Abstract
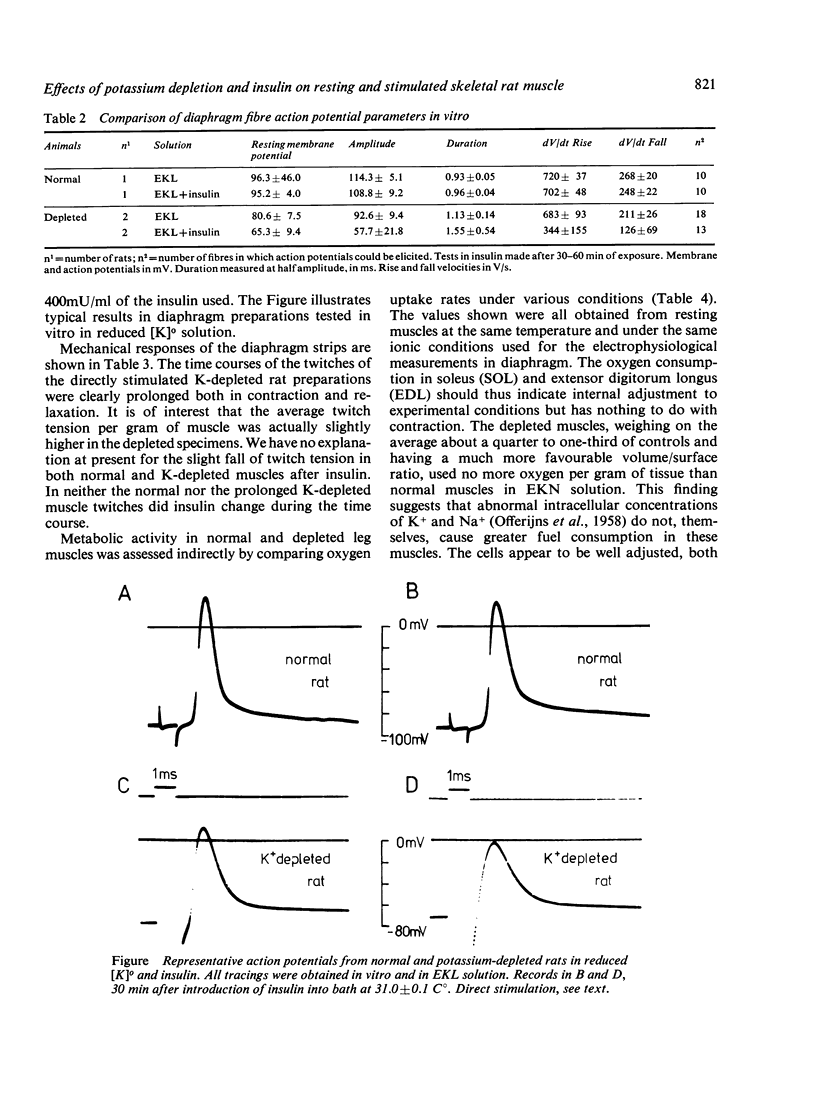
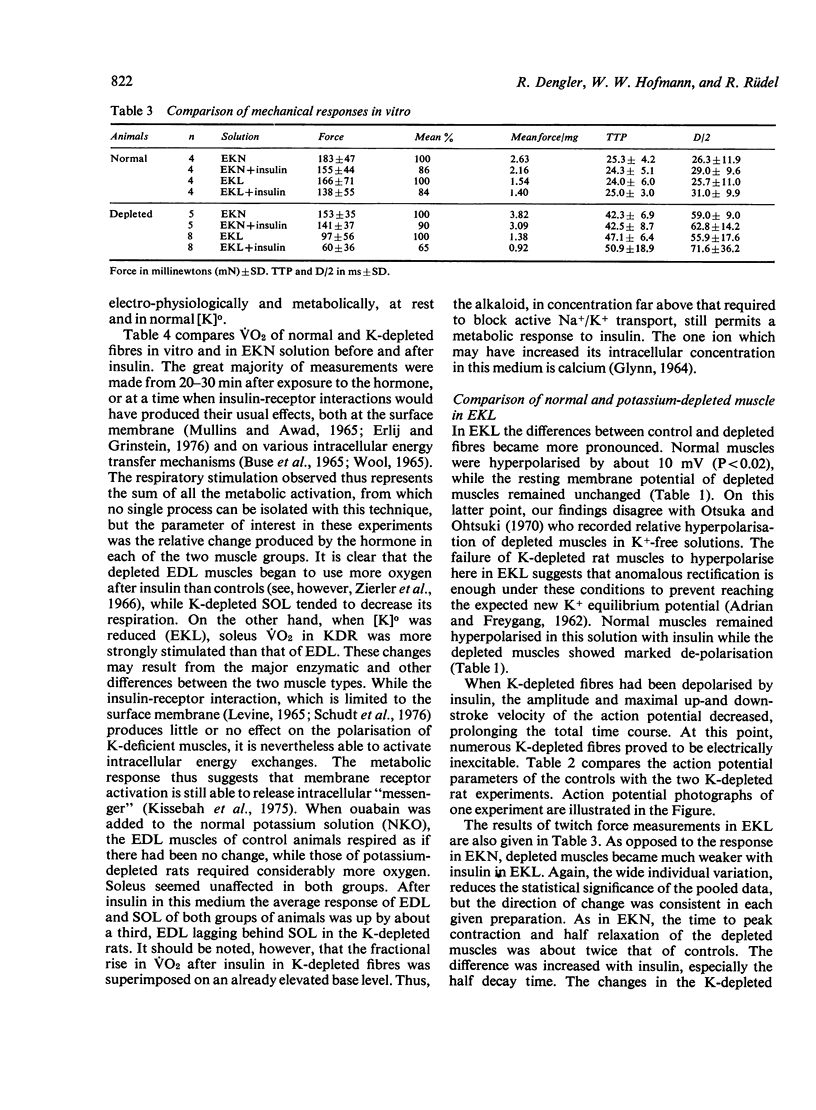
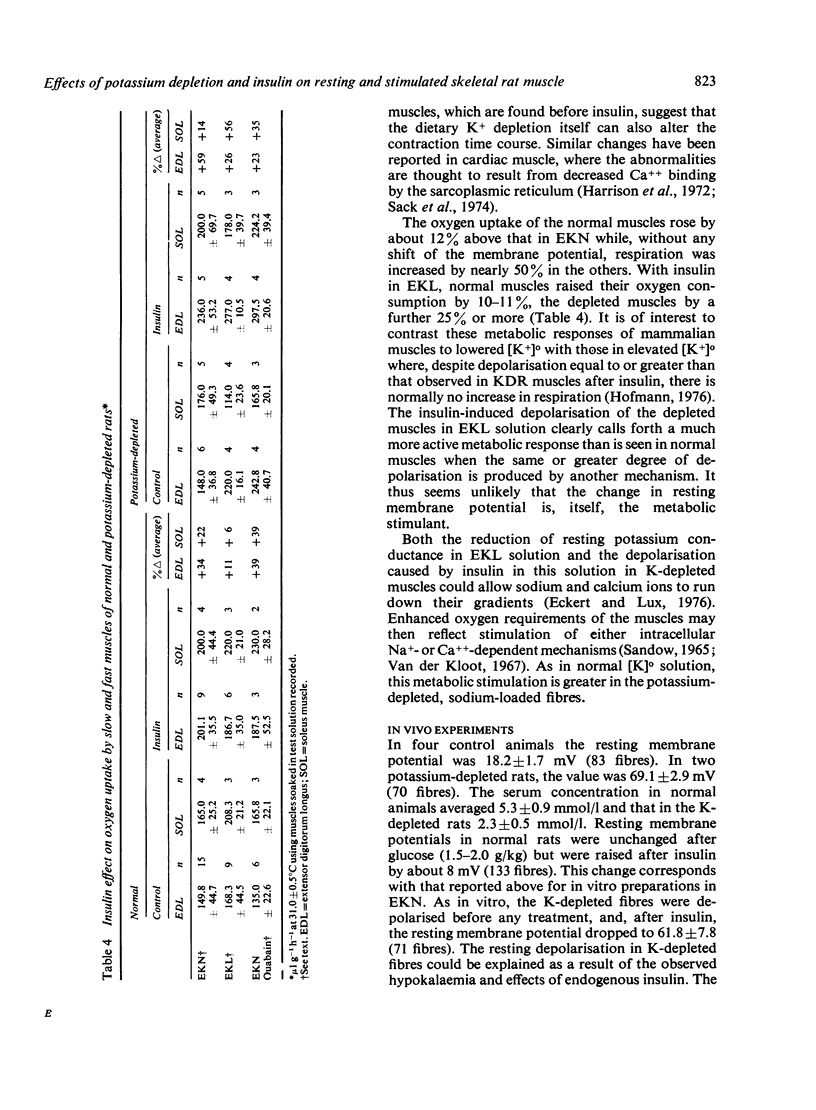
The electrophysiological and metabolic responses to insulin of skeletal muscles from control and potassium-depleted rats were compared. Membrane potentials, action potentials, contraction parameters as well as oxygen uptake were measured in diaphragm strips or intact extremity muscles from the two groups, and similar measurements were made in vivo. The muscles were examined in solutions with normal potassium concentration [K]o , reduced [K]o, and in normal [K]o and in normal [K]o with ouabain, in each case before and after insulin, 400 mU/ml. In normal solution, the depleted muscle contractions were weaker and slower than control. The depleted muscles, already having low potassium conductance, are paralysed by the further reduction of potassium conductance after insulin. Hyperpolarising effects of insulin-induced Na/K pumping are offset in the depleted muscles with a high sodium conductance and low [K]o. Respiration is about normal at rest in depleted muscles, despite increased [Na]i, suggesting that the sodium is sequestered. After insulin, reduction of [K]o, or ouabain plus insulin, the depleted fibres take up more O2 than controls. In the presence of ouabain, this respiratory stimulation is believed to represent response to Ca++ influx. The K-depleted rat does not seem to be an entirely satisfactory model of the human disease hypokalaemic periodic paralysis.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adrian R. H., Freygang W. H. The potassium and chloride conductance of frog muscle membrane. J Physiol. 1962 Aug;163(1):61–103. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1962.sp006959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretag A. H. Synthetic interstitial fluid for isolated mammalian tissue. Life Sci. 1969 Mar 1;8(5):319–329. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buse M. G., McMaster J., Buse J. The effect of denervation and insulin on protein synthesis in the isolated rat diaphragm. Metabolism. 1965 Nov;14(11):1220–1232. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(65)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CREESE R., NORTHOVER J. Maintenance of isolated diaphragm with normal sodium content. J Physiol. 1961 Feb;155:343–357. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1961.sp006632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T., Kohn P. G. The effect of insulin on the transport of sodium and potassium in rat soleus muscle. J Physiol. 1977 Feb;265(1):19–42. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1977.sp011703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creese R. Sodium fluxes in diaphragm muscle and the effects of insulin and serum proteins. J Physiol. 1968 Jul;197(2):255–278. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckert R., Lux H. D. A voltage-sensitive persistent calcium conductance in neuronal somata of Helix. J Physiol. 1976 Jan;254(1):129–151. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlij D., Grinstein S. The number of sodium ion pumping sites in skeletal muscle and its modification by insulin. J Physiol. 1976 Jul;259(1):13–31. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1976.sp011452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frumento A. S. The electrical effects of an ionic pump. J Theor Biol. 1965 Sep;9(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(65)90111-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN I. M. THE ACTION OF CARDIAC GLYCOSIDES ON ION MOVEMENTS. Pharmacol Rev. 1964 Dec;16:381–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOURLEY D. R. Separation of insulin effects on K content and O2 consumption of frog muscle with cardiac glycosides. Am J Physiol. 1961 Jun;200:1320–1326. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.6.1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROB D., JOHNS R. J., LILJESTRAND A. Potassium movement in patients with familial periodic paralysis: relationship to the defect in muscle function. Am J Med. 1957 Sep;23(3):356–375. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(57)90316-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon A. M., Green J. R., Lagunoff D. Studies on a patient with hypokalemic familial periodic paralysis. Am J Med. 1970 Feb;48(2):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(70)90114-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison C. E., Jr, Cooper G., 4th, Zujko K. J., Coleman H. N., 3rd Myocardial and mitochondrial function in potassium depletion cardiomyopathy. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 1972 Dec;4(6):633–649. doi: 10.1016/0022-2828(72)90117-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann W. W. Oxygen consumption by human and rodent striated muscle in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1976 Jan;230(1):34–40. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1976.230.1.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann W. W., Smith R. A. Hypokalemic periodic paralysis studies in vitro. Brain. 1970;93(3):445–474. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.3.445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KEYNES R. D., MAISEL G. W. The energy requirement for sodium extrusion from a frog muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1954 May 27;142(908):383–392. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1954.0031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao I., Gordon A. M. Mechanism of insulin-induced paralysis of muscles from potassium-depleted rats. Science. 1975 May 16;188(4189):740–741. doi: 10.1126/science.1124397. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kissebah A. H., Clarke P., Vydelingum N., Hope-Gill H., Tulloch B., Fraser T. R. The role of calcium in insulin action. III. Calcium distribution in fat cells; its kinetics and the effects of adrenaline, insulin and procaine-HCl. Eur J Clin Invest. 1975 Jul 29;5(4):339–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1975.tb00463.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. Cell membrane as a primary site of insulin action. Fed Proc. 1965 Sep-Oct;24(5):1071–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLINS L. J., AWAD M. Z. THE CONTROL OF THE MEMBRANE POTENTIAL OF MUSCLE FIBERS BY THE SODIUM PUMP. J Gen Physiol. 1965 May;48:761–775. doi: 10.1085/jgp.48.5.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. D. Effect of insulin upon the sodium pump in frog skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1973 Jul;232(1):23–45. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niall J. F., Pak POY R. K. Studies in familial hypokalaemic periodic paralysis. Australas Ann Med. 1966 Nov;15(4):352–358. doi: 10.1111/imj.1966.15.4.352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OFFERIJNS G. J., WESTERINK D., WILLEBRANDS A. F. The relation of potassium deficiency to muscular paralysis by insulin. J Physiol. 1958 May 28;141(3):377–384. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Ohtsuki I. Mechanism of muscular paralysis by insulin with particular reference to familial periodic paralysis. Nature. 1965 Jul 17;207(994):300–301. doi: 10.1038/207300a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otsuka M., Otsuki I. Mechanism of muscular paralysis by insulin with special reference to periodic paralysis. Am J Physiol. 1970 Nov;219(5):1178–1182. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.219.5.1178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEARSON C. M. THE PERIODIC PARALYSES: DIFFERENTIAL FEATURES AND PATHOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS IN PERMANENT MYOPATHIC WEAKNESS. Brain. 1964 Jun;87:341–354. doi: 10.1093/brain/87.2.341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen H., Goodman D. B. Relationships between calcium and cyclic nucleotides in cell activation. Physiol Rev. 1977 Jul;57(3):421–509. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1977.57.3.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riecker G., Bolte H. D. Membranpotentiale einzelner Skeletmuskelzellen bei hypokaliämischer periodischer Muskelparalyse. Klin Wochenschr. 1966 Jul 15;44(14):804–807. doi: 10.1007/BF01711496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. W., Kim N. D., Harrison C. E., Jr Contractility and subcellular calcium metabolism in chronic potassium deficiency. Am J Physiol. 1974 Apr;226(4):756–763. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.4.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandow A. Excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Pharmacol Rev. 1965 Sep;17(3):265–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schudt C., Gaertner U., Pette D. Insulin action on glucose transport and calcium fluxes in developing muscle cells in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Sep;68(1):103–111. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanfield P. R. The effect of zinc ions on the gating of the delayed potassium conductance of frog sartorius muscle. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;251(3):711–735. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Der Kloot W. G. Potassium-stimulated respiration and intra-cellular calcium releae in from skeletal muscle. J Physiol. 1967 Jul;191(1):141–165. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wool I. G. Relation of effects of insulin on amino acid transport and on protein synthesis. Fed Proc. 1965 Sep-Oct;24(5):1060–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIERLER K. L. Effect of insulin on potassium efflux from rat muscle in the presence and absence of glucose. Am J Physiol. 1960 May;198:1066–1070. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.5.1066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIERLER K. L. Hyperpolarization of muscle by insulin in a glucose-free environment. Am J Physiol. 1959 Sep;197:524–526. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.197.3.524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZIERLER K. L. Increase in resting membrane potential of skeletal muscle produced by insulin. Science. 1957 Nov 22;126(3282):1067–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.126.3282.1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zierler K. L., Rogus E., Hazlewood C. F. Effect of insulin on potassium flux and water and electrolyte content of muscles from normal and from hypophysectomized rats. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Jan;49(3):433–456. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.3.433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


