Abstract
Natural genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae is controlled by a quorum-sensing system, which acts through the competence-stimulating peptide (CSP) for transient activation of genes required for competence. More than 100 genes have been identified as CSP regulated by use of DNA microarray analysis. One of the CSP-induced genes required for genetic competence is comW. As the expression of this gene depended on the regulator ComE, but not on the competence sigma factor ComX (σX), and as expression of several genes required for DNA processing was affected in a comW mutant, comW appears to be a new regulatory gene. Immunoblotting analysis showed that the amount of the σX protein is dependent on ComW, suggesting that ComW may be directly or indirectly involved in the accumulation of σX. As σX is stabilized in clpP mutants, a comW mutation was introduced into the clpP background to ask whether the synthesis of σX depends on ComW. The clpP comW double mutant accumulated an amount of σX higher (threefold) than that seen in the wild type but was not transformable, suggesting that while comW is not needed for σX synthesis, it acts both in stabilization of σX and in its activation. Modification of ComW with a histidine tag at its C or N terminus revealed that both amino and carboxyl termini are important for increasing the stability of σX, but only the N terminus is important for stimulating its activity.
Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus) is a naturally transformable bacterium that can become competent to take up exogenous DNA. At a certain cell density during the exponential growth phase, the sudden appearance of competence is controlled in part by a quorum-sensing system, which acts through a secreted pheromone to cause transient activation of many genes required for competence (10, 25). The pheromone is processed from a precursor (a product of comC) by a membrane transporter, ComAB, to release the mature 17-residue competence-stimulating peptide (CSP) (10, 11, 12, 25). When CSP accumulates in the medium, its presence is sensed by a receptor histidine kinase, ComD, and this sensor kinase probably phosphorylates the response regulator, ComE, activating the expression of comAB, comCDE, and several other operons (10, 16, 25, 26).
Operons under control of the response regulator ComE have an imperfect direct-repeat sequence in their promoter regions, and ComE appears to bind this target site to activate gene expression (37). Two identical copies of the comX gene (comX1 and comX2) which depend on ComE for their CSP-induced expression (16, 26, 27) encode a competence-specific alternative sigma factor, σX. Expression of comX allows transcription of many genes encoding components of the machinery for DNA uptake and recombination and thus links the quorum-sensing signal to the DNA uptake pathway (16, 18, 20). Genes under its control share an 8-bp sequence in their promoter regions that is specifically required by σX-containing RNA polymerase (4, 8, 16, 20). Thus, genes involved in genetic transformation can be grouped into two classes by their modes of regulation: early genes are ComE dependent, and their mRNA reaches a maximum 7 to 8 min after CSP treatment, while late competence genes are also σX dependent, and their mRNA peaks at 10 to 11 min (1, 8, 26).
Several surveys, including a promoter-trap study (2), a gene array hybridization survey (28), a bioinformatics promoter sequence search (26), and DNA microarray surveys (26, 27), have identified ∼180 CSP-responsive genes in S. pneumoniae. Although many of these genes are not directly required for transformation or competence induction (27), one of the CSP-induced genes that is required for competence is comW. As the induction of comW does not depend on σX, and as comW is essential for competence, Peterson et al. proposed that it might be a new regulatory gene (27). Recently, Luo et al. (19) reported that the ectopic coexpression of comW and comX leads to the induction of competence and the accumulation of σX in the absence of CSP treatment at 30°C, suggesting that ComW acts as a positive regulator of comX, at least under these experimental conditions.
Although comW was thus identified as a probable actor in the linkage between early and late competence genes, it is not known how it promotes the development of competence or what is the biological significance of this role. Here, we present evidence that ComW contributes to the stabilization of the alternative sigma factor σX against proteolysis. We also provide evidence that comW is required for full activity of σX in directing transcription of late competence genes.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strains, media, antibiotics, and DNA sources.
The pneumococcal strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Tables 1 and 2. CP1250 (25) was used as a transformation recipient to create all new pneumococcal mutations and lacZ fusions. Escherichia coli strain BL21(DE3)/pLysS [F− ompT hsdSB (rB− mB−) gal dcm (DE3)/pLysS] was the host for plasmids pCR T7/CT TOPO (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) and pET16b (Novagen, Madison, WI). Complete CAT medium (15) and Luria-Bertani (LB) medium (3) were used for pneumococcal and E. coli cultures, respectively. DNA from strain CP1500 (5) was used as the donor for transformation assays. Primers used for constructing mutations in this study, listed in Table 2, were obtained from QIAGEN (Valencia, CA). Antibiotics were used at the following concentrations: ampicillin, 100 μg ml−1; chloramphenicol (Cm), 34 μg ml−1 for E. coli and 2.5 μg ml−1 for S. pneumoniae; erythromycin (Erm), 0.25 μg ml−1; kanamycin (Kan), 200 μg ml−1; novobiocin (Nov), 2.5 μg ml−1; tetracycline (Tet), 0.25 μg ml−1.
TABLE 1.
Pneumococcal strains used in this study
| Strain | Description | Sourcea |
|---|---|---|
| CP1250 | S. pneumoniae Rx derivative; low β-galactosidase activity; hex malM511 str-1 bgl-1 Hex− Mal- Smr Bga− | 25 |
| CP1500 | hex nov-r1 bry-r str-1 ery-r1 ery-r2 Novr | 5 |
| CP1359 | CP1250, but clpP::tet Tetr | 17 |
| CP1376 | CP1250, but comW::KANT Kanr | 27 |
| CP1548 | CP1250, but cglA::pEVP3 Cmr | 16 |
| CP1601 | CP1250, but celB::pEVP3 Cmr | 16 |
| CP1714 | comW::KANT ssbB::pEVP3::ssbB+ Cmr Kanr | CP1376 × CPM7 |
| CP1718 | cglA::pEVP3 Cmr Kanr | CP1376 × CP1548 |
| CP1719 | celB::pEVP3 Cmr Kanr | CP1376 × CP1601 |
| CP1721 | CP1250, but comW::pEVP3::comW+ Cmr | pCKS03 × CP1250 |
| CP1723 | comW::KANT comX1::erm comX2::Tet Ermr Kanr Tetr | CP1376 × CPM8 |
| CP1724 | comW::KANT comX1::pEVP3::comX1+ Cmr Kanr | CP1376 × CPM3 |
| CP1731 | CP1721, but comE::erm Ermr Cmr | This study |
| CP1802 | CP1250, but C terminus-V5-H6-ComW-pEVP3 Cmr | pCKS07 × CP1250 |
| CP1805 | CP1250, but N terminus-H6-Xa-ComW-KANT Kanr | This study |
| CP1815 | clpP::tet comW::KANT Kanr Tetr | CP1376 × CP1359 |
| CP1816 | clpP::tet N-H6-Xa-ComW-KANT Kanr Tetr | CP1359 × CP1805 |
| CP1820 | comW::KANT clpP::tet cglA::pEVP3 Cmr Kanr Tetr | CP1376 × CP1821 |
| CP1821 | clpP::tet cglA::pEVP3 Cmr Tetr | CP1548 × CP1359 |
| CP1822 | comW::KANT clpP::tet celB::pEVP3 Cmr Kanr Tetr | CP1376 × CP1823 |
| CP1823 | clpP::Tet celB::pEVP3 Cmr Tetr | CP1601 × CP1359 |
| CP1850 | clpP::Tet C-V5-H6-ComW-pEVP3 Cmr Tetr | CP1359 × CP1802 |
| CP1851 | CP1250, but clpE::erm Ermr | This study |
| CP1852 | comW::KANT clpE::erm clpP::tet Ermr Kanr Tetr | CP1376 × CP1853 |
| CP1853 | clpE::erm clpP::tet Ermr Tetr | CP1359 × CP1851 |
| CP1854 | comW::KANT clpE::Erm Ermr Kanr | CP1376 × CP1851 |
| CPM3 | CP1250, but comX1::pEVP3::comX1+ Cmr | 16 |
| CPM4 | CP1250, but comX1::Erm comX2::pEVP3 Cmr Ermr | 16 |
| CPM7 | CP1250, but ssbB::pEVP3::ssbB+ Cmr | 16 |
| CPM8 | CP1250, but comX1::Erm comX2::tet Ermr Tetr | 16 |
Construction of a strain by transformation between two different mutant strains is shown as DNA × recipient.
TABLE 2.
Plasmids and oligonucleotide primers used in this study
| Plasmid/primer | Description/sequence (5′-3′) | Source or location/use |
|---|---|---|
| Plasmids | ||
| pCKS01 | C-V5-H6-comW in plasmid pCRT7/CT TOPO | This study |
| pCKS02 | N-H6-Xa-comW in plasmid pET16b | This study |
| pCKS03 | comW in plasmid pEVP3 | This study |
| pCKS07 | C-V5-H6-comW in plasmid pEVP3 | This study |
| pEVP3 | Plasmid containing the Cmr-encoding gene and the promoterless lacZ reporter derived from pTV32 | 7 |
| pCR T7/CT TOPO | Plasmid for producing target proteins containing a C-terminal histidine tag | Invitrogen |
| pET16b | Plasmid for producing target proteins containing an N-terminal histidine tag | Novagen |
| pR410 | Plasmid containing the kan gene | 33 |
| Primers | ||
| CKS24 | TATCTAGAGGCTGGTATTTTAACAATTCA | Upstream of comW (CP1721) |
| CKS25 | ATGGATCCTCAACAAGAAATAAACCCCCGATTCA | In comW (CP1721) |
| CKS33 | ATGTTACAAAAAATTTATGAGCAGATGGC | In comW (pCKS01) |
| CKS34 | ACAAGAAATAAACCCCCGATTCATTACCAA | In comW (pCKS01) |
| CKS107 | ATTCTAGAGCAGATGGCTAATTTCTATGATAGT | In comW (CP1802) |
| CKS108 | ATGGATCCTCCGGATATAGTTCCTCCTTTCAG | In pCR T7/CT TOPO (CP1802) |
| CKS109 | GGCATATGATTATGTTACAAAAAATTTATGAGC | In comW (pCKS02) |
| CKS110 | ATGGATCCTCAACAAGAAATAAACCCCCGATTCA | In comW (pCKS02) |
| CKS116 | GATCTAGAAAGGAGATATACCATGGGCCATCA | In pET16b (CP1805) |
| CKS114 | ATGGGCCCTAGAAGTCTCAGCGAGCTCCATT | Upstream of comW (CP1805) |
| CKS115 | GCTCTAGATTATAAACTTATTCTAACAAAAAA | Upstream of comW (CP1805) |
| DAM303 | AAGGGCCCGTTTGATTTTTAATG | In pR410 (KANT) |
| DAM304 | AGGATCCATCGATACAAATTCCTC | In pR410 (KANT) |
| DAM497 | CAATTGACTATATTAGAGGCGAGACA | Upstream of comW (CP1805) |
| CKS113 | ATGGATCCTTCTTCTTAGAAAAGGCCGTTTTA | Upstream of comW (CP1805) |
Construction of new pneumococcal strains.
To create the comW lacZ fusion strain CP1721, a comW fragment was prepared by PCR using the primer pair CKS24 and CKS25. This amplicon and plasmid pEVP3 were digested with XbaI and BamHI (Invitrogen), ligated using T4 DNA ligase (MBI Fermentas, Hanover, MD), and introduced into E. coli DH5α. A recombinant plasmid (pCKS03) from a single Cmr colony was then transferred to competent cells of CP1250. A Cmr transformant was selected, and full circular integration of pCKS03 was verified by amplification and sequencing of new junction fragments. A similar strategy was used to create strain CP1802, expressing a C-terminally histidine-tagged ComW. Once pCKS01 was constructed in E. coli BL21(DE3)/pLysS using a comW PCR fragment (primers CKS33 and CKS34) and plasmid pCR T7/CT TOPO, the gene fusion encoding a His-tagged ComW was amplified from it using the primer pair CKS107 (XbaI) and CKS108 (BamHI). This amplicon was cloned into plasmid pEVP3, and the structure of the product (pCKS07) was verified by sequencing of new junctions. After transforming strain CP1250 with pCKS07 and verifying the expected insertion structure by PCR, a Cmr colony was selected for further study and named CP1802.
To construct strain CP1805, expressing N-terminally histidine-tagged ComW, comW (amplified with primers CKS109 and CKS110) was fused to the N-terminal histidine tag-encoding sequence in plasmid pET16b (using NdeI and BamHI sites). From the resulting plasmid, pCKS02, the gene encoding N-His-tagged ComW was amplified using primers CKS116 (XbaI) and CKS110. PCR ligation mutagenesis was used to introduce the gene encoding the N-His-tagged protein with a ComE-responsive promoter into CP1250. The promoter sequence of comW (primers CKS114 [ApaI] and CKS115 [XbaI]) and a Kan resistance cassette (KANT; primers DAM303 [ApaI] and DAM304 [BamHI]) were amplified from chromosomal DNAs of CP1250 and plasmid pR410 (33), respectively. A fragment (UP fragment) upstream of comW was also amplified using primers DAM497 and CKS113 (BamHI). All four fragments (UP fragment, KANT, ComE promoter, and N-His-comW) were digested by the corresponding restriction enzymes, ligated, and introduced into CP1250. A Kanr colony resulting from targeted recombination was retained as CP1805, and the structure of the chimeric locus was verified by PCR and sequencing of all three new junctions. Other new pneumococcal strains were made by transformation crosses, as indicated in Table 1.
Beta-galactosidase activity assay.
For assay of lacZ activity in CP1724, CPM3, and CPM4, cells were grown in complete CAT medium supplemented with 8 mM HCl to avoid endogenous induction of competence. Optical density at 550 nm (OD550) was determined in 18-mm-diameter round cuvettes in the Coleman Jr II colorimeter. At an OD550 of 0.05, each culture was induced by addition of CSP-1 (200 ng ml−1), bovine serum albumin (BSA) (0.2%), and CaCl2 (0.5 mM), and 1-ml samples were withdrawn at 5-min or 10-min intervals for 60 min. Each sample was lysed with 0.2% Triton X-100 at 37°C for 10 min, mixed with 1 ml of substrate buffer (1.6 mg o-nitrophenyl-β-d-galactopyranoside [ONPG], 20 mM sodium phosphate [16.4 mM Na2HPO4 and 3.6 mM NaH2PO4; pH 7.5], 20 mM NaOH, 2 mM MgCl2, and 90 mM β-mercaptoethanol) (30). After 40 min at 37°C and addition of 1 ml of 1 M Na2CO3, the optical density was measured at 420 nm. For other lacZ fusion strains, cells were grown to an OD550 of 0.05, and both a noncompetent culture and a parallel sample of the same culture treated with CSP for 20 min were lysed and assayed for beta-galactosidase as described above.
Immunoblotting.
Cells were grown in complete CAT medium containing 8 mM HCl to an OD550 of 0.05. A 10-ml sample was chilled and centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 min as an uninduced control. For the induced samples, each culture was treated with 200 ng ml−1 of CSP, and 10-ml samples were withdrawn at the indicated times. The samples were chilled rapidly in 1-liter steel beakers on ice, centrifuged at 10,000 rpm for 10 min at 4°C, and resuspended in 0.1 ml of gel loading buffer (50 mM Tris-Cl, pH 6.8, 100 mM dithiothreitol, 2% sodium dodecyl sulfate [SDS], 0.1% bromophenol blue, and 10% glycerol) (30). After being heated at 95°C for 5 min, each extract was subjected to SDS gel eletrophoresis, using either 12% Tris-glycine SDS gels with 4% stacking or 4 to 20% gradient Ready Gel Tris-HCl gels (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA). Electrophoresis at 15 V/cm in Tris-glycine buffer was followed by transfer to a polyvinylidene difluoride membrane (Millipore, Bedford, MA) for 75 min at 46 V in transfer buffer (48 mM Tris, 39 mM glycine, pH 9.2). This membrane was blocked overnight at 4°C in TBST buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.6, 140 mM NaCl, and 0.1% Tween 20) containing 5% nonfat milk solids (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA) and then probed with a purified polyclonal antibody against σX (20) at a dilution of 1:2,000 in TBST containing 1% nonfat milk solids for 2 h at room temperature. After being washed in 30 ml of TBST five times at room temperature, the membrane was incubated with a secondary peroxidase-conjugated anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G antibody (1:20,000 dilution; Amersham Biosciences, Piscataway, NJ) in TBST containing 1% nonfat milk solids for 1 h at room temperature and washed in TBST five times. The signal was detected by using ECL-Plus Western blotting reagents (Amersham Biosciences) and X-OMAT Imaging films (Kodak, Rochester, NY). The films were scanned using a ScanMaker 4850 (Microtek International Inc.) at 600-dot/in resolution, and band intensities were then compared with standards included in the same gels by using AlphaEase FC (Alpha Innotech, San Leandro, CA) for quantification.
Competence assay.
Wild-type (WT) strain CP1250 and mutant pneumococcal strains were grown in CAT containing 8 mM HCl, 0.2% BSA, and 0.5 mM CaCl2. At an OD550 of 0.05, each culture was split in half, and one half was induced by addition of CSP (200 ng ml−1). One hundred ng ml−1 of Novr donor DNA (from strain CP1500) was added to both induced and uninduced cultures, and then each sample was incubated at 37°C for 1 h. After serial dilution, 0.1 ml of cells and 1.5 ml of CAT were mixed with 1.5 ml of melted CAT agar and poured onto a 3-ml-thick layer of CAT agar in a 60-mm-diameter petri dish. The plate was then covered with a 3-ml layer of CAT agar and another layer of CAT agar containing 30 μg Nov. Novr transformants were counted after 20 h at 37°C. For the experiment depicted in Fig. 1, cells were grown at 37°C in CAT supplemented with 8 mM HCl. At an OD550 of 0.05, 1 ml of each culture was added to 9 ml of warm CAT containing 8 mM HCl, 0.5 mM CaCl2, and 0.2% BSA, and 1 ml of the dilution was transferred to a warm Eppendorf tube. After 20 min at 37°C, CSP was added to 200 ng ml−1. At the indicated times, 0.1-ml culture samples were mixed with 10 ng of Novr DNA, incubated for 5 min at 37°C, and then diluted 1:150 into 1.5 ml of CAT containing 7.5 μg DNase. After 60 min at 37°C, the entire culture was mixed with 1.5 ml of melted CAT agar and plated as described above. Novr transformants were counted after 20 h at 37°C.
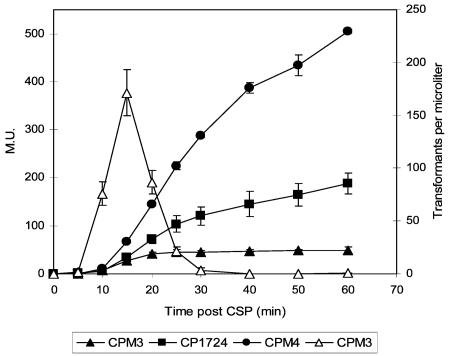
FIG. 1.
Effect of comW mutation on the transcription of comX. Beta-galactosidase activities in CPM3 (comX lacZ; WT), CPM4 (comX lacZ; ΔcomX), and CP1724 (comX lacZ; ΔcomW) were assayed at the indicated times after CSP treatment. Competence of CPM3 is also shown (▵). Transformation of CPM4 and CP1724 yielded fewer than 100 Novr/ml. Error bars, standard deviation among three replicate experiments. M.U., Miller units.
RESULTS
comW is required for the induction of late competence genes.
The temporal transcription pattern of comW is typical of early CSP-induced genes that are dependent on ComE but not on σX for their CSP responses, and its induction is not blocked in comX mutants (27). To determine more directly whether the competence regulators ComE and σX are required for the induction of comW, a comW-lacZ fusion reporter was assayed in an isogenic wild-type (CP1721), comE mutant (CP1731), or comX mutant (CP1723) background. Consistent with the known temporal expression pattern of comW, the induction of this comW transcriptional fusion depended on the competence regulator ComE, but not on the alternative sigma factor σX (Table 3). Indeed, CSP-induced transcription of the comW reporter was higher in the comX background than in the WT, as is typical of other early genes (16, 27). Previous work (2, 27) showed that comW is essential for competence for genetic transformation, and here we show that this gene is under the control of ComE and is independent of σX for its induction by CSP. It therefore seems possible that the deficiency of competence in comW mutants might be caused by reduced expression of late competence genes that are downstream of comX and are required for the processes of DNA uptake or recombination. To ask whether there was such an effect on late gene expression, the lacZ reporter was fused to the late competence genes, celB, cglA, and ssbB, which are required for genetic transformation, in either wild-type or comW-deficient backgrounds. The CSP-dependent induction of all three late competence genes was reduced in the comW background by at least 90% compared to that of the same late genes in the wild type (Table 3). This shows that comW precedes at least these three late genes in the CSP-induced signal cascade and is essential for maximal induction of DNA machinery genes. This result also suggests that the competence deficiency of a comW mutant may be due to reduction in the levels of DNA-processing machinery components.
TABLE 3.
CSP induction of lacZ fusions to comW, ssbB, celB, and cglA genes in different genetic backgrounds
| Strain and relevant genotype | lacZ fusion sitea | Beta-galactosidase activityb
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
| W/o CSP | CSP | ||
| CP1721 WT | comW | 0.5 ± 1 | 140 ± 100 |
| CP1731 comE | comW | 1 ± 1 | 0.5 ± 1 |
| CP1723 comX | comW | 0.5 ± 1 | 450 ± 250 |
| CPM7 WT | ssbB | 0 | 80 ± 40 |
| CP1714 comW | ssbB | 0.5 ± 1 | 10 ± 1 |
| CP1601 celB | celB | 1 ± 1 | 60 ± 40 |
| CP1719 celB comW | celB | 2 ± 2 | 2 ± 1 |
| CP1822 celB comW clpP | celB | 1 ± 1 | 5 ± 5 |
| CP1823 celB clpP | celB | 2 ± 1 | 30 ± 20 |
| CP1548 cglA | cglA | 0 | 300 ± 300 |
| CP1718 cglA comW | cglA | 1 ± 1 | 20 ± 10 |
| CP1820 cglA comW clpP | cglA | 1 ± 1 | 20 ± 20 |
| CP1821 cglA clpP | cglA | 2 ± 0 | 150 ± 100 |
lacZ reporter gene was inserted into indicated locus.
In each of three experiments, cells were grown in complete CAT medium supplemented with 8 mM HCl to an OD550 of 0.05, and a noncompetent culture and a parallel sample of the same culture treated with CSP for 20 min were prepared. Both samples were lysed and assayed for β-galactosidase as described in Materials and Methods. The average activity (Miller units) for three experiments is also shown, with standard deviations (SD) or range. W/o, without.
Transcription of comX is strongly induced in a comW mutant.
Since several σX-dependent late genes were only weakly induced by CSP in the comW background, it seemed possible that the expression of comX itself might be affected by the comW deletion. To test this hypothesis, a comX-lacZ transcriptional fusion was examined in either a wild-type (CPM3) or comW (CP1724) background in comparison to the comX-deficient comX-lacZ fusion strain CPM4, which was included in the study to reflect the strong negative autoregulatory effect of σX. The transcriptional pattern of comX in the comW mutant was very similar to that in the comX double mutant: both were higher than that seen in the wild-type background, and both continued well beyond 25 min (Fig. 1). Since the comX-lacZ fusion in both CP1724 and CPM3 has a native comX promoter, this result indicates that ComW is not needed for the strong induction of transcription of comX upon CSP treatment.
The rapid shutoff of expression of early competence genes, including comCDE, comX, and comW, appears to depend on σX, since in its absence, the transcription of early genes induced by CSP does not promptly return to the initial basal level, like that of the same genes in a wild-type background, but continues for at least two generations (16, 27). As shown in Fig. 1, beta-galactosidase activity was higher in the comW mutant (CP1724; comX-lacZ ΔcomW) than in the comW+ isogenic control (CPM3; comX-lacZ). The activity of beta-galactosidase also rose continuously for at least 60 min in CP1724, while the activity in the wild-type background leveled off after 20 min. Therefore, the negative autoregulatory mechanism that is proposed to be mediated by comX or a comX-dependent late gene(s) is similarly dependent on comW.
The amount of the σX protein is very small in comW mutants.
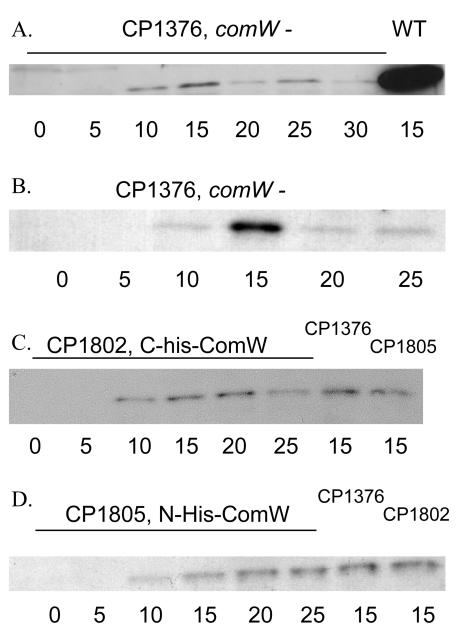
Since in comW mutants there was a high level of comX transcription but a very low transformation rate and low expression of comX-dependent genes, indicating an apparent strong reduction of σX activity, we sought to determine the actual level of σX in comW mutants directly. Western blotting analysis was performed in the comW mutant CP1376 and its parent, CP1250, using an antibody against σX. One might expect to see an elevated level of σX in CP1376, since the comX-lacZ transcriptional fusion in strain CP1724 had such a high expression level. However, in contrast to the pattern observed for the transcriptional reporter, the level of σX found in the comW mutant was low, although it did appear transiently, with kinetics similar to those of the wild type and with a maximum at 15 min (Fig. 2A and B). The maximal σX level was ∼10% of that seen in the wild-type strain (Fig. 3 and Table 4). Therefore, ComW appears to act after initiation of transcription of comX and to affect the level of σX protein that accumulates. Thus, ComW may act during translation of comX (e.g., by stabilization of mRNA or initiation of translation) or for the stabilization of σX after its synthesis.
FIG. 2.
Accumulation of the σX protein requires ComW. The WT (CP1250) and a comW mutant (CP1376), a C-His-tagged ComW mutant (CP1802; 0- to 25-min samples in panel C), and an N-His-tagged ComW mutant (CP1805; 0- to 25-min samples in panel D) were treated with CSP (at time zero), and samples were collected as described in Materials and Methods at the indicated times (in minutes). An extract representing 1 ml of culture was loaded into each well. Samples of CP1376 from two independent preparations were loaded onto different gels (A and B). The gels were assayed by Western blotting using an antibody against σX.
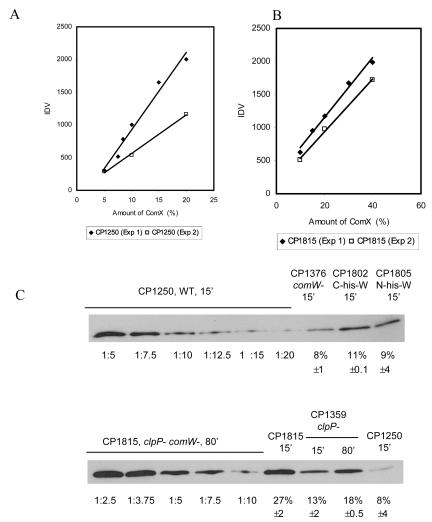
FIG. 3.
Quantification of σX in various genetic backgrounds. (A) σX standard curve prepared from a 15-min extract of CP1250 (WT). A sample (100%) was prepared from CP1250 at 15 min post-CSP treatment, and then different amounts (dilutions of 1:5, 1:7.5, 1:10, 1:12.5, 1:15, or 1:20) were subjected to SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and immunoblotting. The relationship between the integrated density values (IDV) of enhanced chemiluminescence assay bands and relative amounts of protein is shown. (B) σX standard curve prepared from an 80-min extract from CP1815 (clpP comW double mutant). The extract was serially diluted in a blank extract of CPM8 (ΔcomX) (dilutions of 1:2.5, 1:3.75, 1:5, 1:7.5, or 1:10) before assay by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting. (C) Immunoblotting image of σX in a wild-type strain and various mutant strains. The relative amount of σX in each strain is shown, with a range. The intensities of CP1376, CP1802, and CP1805 were compared to the CP1250 standard curve (A), while those of CP1250, CP1815, and CP1359 were compared to the CP1815 standard curve (B).
TABLE 4.
Quantification of ComX in various pneumococcal strains
| Protein sample and timea | IDVb | Avg relative amt (%) ± rangec |
|---|---|---|
| CP1250 (WT) 15 | 100 | |
| CP1376 (ΔcomW) 15 | 600 ± 180 | 8 ± 1 |
| CP1802 (C-his-ComW) 15 | 800 ± 200 | 11 ± 0.1 |
| CP1805 (N-his-ComW) 15 | 750 ± 400 | 9 ± 4 |
| CP1815 (ΔclpP, ΔcomW) 80 | 100 | |
| CP1815 (ΔclpP, ΔcomW) 15 | 1,300 ± 170 | 27 ± 2 |
| CP1359 (ΔclpP) 15 | 750 ± 100 | 13 ± 2 |
| CP1359 (ΔclpP) 80 | 1,000 ± 100 | 18 ± 0.5 |
| CP1250 (WT) 15 | 550 ± 50 | 8 ± 4 |
Samples were prepared at indicated times (in min) post-CSP treatment.
The intensity of each band was converted into an IDV using Alpha-Ease FC.
The average of the relative amounts of ComX determined by two independent experiments is shown, with a range. The relative amount of the ComX protein was determined by the IDV of each sample and standard curve graphs. (The graph of serially diluted samples of CP1250 at 15 min [Fig 3A] was used for CP1376, CP1802, and CP1805; the graph of serially diluted samples of CP1815 at 80 min [Fig 3B] was used for CP1815 at 15 min, CP1359 at 15 min, CP1359 at 80 min, and CP1250 at 15 min.)
ComW is required for protection of σX from proteolysis.
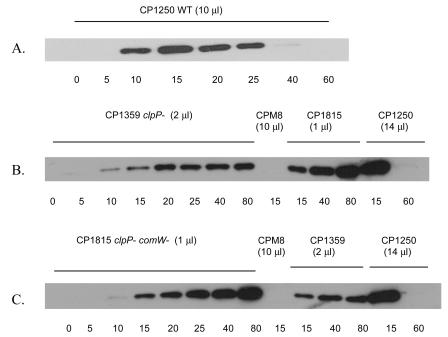
The ATP-dependent ClpP protease is responsible for degradation of many regulatory proteins in both gram-positive and -negative bacteria (35, 38, 39), as well as for removal of misfolded proteins (14). In S. pneumoniae, clpP-deficient mutant strains can exhibit a precocious and extended period of endogenous competence (29), which is partly explained by an elevated basal expression level of the comC gene encoding the competence pheromone (6). It has also been reported that mutation of the clpP genes in S. pneumoniae and S. pyogenes leads to increased accumulation of σX, suggesting that ClpP protease may negatively control σX in both of these streptococci (17, 23). As σX is more stable in a clpP mutant, and as its accumulation depended on the ComW protein (Fig. 2), we created a clpP::Tet comW::KANT double mutant to distinguish whether ComW is involved in translation of comX or in the stability of σX after translation. If the synthesis of σX depends on ComW, the amount of σX produced in response to CSP treatment would be low in this clpP comW double mutant. However, σX would accumulate to high levels after CSP induction in the double mutant if ComW acts later, by preventing ClpP-proteolysis of σX, as the clpP mutation would replace the missing protective function.
In the double mutant CP1815, the level of σX at 15 min postinduction was in fact higher (threefold) than that seen at 15 min in the wild type and approximately twice that in the clpP single mutant (Fig. 3 and 4 and Table 4), indicating that in this strain, production of σX does not depend on ComW. Therefore, translation of comX is independent of ComW, and the role of ComW in determining the level of σX appears to be protection of the protein from proteolysis by ClpP. The immunoblotting results also indicate that σX accumulated to a higher level (fivefold by 80 min) (Fig. 3) in CP1815 (clpP comW) than in the clpP single mutant CP1359. This greater accumulation of σX in CP1815 may be explained by increased and prolonged transcription of the comX gene in the comW-deficient mutant strain due to reduction of the σX-dependent shutoff processes, as indicated in Fig. 1.
FIG. 4.
Deletion of both comW and clpP leads to the accumulation of σX after competence induction. The wild-type (CP1250; 0- to 60-min samples in panel A), a comX mutant (CPM8), a clpP single mutant (CP1359; 0- to -80-min samples in panel B), and a comW clpP double mutant (CP1815; 0- to 80-min samples in panel C) were induced by CSP (at time zero), and samples were withdrawn at the indicated times (in min) after induction. The indicated amount of each extract (0.1 ml of original culture per μl extract) were assayed by Western blotting analysis and probed with anti-ComX antibody.
ComW is also required for full activity of σX.
To ask whether absence of the σX-degrading ClpP protease rescues the deficiency of competence found in the comW single-mutant strain, a clpP comW double mutant, CP1815, was also examined for its competence. Surprisingly, the competence of CP1815 was <0.1% of normal (Table 5), even though this mutant had a normal amount of σX after CSP treatment (Fig. 3C and 4C). Thus, ComW is still required for genetic transformation in the clpP-deficient background. To ask whether the competence deficiency of the clpP comW double mutant could reflect a deficiency in expression of late genes that are essential for the DNA uptake process and recombination, late lacZ reporter fusions were examined in clpP single- or clpP comW double-mutant backgrounds. In the clpP comW double mutant, transcription of the late genes, celB and cglA, was ∼10% of that seen in CSP-treated clpP single mutants (Table 3). As the quantitative relationship between competence and late-gene expression is not known in detail, and as only two late genes were sampled, it is not clear whether the 90% decrease in transcription of celB and cglA fully explains the 99.9% decrease in competence. Nevertheless, we conclude that the deficiency of competence in the clpP comW strain was due, at least in part, to reduced expression of DNA machinery genes, possibly caused in turn by low activity of the abundant σX. Thus, ComW appears to have another important function in genetic transformation, a function needed for full activity of the competence-specific σ. It is possible that this other function of ComW could be to modify σX to an active form, to release it from sequestration, or to cooperate with it in transcription.
TABLE 5.
Competence for transformation in WT and comW, clpE, and clpP mutants of S. pneumoniae
| Strain | Description | Transformants/ml (± SD or range)a
|
Relative competenceb (%) (± SD or range) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| W/o CSP | CSP | |||
| CP1250 | WT | <0.01 | 680 ± 310 | 100 |
| CP1376 | comW | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.01 |
| CP1802 | C-V5-H6-ComW | <0.01 | 440 ± 170 | 80 (±10) |
| CP1805 | N-H6-Xa-ComW | <0.01 | <0.1 | <0.1 |
| CP1359 | clpP | <0.01 | 530 ± 350 | 80 (±15) |
| CP1815 | clpP comW | <0.01 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | <0.05 |
| CP1816 | clpP N-H6-Xa-ComW | <0.01 | 0.3 ± 0.1 | <0.05 |
| CP1850 | clpP C-V5-H6-ComW | <0.01 | 270 ± 35 | 70 (±10) |
| CP1851 | clpE | <0.01 | 720 ± 480 | 90 (±30) |
| CP1852 | clpP clpE comW | <0.01 | 0.2 ± 0.0 | <0.05 |
| CP1853 | clpP clpE | <0.01 | 1,100 ± 120 | 110 (±10) |
| CP1854 | clpE comW | <0.01 | <0.01 | <0.001 |
The average number of transformants determined by two or three independent experiments is shown, with a range or standard deviation. CP1500 Novr donor DNA was used in each assay. W/o, without.
Transformant yield compared to CSP-induced WT (CP1250) in parallel control cultures.
A clpE mutant still requires comW for genetic transformation.
The ClpP proteolytic subunit is known to associate with several different ATP-binding subunits to recognize and degrade different substrates (9). In S. pneumoniae, the putative ATP-binding subunits of Clp protease include ClpC, ClpE, ClpL, and ClpX (34). Luo recently found that σX remains stable after competence induction in clpE or clpP (but not in clpC or clpL) backgrounds, suggesting that ClpE may associate with the ClpP proteolytic domain for proteolytic regulation of σX (17). To explore the possibility that the inactive state of σX in the clpP comW mutant was caused by ClpE-mediated sequestration, a clpE deletion mutation was introduced into this double mutant, creating the clpP clpE comW mutant, CP1852, and the competence of this triple mutant was determined. The transformation rate of the clpP clpE comW mutant was the same as that of the clpP comW parent (<0.1% of that seen in the wild-type strain) (Table 5). Thus, the activity of σX in a clpP comW mutant was not increased by an additional clpE mutation, and its low apparent activity in the clpP comW genetic background must not be due to sequestration by ClpE.
Antiprotease activity is genetically distinguishable from the activation function of ComW.
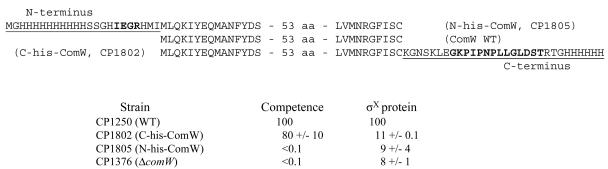
N- or C-terminal portions of many bacterial regulators fulfill separate roles or target different molecules (21, 22, 24, 32). Since the ComW protein appears to have dual functions, both protecting and activating σX, it is possible that its termini might also be important for different roles. To explore this possibility, mutant strains having C- or N-terminal histidine modifications of σX (Fig. 5) were constructed and examined by immunoblotting and a competence assay. The levels of σX in cells expressing N- or C-tagged ComW forms were low, similar to that seen in the comW deletion mutant CP1376 (Fig. 4C and Table 5). Thus, both ends of this protein are important for the stabilization or protection of σX. However, the levels of competence of the two mutant strains differed. Competence was <0.1% of the control in the strain expressing an N-His-tagged ComW, just as for a comW deletion mutant (Table 5). In contrast, the competence of the strain expressing a C-His-tagged ComW was 70% of the normal level (Table 5), even though the amount of σX in this strain after CSP induction was 11% of that in a wild-type strain (Fig. 3C and Table 4). Therefore, the amino terminus is important for the activity of σX, but both amino and carboxyl termini of ComW are important for promoting its stability.
FIG. 5.
Effects of terminal extensions of the ComW protein on competence and σX accumulation. The sequences of WT ComW (middle), amino-terminally His-tagged ComW (CP1805; top), and carboxyl-terminally His-tagged ComW (CP1802; bottom). His tags introduced into the wild-type ComW are underlined; boldface residues in N-His-ComW indicate a factor Xa cleavage site; boldface residues in C-His-ComW indicate a V5 epitope. Omitted 53 residues: IEEEYGPTFGDNFDWEHVHFKFLIYYLVRYGIGCRKDFIVYHYRVAYRLYLEK. The corresponding competence phenotype (mean relative number of transformants ± standard deviation) and relative amount of σX (mean and range) observed 15 min after CSP induction are also shown. aa, amino acids.
DISCUSSION
The alternative sigma factor σX is known to provide a link between the early quorum-sensing signal and the expression of late DNA machinery genes during development of competence in S. pneumoniae, and here we report evidence that another early competence gene product, ComW, also plays important roles in that linkage through the regulation of comX.
Regulation of a number of proteins, including alternative sigma factors, by proteolysis has been observed in a wide variety of bacterial species (reviewed in reference 13). Among well-known proteases, ClpP is an important regulatory factor. ClpP degrades sigma factor S in nonstress growth conditions in E. coli (31), in a proteolytic process that depends on a targeting factor, RssB, for delivery of sigma S to the ClpXP protease (39). ClpP also controls the development of competence in B. subtilis by degrading a competence-specific activator, ComK (35). B. subtilis does not possess a secondary sigma factor linking quorum sensing and DNA machinery gene expression, but the release of the transcriptional activator ComK from the ClpCP/MecA complex by ComS leads to the development of competence (36). In S. pneumoniae, endogenous competence induction in a clpP-deficient mutant strain can extend longer than in the WT, suggesting that ClpP may also, as in B. subtilis, be a negative regulator of competence induction (29). Chastanet et al. showed that deletion of the clpP gene caused an elevated basal expression level of the comC gene encoding the pneumococcal competence pheromone (6). Mutation of the clpP gene also leads to an increased accumulation of the alternative sigma factor σX, indicating that the ClpP protease negatively affects σX levels in this species (17). The induction of ComW by the quorum-sensing circuit seems to prevent this proteolytic process temporarily, so as to amplify the effect of comX induction in coordinating competence development. In the wild-type pneumoccocal cell, σX disappears after activating the DNA machinery genes by a ClpP-mediated proteolytic process. This suggests that ComW may protect σX only briefly, at the start of competence. The basis of this temporary protection is not known, but possibilities include that ComW itself may be very unstable, perhaps having strong affinity to a Clp protease, or an initial ComW-σX complex may be dissociated by a late competence protein, allowing the Clp protease access to σX.
ComW is also required for activity of σX by an unknown mechanism. If σX is initially produced as an inactive form that needs to be processed to cooperate with RNA polymerase, ComW may participate in its processing to an active form. Another possibility is that ComW may release σX from sequestration. The ATP-dependent Clp protease subunits are known to recognize substrates in a specific manner, allowing access to the proteolytic subunit, ClpP. Thus, candidates for sequestration of σX include the ATP-binding subunits ClpC, ClpE, ClpL, and ClpX. A genetic test of the most likely of these candidates, clpE, indicated that it is not responsible for the inactivity of σX in the clpP comW background, but other factors may cause it to be inactive in the absence of ComW. It is also possible that ComW may cooperate directly with σX or RNA polymerase in the initiation of transcription to promote the interaction or combined functions of these two molecules.
CSP-induced mRNA levels for early competence genes, including comCDE, comX, and comW, reach a maximum at ∼7.5 min and then sharply decline. This decay depends on comX, since the induced transcription of these genes persists much longer in a comX-deficient background (16, 27). In a comW mutant (CP1724), the transcriptional expression pattern of comX was initially similar to that observed in a WT strain (CP1250). After 15 min, however, a significant amount of comX mRNA continued to be made in CP1724 for at least 60 min, while no message was evident in the WT after 25 min, presumably due to the putative competence repressor(s) (Fig. 1). Since this expression pattern indicates that the comW mutant is deficient in competence (or early-gene) shutoff, the negative regulatory mechanism appears to be dependent on comW. Figure 1 also shows that the accumulation of beta-galactosidase in CP1724 slows slightly after 20 min. This suggests that the shutoff mechanism for early genes may be partially functional in the comW background. As a comW mutant accumulates ∼10% of the normal σX level after induction and achieves 5 to 10% of the normal levels of expression of several late genes, this partial shutoff may be explained by such residual activity of σX.
N- or C-terminal domains of many bacterial regulators have separate roles, such as targeting different molecules (21, 22, 24, 32). In Bacillus subtilis, MecA, which acts as an adapter protein targeting the competence transcription activator ComK for Clp degradation (35, 36), appears to bind two different molecules, ComK and ClpC, at its N- and C-terminal domains, respectively. The amino-terminal domain of MecA binds to transcription factor ComK, while the carboxy-terminal domain interacts with an ATP-binding subunit, ClpC. These interactions cause the formation of a ternary complex, leading to degradation of the ComK protein by the ClpP proteolytic subunit (24, 35, 36). The results presented here indicate that the N and C termini of ComW may also have different targets. Both the C and N termini of the ComW protein are required for the protection of σX from proteolysis, but only its amino terminus appears to be important for its activation. However, functionally important portions of this protein could be mapped more precisely in the future by use of mutant proteins.
While alternative sigma factors are powerful regulatory devices, coordinating global regulation, they have drawbacks. Transcription read-through into such genes might lead to initiation of a signal pathway at the wrong time, while mutations affecting expression or function of these cellular regulators may easily have serious pleiotropic effects. Thus, many bacteria possess additional factors that help to tighten the regulation of alternative sigma factor activity. In the case of S. pneumoniae competence, σX is subjected to primary transcriptional control by ComE and the quorum-sensing circuit, but a more secure regulation of genetic competence may be achieved by means of an additional regulatory factor, ComW, which is required for both stabilization and activation of this alternative σ.
Acknowledgments
We thank Marc Prudhomme and Jean-Pierre Claverys for providing plasmid pR410.
This work was supported in part by the U.S. National Science Foundation (MCB-0110311).
REFERENCES
- 1.Alloing, G., B. Martin, C. Granadel, and J. P. Claverys. 1998. Development of competence in Streptococcus pneumoniae: pheromone autoinduction and control of quorum sensing by the oligopeptide permease. Mol. Microbiol. 29:75-83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bartilson, M., A. Marra, J. Christine, J. S. Asundi, W. P. Schneider, and A. E. Hromockyj. 2001. Differential fluorescence induction reveals Streptococcus pneumoniae loci regulated by competence stimulatory peptide. Mol. Microbiol. 39:126-135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bertani, G. 1951. Studies on lysogenesis. I. The mode of phage liberation by lysogenic Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 62:293-300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Campbell, E. A., S. Y. Choi, and H. R. Masure. 1998. A competence regulon in Streptococcus pneumoniae revealed by genomic analysis. Mol. Microbiol. 27:929-939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cato, A., Jr., and W. R. Guild. 1968. Transformation and DNA size. I. Activity of fragments of defined size and a fit to a random double cross-over model. J. Mol. Biol. 37:157-178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chastanet, A., M. Prudhomme, J. P. Claverys, and T. Msadek. 2001. Regulation of Streptococcus pneumoniae clp genes and their role in competence development and stress survival. J. Bacteriol. 183:7295-7307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Claverys, J. P., A. Dintilhac, E. V. Pestova, B. Martin, and D. A. Morrison. 1995. Construction and evaluation of new drug-resistance cassettes for gene disruption mutagenesis in Streptococcus pneumoniae, using an ami test platform. Gene 164:123-128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Claverys, J. P., and L. S. Håvarstein. 2002. Extracellular-peptide control of competence for genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Front. Biosci. 7:1798-1814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gottesman, S. 1996. Proteases and their targets in Escherichia coli. Annu. Rev. Genet. 30:465-506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Håvarstein, L. S., G. Coomaraswamy, and D. A. Morrison. 1995. An unmodified heptadecapeptide pheromone induces competence for genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92:11140-11144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hui, F. M., and D. A. Morrison. 1991. Genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae: nucleotide sequence analysis shows comA, a gene required for competence induction, to be a member of the bacterial ATP-dependent transport protein family. J. Bacteriol. 173:372-381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hui, F. M., L. Zhou, and D. A. Morrison. 1995. Competence for genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae: organization of a regulatory locus with homology to two lactococcin A secretion genes. Gene 153:25-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Jenal, U., and R. Hengge-Aronis. 2003. Regulation by proteolysis in bacterial cells. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 6:163-172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kock, H., U. Gerth, and M. Hecker. 2004. The ClpP peptidase is the major determinant of bulk protein turnover in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 186:5856-5864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lee, M. S., B. A. Dougherty, A. C. Madeo, and D. A. Morrison. 1999. Construction and analysis of a library for random insertional mutagenesis in Streptococcus pneumoniae: use for recovery of mutants defective in genetic transformation and for identification of essential genes. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 65:1883-1890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lee, M. S., and D. A. Morrison. 1999. Identification of a new regulator in Streptococcus pneumoniae linking quorum sensing to competence for genetic transformation. J. Bacteriol. 181:5004-5016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Luo, P. 2003. Ph.D. thesis. University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, Ill.
- 18.Luo, P., H. Li, and D. A. Morrison. 2003. ComX is a unique link between multiple quorum sensing outputs and competence in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol. Microbiol. 50:623-633. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Luo, P., H. Li, and D. A. Morrison. 2004. Identification of ComW as a new component in the regulation of genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol. Microbiol. 54:172-183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Luo, P., and D. A. Morrison. 2003. Transient association of an alternative sigma factor, ComX, with RNA polymerase during the period of competence for genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Bacteriol. 185:349-358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Morona, J. K., R. Morona, D. C. Miller, and J. C. Paton. 2003. Mutational analysis of the carboxy-terminal (YGX)4 repeat domain of CpsD, an autophosphorylating tyrosine kinase required for capsule biosynthesis in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J. Bacteriol. 185:3009-3019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Morona, J. K., J. C. Paton, D. C. Miller, and R. Morona. 2000. Tyrosine phosphorylation of CpsD negatively regulates capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol. Microbiol. 35:1431-1442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Opdyke, J. A., J. R. Scott, and C. P. Moran, Jr. 2003. Expression of the secondary sigma factor sigmaX in Streptococcus pyogenes is restricted at two levels. J. Bacteriol 185:4291-4297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Persuh, M., K. Turgay, I. Mandic-Mulec, and D. Dubnau. 1999. The N- and C-terminal domains of MecA recognize different partners in the competence molecular switch. Mol. Microbiol. 33:886-894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pestova, E. V., L. S. Håvarstein, and D. A. Morrison. 1996. Regulation of competence for genetic transformation in Streptococcus pneumoniae by an auto-induced peptide pheromone and a two-component regulatory system. Mol. Microbiol. 21:853-862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Peterson, S., R. T. Cline, H. Tettelin, V. Sharov, and D. A. Morrison. 2000. Gene expression analysis of the Streptococcus pneumoniae competence regulons by use of DNA microarrays. J. Bacteriol. 182:6192-6202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Peterson, S. N., C. K. Sung, R. Cline, B. V. Desai, E. C. Snesrud, P. Luo, J. Walling, H. Li, M. Mintz, G. Tsegaye, P. C. Burr, Y. Do, S. Ahn, J. Gilbert, R. D. Fleischmann, and D. A. Morrison. 2004. Identification of competence pheromone responsive genes in Streptococcus pneumoniae by use of DNA microarrays. Mol. Microbiol. 51:1051-1070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Rimini, R., B. Jansson, G. Feger, T. C. Roberts, M. de Francesco, A. Gozzi, F. Faggioni, E. Domenici, D. M. Wallace, N. Frandsen, and A. Polissi. 2000. Global analysis of transcription kinetics during competence development in Streptococcus pneumoniae using high density DNA arrays. Mol. Microbiol. 36:1279-1292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Robertson, G. T., W. L. Ng, J. Foley, R. Gilmour, and M. E. Winkler. 2002. Global transcriptional analysis of clpP mutations of type 2 Streptococcus pneumoniae and their effects on physiology and virulence. J. Bacteriol. 184:3508-3520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Sambrook, J., and D. Russell. 2001. Molecular cloning, 3rd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
- 31.Schweder, T., K. H. Lee, O. Lomovskaya, and A. Matin. 1996. Regulation of Escherichia coli starvation sigma factor (sigma s) by ClpXP protease. J. Bacteriol. 178:470-476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Sorg, I., C. Hoffmann, J. Dumbach, K. Aktories, and G. Schmidt. 2003. The C terminus of YopT is crucial for activity and the N terminus is crucial for substrate binding. Infect. Immun. 71:4623-4632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sung, C. K., H. Li, J. P. Claverys, and D. A. Morrison. 2001. An rpsL cassette, JANUS, for gene replacement through negative selection in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67:5190-5196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Tettelin, H., K. E. Nelson, I. T. Paulsen, J. A. Eisen, T. D. Read, S. Peterson, J. Heidelberg, R. T. DeBoy, D. H. Haft, R. J. Dodson, A. S. Durkin, M. Gwinn, J. F. Kolonay, W. C. Nelson, J. D. Peterson, L. A. Umayam, O. White, S. L. Salzberg, M. R. Lewis, D. Radune, E. Holtzapple, H. Khouri, A. M. Wolf, T. R. Utterback, C. L. Hansen, L. A. McDonald, T. V. Feldblyum, S. Angiuoli, T. Dickinson, E. K. Hickey, I. E. Holt, B. J. Loftus, F. Yang, H. O. Smith, J. C. Venter, B. A. Dougherty, D. A. Morrison, S. K. Hollingshead, and C. M. Fraser. 2001. Complete genome sequence of a virulent isolate of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Science 293:498-506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Turgay, K., J. Hahn, J. Burghoorn, and D. Dubnau. 1998. Competence in Bacillus subtilis is controlled by regulated proteolysis of a transcription factor. EMBO J. 17:6730-6738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Turgay, K., L. W. Hamoen, G. Venema, and D. Dubnau. 1997. Biochemical characterization of a molecular switch involving the heat shock protein ClpC, which controls the activity of ComK, the competence transcription factor of Bacillus subtilis. Genes Dev. 11:119-128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ween, O., P. Gaustad, and L. S. Håvarstein. 1999. Identification of DNA binding sites for ComE, a key regulator of natural competence in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol. Microbiol. 33:817-827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Zhou, Y., and S. Gottesman. 1998. Regulation of proteolysis of the stationary-phase sigma factor RpoS. J. Bacteriol. 180:1154-1158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zhou, Y., S. Gottesman, J. R. Hoskins, M. R. Maurizi, and S. Wickner. 2001. The RssB response regulator directly targets σS for degradation by ClpXP. Genes Dev. 15:627-637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]