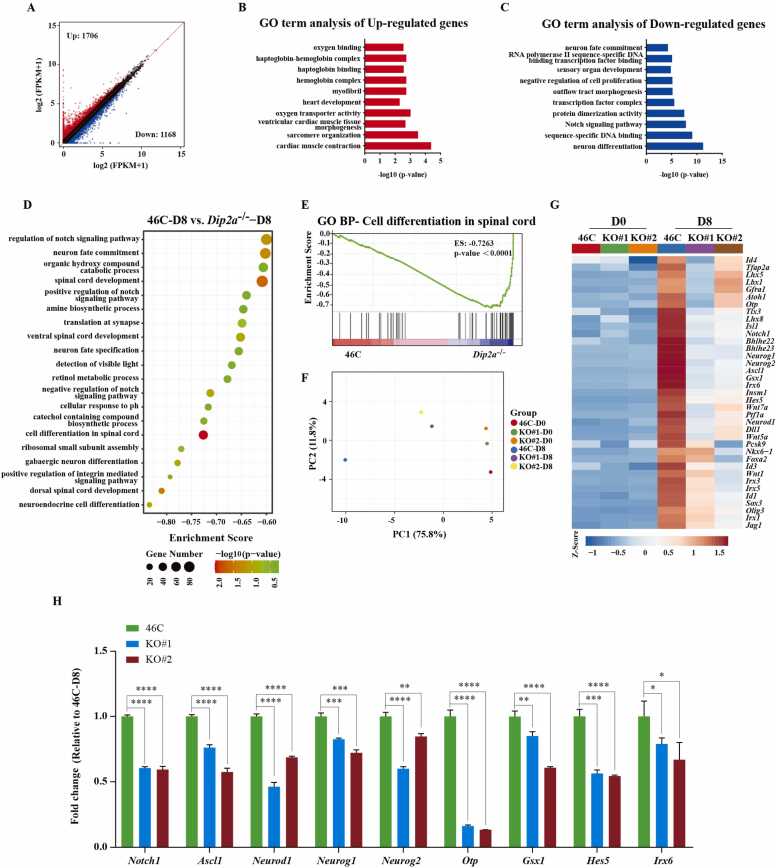
To further investigate the function of Dip2a during neural differentiation, RNA-seq analysis was performed for 46 C and Dip2a-/- cells at D0 and D8 post differentiation in N2B27 medium, respectively. As a result, we identified 2874 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in Dip2a-/- compared with 46 C cells at D8, including 1706 up-regulated genes and 1168 down-regulated genes (Fig. 4A). Gene Ontology (GO) analysis showed that up-regulated genes were enriched in ‘cardiac musle contraction’, ‘sarcomere organiztion’, etc. Whereas down-regulated genes were mainly enriched in neurodevelopment-related terms such as ‘neuron differentiation’, ‘Notch signaling pathway’ and ‘neuron commitment’ (Fig. 4B-4 C), indicating that depletion of Dip2a affects mESCs differentiate to neural fate. Further Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) was applied to identify the potential affected biological process upon Dip2a depletion in the neural differentiation. As shown in Fig. 4D, most of the top 20 GO terms were associated with the development of neural system. Consistently, the GO term of ‘cell differentiation in spinal cord’ was confirmed by GSEA (Fig. 4E). The principal component analysis (PCA) showed consistent differences between the two KO lines and 46 C cells, suggesting the reproducibility of the molecule phenotype of Dip2a KO. Thus, our cell lines are suitable for studying the function of Dip2a in neural differentiation (Fig. 4F). Finally, the heatmap analysis exhibited that neural differentiation-related genes were significantly down-regulated in Dip2a-/- cells compared with 46 C at D8 post differentiation (Fig. 4G). And nine genes associated with neural differentiation were confirmed by RT-qPCR (Fig. 4H). Our data supports the notion that DIP2A may function as a key regulator during neural differentiation in N2B27 medium.
Fig. 4.
Transcriptome analysis of 46 C and Dip2a-/- cell line at D8 post differentiation in N2B27 medium. (A). DEGs of Dip2a-/- versus 46 C cells at D8. Up-and down-regulated genes with log2 fold change greater than 0.58 are indicated by red and blue dots respectively. (B-C). GO terms analysis of up-and down-regulated genes of Dip2a-/- versus 46 C cells at D8 post differentiation. (D).The top 20 enriched GO terms of down-regulated genes using GSEA. (E). Line plot shows ‘cell differentiation in spinal cord’ in Dip2a-/- compared with 46 C cells. (F).The PCA analysis showed that the transcriptome is differ in Dip2a-/- compared with 46 C cells at D8. (G). Heatmap showing the DEGs associated with neural differentiation in Dip2a-/- compared with 46 C cell at D0 and differentiated D8. (H).The expression of nine genes displayed in heatmap were verified by RT-qPCR (n = 3). (NS means not statistically significant, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001).
2.5. Transcriptome characteristics analysis reveal the potential function of Dip2a during neural differentiation in KSR medium
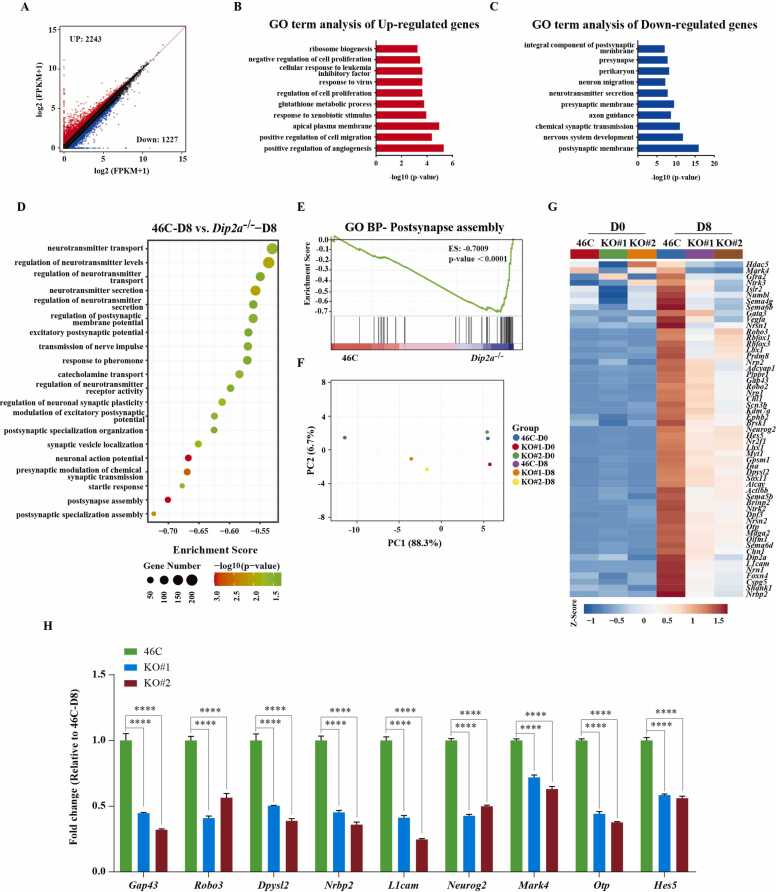
Consistently, we performed RNA-seq for 46 C and Dip2a-/- cells at D0 and D8 during neural differentiation in KSR differentiation assay. Our RNA-seq analysis uncovered 2243 up-regulated genes and 1227 down-regulated genes from Dip2a-/- cells compared with 46 C cells at D8 post differentiation in KSR assay (Fig. 5A). The up-regulated genes were enriched in ‘positive regulation of angiogensis’, ‘positive regulation of cell migration’ and ‘apical plasma’ etc. The downregulated genes were mostly enriched in GO terms associated with neurodevelopment, such as ‘postsynaptic membrane’, ‘nervous system development’ and ‘chemical synaptic transmission’, etc. (Fig. 5B-C), confirming that Dip2a indeed plays an important regulatory role during neural differentiation in KSR assays. Interestingly, GSEA analysis showed that the down-regulated genes were mainly enriched in GO terms associated with the terminal neural differentiation, such as ‘postsynapse assembly’, ‘presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission’ and ‘neuronal action potential’, etc. (Fig. 5D-E). The PCA analysis of transcriptomic profiles showed that the molecular phenotype of the two replicate KO lines has a good reproducibility (Fig. 5F). Expectedly, the heatmap analysis revealed that the down-regulated genes were associated with neural differentiation and nine genes were confirmed experimentally by RT-qPCR (Fig. 5G-H). In conclusion, knockout of Dip2a in mESCs can disrupt the neural differentiation cultured in KSR medium.
Fig. 5.
Transcriptomic analysis of 46 C and Dip2a-/-cell line at D8 post differentiation in KSR medium. (A).The scatterplot shows the Differentially Expressed Genes (DEGs) in Dip2a-/- compared with 46 C cells at D8. Up- and down -regulated genes are indicated by red and blue dots respectively. (B-C). GO term enrichment of DEGs in Dip2a-/- cells compared with 46 C cells at D8 post differentiation. (D).The top 20 enriched GO terms of down-regulated genes using GSEA. (E). Line plot shows ‘postsynapse assembly’ in Dip2a-/- compared with 46 C in mESCs. (F).The PCA analysis showed that the transcriptome is differ in Dip2a-/- compared with 46 C cells at D8. (G). Heatmap showing the DEGs associated with neural differentiation in Dip2a-/- compared with 46 C cell at D0 and differentiated D8. (H).The expression of nine genes displayed in heatmap was verified by RT-qPCR (n = 3). (NS means not statistically significant, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001).
3. Discussion
Dip2a is expressed in the nervous system in both developing embryonic and adult brain. Knockout of Dip2a affects multiple biological processes including synaptic transmission [27], mitochondrial metabolism [36], and hippocampus morphology [37]. Although the potential functions of Dip2a have been revealed, the role of Dip2a in neural differentiation of mESCs has yet to be determined.
In this study, mESCs were used as an in vitro model, N2B27 (monolayer culture) and KSR (three-dimensional culture) culture were performed as two neural differentiation methods to systemically investigate the role of Dip2a in the process of neural differentiation. In previous studies, depletion of DIP2A was found to lead to significantly altered expression of multiple genes associated with lung development in mice, including the genes Crh and Pdgfra, which are essential for cell proliferation [28]. In our experiments, we found that knockout of Dip2a does not affect the mESCs pluripotency, but reduced cell proliferation and prolonged the G1 phase under 2iL culture condition. These findings suggest that DIP2A may be involved in the regulation of cell proliferation in both pluripotent stem cells and differentiated somatic cells.
In the N2B27 neural differentiation assay, our results of monolayer differentiation showed that knockout of Dip2a inhibited the expression of neural stem cell and neuronal marker genes, with obstruction of neural rosettes and nerve fibers. RNA-seq analysis of Dip2a-/- cells compared with 46 C cells during neural differentiation showed that loss of DIP2A reduced the expression level of neural development-related genes. For instance, ASCL1 can promote neuronal maturation and trigger late neurogenesis in the amniote spinal cord [38], [39]. GSX1 promotes progenitor maturation and locomotor functional recovery after spinal cord injury [40] and the dynamic, spatial periodicity and micropattern of HES5 are the basis of spinal cord neurogenesis in mice. The down-regulated genes from Dip2a-/- cells versus 46 C were mainly enriched in spinal cord development-related biological process, such as ‘dorsal spinal cord development’, ‘cell differentiation’ and ‘ventral spinal cord development’. These results showed that depletion of DIP2A disrupted the spinal cord development which was consistent with previous reports [41], [42]. Furthermore, we performed three-dimensional culture for 46 C and Dip2a-/- cells in KSR medium. Similar to N2B27 culture, knockout of Dip2a reduced the expression of neural stem cell and neuronal marker genes. RNA-seq analysis demonstrated that knockout of Dip2a significantly reduced the expression of neural development-related genes such as GAP43 is a neuron-specific phosphoprotein, which plays critical role in axon growth and synapses functions during neurogenesis [43], ROBO3 has been tightly associated with development of specific axons and synaptic connection mature [44]. Moreover, the down-regulated genes were significant enriched in ‘postsynapse assembly’, ‘presynaptic modulation of chemical synaptic transmission’, etc. These results provided additional evidence for the previous observation that loss of Dip2a affects the synapse development [7], [27], [34], [36]. We then carried out transcription factor binding motif screening in the promoters of genes in ‘spinal cord differentiation’ and ‘postsynapse assembly’ categories. We found that defective activation of some genes, such as Tbx20, Olig2, and Ascl1, may perturbated the gene regulatory toward neural differentiation, thus lead to neural differentiation defects upon Dip2a-/- (Fig. S5). It may be provide a working molecular model for the role of DIP2A in neural differentiation.
It was previously found that DIP2A also localizes preferentially to the mitochondria [5], the main source of endogenous reactive oxygen species (ROS), and is correlated with superoxide dismutase (SOD), SOD1 and SOD2 [46]. Knockout of DIP2A leads to decreased SOD activity and increased ROS level in the mouse brain. In addition, both mitochondrial morphology and mitochondrial energy metabolism are altered in the brains of Dip2a KO mice [46]. Knockout of DIP2A in mice even can result in the body composition differences under different dietary regimens [47]. While initial investigation found that Dip2a expression is restricted to brain of mouse, a recent systematical investigation expanded this notion and found that this protein is expressed broadly in a number of different organs at the lower level, including reproductive and vascular tissues, heart, kidney, liver and lung, etc. [26]. Analysis of embryonic brain and lung of DIP2A knockout mice discovered significant number of genes that may be affected by DIP2A[28]. In consistence with those findings, our RNA-sequencing-based transcriptome analysis uncovered thousands of genes that were affected by knockout of Dip2a in mESCs during neural differentiation. Those findings also imply the multiple structural and physiological roles of DIP2A during animal development.
3.1 Conclusions
In summary, knockout of Dip2a in mESCs inhibited the neural differentiation cultured in N2B27 and KSR medium. Our data demonstrated that Dip2a was important to neural differentiation at multiple levels and required for spinal cord and synapse development. In addition, our study provides model that can be used to investigate the regulatory mechanisms of Dip2a in neural differentiation.
4. Materials and methods
4.1. Cell lines and cell culture
mESCs 46 C (46 C with SOX1-GFP knock-in reporter) cell line was given as a gift by Dr. Hongjie Yao [30]. Dip2a-/- mESC was generated by knocking out the Dip2a gene in 46 C mESCs using CRISPR/Cas9 technology. PGK-Puro-P2A-mCherry was knocked into the 8th exon of Dip2a. After three days screening by puromycin, Dip2a homozygous knockout clones were characterized by genomic PCR and RT-qPCR.
The 46 C and Dip2a-/- cell lines were routinely grown on 0.2% gelatin-coated plate in 2iL medium [High Glucose Dulbecco's modified Eagle medium contain 20% fetal bovine serum (FBS, SORFA), 1000 U/ml mLIF (Sino Biological lnc.), 1 μM PD0325901 (Selleck) and 3 μM CHIR99021-HCl (Selleck), 1 × GlutaMAX (Gibco), 1 × Sodium pyruvate (Gibco), 1 ×Non-Essential Amino Acids Solution (Gibco), 0.1 mM β-Mercaptoethanol (Sigma), 1 ×penicillin-streptomycin (Gibco)] and cultured in a humidified atmosphere containing 5% CO2 at 37 °C. The 2iL medium was replaced every day.
4.2. Cell differentiation
Prior to differentiation induction, mESCs were cultured for in N2B27 medium + 2iL (N2B27 medium supplemented with 1 × Sodium pyruvate,1000 U/ml mLIF, 1 μM PD0325901, and 3 μM CHIR99021-HCl). Next, 46 C and Dip2a-/- mESCs were dissociated by Accutase (Biolengend) and then seeded in N2B27 medium [50% DMEM/F12 (Sevenbio, Beijing, China), 50% Neurobasal medium (Gibco), 0.5% N2 (Gibco), 1% B27 (Gibco), 1 × GlutaMAX, 1 × NEAA, 0.1 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 1 × penicillin-streptomycin (Gibco)] at a density of 4 × 104 cells/well in 12-well plate coated with 0.2% gelatin.
For neural differentiation in KSR medium [G-MEM (Gibco) supplemented with 7% Knockout Serum Replacement (Gibco), 1 × GlutaMAX, 1 × NEAA, 1 × Sodium pyruvate, 1 × penicillin-streptomycin, 0.1 mM β-mercaptoethanol], WT and Dip2a-/- mESCs were dissociated by 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA (Gibco) and maintained in a 60 mm dish at a density of 5 × 104 /ml cells in KSR medium.
4.3. Cell proliferation assay
46 C and Dip2a-/- mESCs were seeded into a 96-well culture plate at a density 2 × 103 cells/well in 2iL medium. At 24 h, 48 h, 96 h and 120 h of culture, cells in 100 μl medium were incubated with 10 μl Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK8, Beyotime) for 2 h at 37 °C in dark. The absorbance at 450 nm was recorded using a Synergy H1MD plate reader (BioTek).
4.4. Cell cycle analysis
To analyze cell cycle, 46 C and Dip2a-/- mESCs were cultured in 60-mm cell plates for 5 days. Cells were dissociated into single cell by 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA (Gibco) and then washed with Dulbecco’s Phosphate-Buffered Saline (DPBS). About 5 × 105 cells were fixed in 70% ethanol at 4 °C for 24 h, washed two times with DPBS (Hyclone), added with 500 μl PI staining reagent (20 × propidium iodide, 50 × RNAse in 500 μl sodium citrate buffer), and then incubated in the dark at 37 °C for 30 min. The cell cycle was measured using flow cytometer (BECKMAN COULTER), and the raw data were analyzed to determine the percentage of G1, S, G2 using FlowJo 10.8.1 and GraphPad Prism.
4.5. Flow cytometry
Cells were trypsinized by 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA and filtered through a cell strainer (40 µm). Cells were re-suspended in Phosphate Buffer Solution (PBS) and then analyzed using Flow Cytometry (BD LSRForessaTMX-20). SOX1-GFP+ cells were sorted and data was analyzed using FlowJo 10.8.1 software.
4.6. Immunofluorescence staining
For monolayer cell immunostaining, cells were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde (PFA), permeabilized in blocking buffer [10% donkey serum (Gibco) and 0.3% Triton X – 100 in PBS], and then incubated with primary antibodies (diluted in blocking buffer) at 4 °C overnight. Cells were washed with PBS, incubated with secondary antibodies (diluted in PBS), and then stained with 4′, 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) for 15 min. Then the slides were washed with PBS for three times and mounted with coverslips using ProLong Glass (Invitrogen).
EBs were fixed with 4% PFA, incubated in 20% sucrose solution at 4 °C overnight, embedded in Tissue-Tek O.C.T. compound (Sakura), and then frozen in liquid nitrogen. The frozen sections (10 μM) were soaked in PBS for 10 min, blocked with PBS containing 0.3% Triton X – 100, 0.5% donkey serum and 5% Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA), and then incubated with primary antibodies at 4 °C overnight. Next day, the slides were washed with PBS, incubated with secondary antibodies (diluted in PBS), and then stained with DAPI. After washing, slides were mounted with coverslips using ProLong Glass.
The following antibodies were used: rabbit anti-NANOG (1: 200, Cell Signaling Technology, 4903), mouse anti-OCT3/4 (1: 200, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, sc-5279), rabbit anti-PAX6 (1: 250, Proteintech, 12323–1-AP), mouse anti-β-Ⅲ-TUBULIN (1: 200, ABclonal, A18132), donkey anti-mouse 647 (1: 1000, Invitrogen, A-31571), donkey anti-rabbit 647 (1: 1000, Invitrogen, A-31573). All the slides were imaged on Zeiss scanning microscope (Zeiss LSM 710).
4.7. RT-qPCR
Total RNA was isolated using RNA Purification Kit (EZBioscience). 1 μg purified RNA was used for reverse transcription with HiScriptⅢ 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Vazyme), and RT-qPCR was performed by using Taq Pro Universal SYBR qPCR Master Mix(Vazyme) on LightCycler 480 system(Roche). All RT-PCR experiment were done with three replicates and gene expression was normalized to Gapdh. The qPCR primers are listed in Table 1.
Table 1.
RT-qPCR primer sequence.
| Gene | Primer-forward | Primer-reverse |
|---|---|---|
| Gapdh | AACTTTGGCATTGTGGAAGGGCTCA | TTGGCAGCACCAGTGGATGCAGGGA |
| Nanog | CTCAAGTCCTGAGGCTGACA | TGAAACCTGTCCTTGAGTGC |
| Oct4 | TAGGTGAGCCGTCTTTCCAC | GCTTAGCCAGGTTCGAGGAT |
| Sox2 | CTGCAGTACAACTCCATGACCAG | GGACTTGACCACAGAGCCCAT |
| Klf4 | AACATGCCCGGACTTACAAA | TTCAAGGGAATCCTGGTCTTC |
| Dip2a | CCTGAGGGGGATCAGATG | GGCTTTCCCCGCTGTGTC |
| Sox1 | GCACACAGCGTTTTCTCGG | ACATCCGACTCCTCTTCCC |
| Pax6 | GCAGATGCAAAAGTCCAGGTG | CAGGTTGCGAAGAACTCTGTTT |
| Nestin | CCCTGAAGTCGAGGAGCTG | CTGCTGCACCTCTAAGCGA |
| β-III-Tubulin | ACTTGGAACCTGGAACCATGG | GGCCTGAATAGGTGTCCAAAGG |
| Neurod1 | ATGACCAAATCATACAGCGAGAG | TCTGCCTCGTGTTCCTCGT |
| Map2 | AGCACTGATTGGGAAGCACT | CAATTCAAGGAAGTTGTAAAGTAGTGAAGTTTG |
| Notch1 | CACACATACGCACCCTCGC | AACTGGAGACTGAGACACACCTAGA |
| Ascl1 | AGGGTGGCAAATACTCAGTGAA | GCTGCCAAAGGCCTTCTCTT |
| Neurod1 | CTCCGGCCCAGAAGCC | AGAAAAACGTGGCCAAAGCC |
| Neurog1 | GAGCAGCCTCCTGCCAC | CATTGGCTCTCCCTGTCGG |
| Neurog2 | CAACTGCCAGAACCTTGTGC | AGAGTGACGTCAATGCCTCG |
| Otp | ACACGGCCAGTGATGTGAG | AGGAGCCGGTCACTCTGG |
| Gsx1 | ACTTTGACAGTTCAAGAGCCG | CTGACTCCCCTCTCTCCTCC |
| Hes5 | AAGTCTCTCGTGAACCGCAG | TGATCTTGGCTTCGTGCTGT |
| Irx6 | GCTATGGTGTTGGCAGTCCT | CGGGGTCAGTGGGATCTGTT |
| Gap43 | GGTCAGGGCAAACACCTGC | CTGTAGCGTCTTCCGGTGTC |
| Robo3 | GCATGCCAGTGTGCAAGAAA | ACCCGCAAAGGCCTACATAC |
| Dpysl2 | GTGTCGCTGCTCGGTGT | AGAATGACCTGTTCGGGCTG |
| Nrbp2 | CAGATGAACAACGCAGTGCC | CACCATCAGAATTTCCTACTGCC |
| L1cam | CGCCTGGAGCCGAAATCAT | TGCAGTCCTTCTTCCTCCCT |
| Neurog2 | CACAGTACCCCCAAGGATGG | GACGGTTCGTCGCTGTCA |
| Mark4 | CTCTGTAGCTGACAGGCTGG | GCTTCCCACCACGGATACTT |
| Otp | GAGCGTGAGTGGGATCAGTG | GCTTAGCAGATCCCTGCTTCT |
| Hes5 | ATCTGCGAGACCAAAGCTCG | CCCCGACAATCAGATAGGGC |
4.8. RNA-seq data analysis
Raw fastq files were subjected to quality control using AdapterRemoval [48], including removal of the low-quality, contaminated reads and adapter sequences. The remianing reads were aligned to the mm10 mouse reference genome using the Spliced Transcripts Alignment to a Reference (STAR) aligner [49]. Then, cufflinks was used for gene expression qualtification using the GENCODE gencode. vM25 annotation GTF file as reference. Prior to differential expression analysis, the expression values were normalized with FPKM. Differentially expressed transcripts were determined in Dip2a-/- cells compared with 46 C using log2 (fold change) greater than 0.58 as a cut-off.
4.9. Gene ontology
The up-regulated and down-regulated DEGs were subjected to functional enrichment analysis using the Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery (DAVID)[50]. The R package clusterProfiler [51] was used to perform illustration on functional enrichment results.
4.10. Gene set enrichment analysis
Gene Set Enrichment Analysis was performed using the GSEA software (v4.3.2) from https://www.gsea-msigdb.org/gsea/index.jsp.
4.11. Transcriptional regulatory network analysis
We performed motif scanning across the promoters of all expressed genes in D8 using FIMO (https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/43/W1/W39/2467905) (MEME suite, https://meme-suite.org/meme/doc/download.html), then the transcription factors (TFs)-gene regulatory network is established. To further investigate the sub-network involved in "spinal cord differentiation" and "postsynapse assembly“ categories, the sub-network is visualized using networkX package (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37450166/).
4.12. Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using GraphPad Prism (version 8.0.2; GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA) and represented as mean ± standard deviation (S.D.). For groups with a normal distribution, statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed t-test or one-way ANOVA test (NS P > 0.05,* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001).
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32070654, 32270843), the Central Government Guidance on Local Science and Technology Development Fund (YDZJSX2022B002), Shanxi Province Science Foundation for Youths (202203021212083) and the Four Batches Innovation Project of Invigorating Medical through Science and Technology of Shanxi Province China (2023XM058), Lvliang City high-level talent introduction special project (2023RC28). The funding bodies played no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript.
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Mingze Yao: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing - review & editing. Lei Zhang: Experiments, Data analysis, Figure generation, Writing – original draft, Validation. Xiaojuan Teng: Software, Data curation. Yu Lei: Methodology, Experiments. Xiaoyu Xing: Visualization. Tinglin Ren: Visualization. Yuanqing Pan: Visualization, Data analysis. Liwen Zhang: Software. Zhengfeng Li: Visualization. Jingxia Lin: Software. Yaowu Zheng: Resources, Supervision. Li Xing: Writing - review & editing. Jiajian Zhou: Supervision, Writing - review & editing. Changxin Wu: Supervision, Resources. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Hongjie Yao from Guangzhou Laboratory for the kind gift of 46 C cells.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Footnotes
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found in the online version at doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2023.12.032.
Contributor Information
Mingze Yao, Email: yaomz@sxu.edu.cn.
Jiajian Zhou, Email: zhoujj2013@smu.edu.cn.
Changxin Wu, Email: cxw20@sxu.edu.cn.
Appendix A. Supplementary material
Supplementary material.
.
Supplementary material.
.
Supplementary material.
.
Supplementary material.
.
Supplementary material.
.
References
- 1.Mukhopadhyay M., et al. Cloning, genomic organization and expression pattern of a novel Drosophila gene, the disco-interacting protein 2 (dip2), and its murine homolog. Gene. 2002;293(1-2):59–65. doi: 10.1016/s0378-1119(02)00694-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Campos A.R., Fischbach K.F., Steller H. Survival of photoreceptor neurons in the compound eye of drosophila depends on connections with the optic ganglia. Development. 1992;114(2):355–366. doi: 10.1242/dev.114.2.355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Heilig J.S., et al. Isolation and characterization of the disconnected gene of drosophila-melanogaster. EMBO J. 1991;10(4):809–815. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Campos A.R., Lee K.J., Steller H. Establishment of neuronal connectivity during development of the drosophila larval visual-system. J Neurobiol. 1995;28(3):313–329. doi: 10.1002/neu.480280305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sorrentino N.C., et al. Enhancing the therapeutic potential of sulfamidase for the treatment of mucopolysaccharidosis IIIA. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2019;15:333–342. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2019.10.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Noblett N., et al. DIP-2 suppresses ectopic neurite sprouting and axonal regeneration in mature neurons. J Cell Biol. 2019;218(1):125–133. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201804207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Nitta Y., et al. DISCO Interacting Protein 2 regulates axonal bifurcation and guidance of Drosophila mushroom body neurons. Dev Biol. 2017;421(2):233–244. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2016.11.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nitta Y., Sugie A. DISCO interacting protein 2 determines direction of axon projection under the regulation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in the Drosophila mushroom body. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;487(1):116–121. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.04.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Poelmans G., et al. Identification of novel dyslexia candidate genes through the analysis of a chromosomal deletion. Am J Med Genet Part B-Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2009;150b(1):140–147. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.30787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kong R., et al. Genetic variant in DIP2A gene is associated with developmental dyslexia in Chinese population. Am J Med Genet Part B-Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2016;171(2):203–208. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.b.32392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Iossifov I., et al. The contribution of de novo coding mutations to autism spectrum disorder. Nature. 2014;515(7526):216–U136. doi: 10.1038/nature13908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Iossifov I., et al. De novo gene disruptions in children on the autistic spectrum. Neuron. 2012;74(2):285–299. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.04.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Egger G., et al. Identification of risk genes for autism spectrum disorder through copy number variation analysis in Austrian families. Neurogenetics. 2014;15(2):117–127. doi: 10.1007/s10048-014-0394-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wang T., et al. De novo genic mutations among a Chinese autism spectrum disorder cohort. Nat Commun. 2016;7:13316. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Winnepenninckx B., et al. CGG-repeat expansion in the DIP2B gene is associated with the fragile site FRA12A on chromosome 12q13.1. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;80(2):221–231. doi: 10.1086/510800. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hayashi T., et al. Exosomal microRNA transport from salivary mesenchyme regulates epithelial progenitor expansion during organogenesis. Dev Cell. 2017;40(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2016.12.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Larsson C., et al. Loss of DIP2C in RKO cells stimulates changes in DNA methylation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Bmc Cancer. 2017;17 doi: 10.1186/s12885-017-3472-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Li J., et al. DIP2C expression in breast cancer and its clinical significance. Pathol Res Pract. 2017;213(11):1394–1399. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2017.09.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.DeScipio C., et al. Subtelomeric deletion of chromosome 10p15.3: clinical findings and molecular cytogenetic characterization. Am J Med Genet Part A. 2012;158a(9):2152–2161. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.35574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tanaka M., et al. DIP2 disco-interacting protein 2 homolog A (Drosophila) is a candidate receptor for follistatin-related protein/follistatin-like 1-analysis of their binding with TGF-beta superfamily proteins. FEBS J. 2010;277(20):4278–4289. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2010.07816.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yu T., et al. A mouse model of Down syndrome trisomic for all human chromosome 21 syntenic regions. Hum Mol Genet. 2010;19(14):2780–2791. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Poelmans G., et al. A theoretical molecular network for dyslexia: integrating available genetic findings. Mol Psychiatry. 2011;16(4):365–382. doi: 10.1038/mp.2010.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Iossifov I., et al. De Novo gene disruptions in children on the autistic spectrum. Neuron. 2012;74(2):285–299. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.04.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wang T.Y., et al. De novo genic mutations among a Chinese autism spectrum disorder cohort. Nat Commun. 2016;7 doi: 10.1038/ncomms13316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Nie E., et al. Fstl1/DIP2A/MGMT signaling pathway plays important roles in temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma. Oncogene. 2019;38(15):2706–2721. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0596-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhang L.Q., et al. Expression patterns and potential biological roles of Dip2a. PLOS One. 2015;10(11) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ma J., et al. Autism candidate gene DIP2A regulates spine morphogenesis via acetylation of cortactin. PLOS Biol. 2019;17(10) doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Sah R.K., et al. Transcriptome profiling of mouse brain and lung under Dip2a regulation using RNA-sequencing. PLOS One. 2019;14(7) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Yao M., et al. Generation of Dip2a homozygous knockout murine ES cell line IBMSe001-A-1 via CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Stem Cell Res. 2020;45 doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2020.101778. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Aubert J., et al. Screening for mammalian neural genes via fluorescence-activated cell sorter purification of neural precursors from Sox1-gfp knock-in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100(Suppl 1):11836–11841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1734197100. Suppl 1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Correia B., et al. Leucine and arginine availability modulate mouse embryonic stem cell proliferation and metabolism. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(22) doi: 10.3390/ijms232214286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wang Y., et al. Embryonic stem cell-specific microRNAs regulate the G1-S transition and promote rapid proliferation. Nat Genet. 2008;40(12):1478–1483. doi: 10.1038/ng.250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ying Q.L., et al. Conversion of embryonic stem cells into neuroectodermal precursors in adherent monoculture. Nat Biotechnol. 2003;21(2):183–186. doi: 10.1038/nbt780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Watanabe K., et al. Directed differentiation of telencephalic precursors from embryonic stem cells. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8(3):288–296. doi: 10.1038/nn1402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Furukawa Y., et al. Effects of knockout serum replacement on differentiation of mouse-induced pluripotent stem cells into odontoblasts. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 2022;63(2):75–83. doi: 10.2209/tdcpublication.2021-0042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bai L.L., et al. DIP2A is involved in SOD-mediated antioxidative reactions in murine brain. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;168:6–15. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.03.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ma J., et al. Dysregulation of AMPK-mTOR signaling leads to comorbid anxiety in Dip2a KO mice. Cereb Cortex. 2022 doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhac393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Rao Z., et al. Molecular mechanisms underlying Ascl1-mediated astrocyte-to-neuron conversion. Stem Cell Rep. 2021;16(3):534–547. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2021.01.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Di Bella D.J., et al. Ascl1 balances neuronal versus ependymal fate in the spinal cord central canal. Cell Rep. 2019;28(9):2264–2274.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.07.087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Patel M., et al. Gsx1 promotes locomotor functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Mol Ther. 2021;29(8):2469–2482. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.04.027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zhang L., et al. Expression patterns and potential biological roles of Dip2a. PLOS One. 2015;10(11) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0143284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ma J., et al. Autism candidate gene DIP2A regulates spine morphogenesis via acetylation of cortactin. PLOS Biol. 2019;17(10) doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhao J.C., et al. The differential regulation of Gap43 gene in the neuronal differentiation of P19 cells. J Cell Physiol. 2012;227(6):2645–2653. doi: 10.1002/jcp.23006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Michalski N., et al. Robo3-driven axon midline crossing conditions functional maturation of a large commissural synapse. Neuron. 2013;78(5):855–868. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Bai L.L., et al. DIP2A is involved in SOD-mediated antioxidative reactions in murine brain. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;168:6–15. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.03.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kinatukara P., et al. Peri-natal growth retardation rate and fat mass accumulation in mice lacking Dip2A is dependent on the dietary composition. Transgenic Res. 2020;29(5-6):553–562. doi: 10.1007/s11248-020-00219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Schubert M., Lindgreen S., Orlando L. AdapterRemoval v2: rapid adapter trimming, identification, and read merging. BMC Res Notes. 2016;9(1) doi: 10.1186/s13104-016-1900-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Dobin A., et al. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics. 2013;29(1):15–21. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bts635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Sherman B.T., et al. DAVID: a web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update) Nucleic Acids Res. 2022;50(W1):W216–W221. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wu T., et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: a universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation. 2021;2(3) doi: 10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary material.
Supplementary material.
Supplementary material.
Supplementary material.
Supplementary material.