Abstract
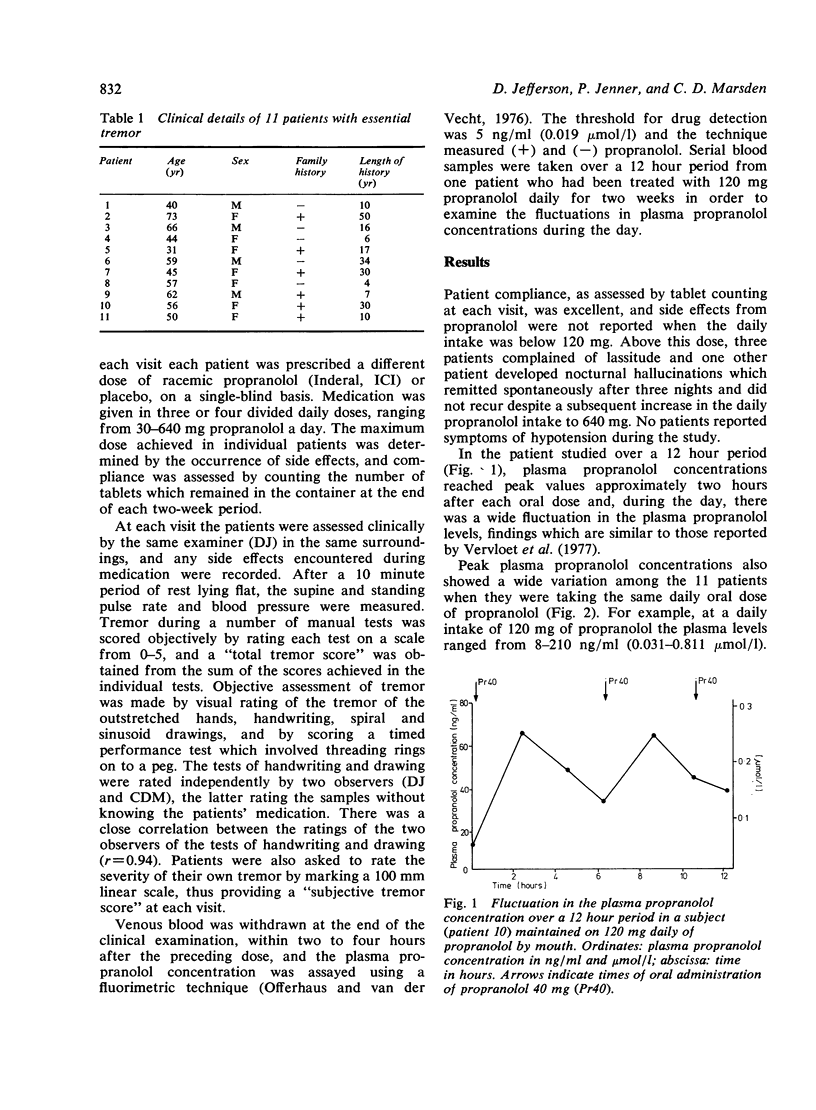
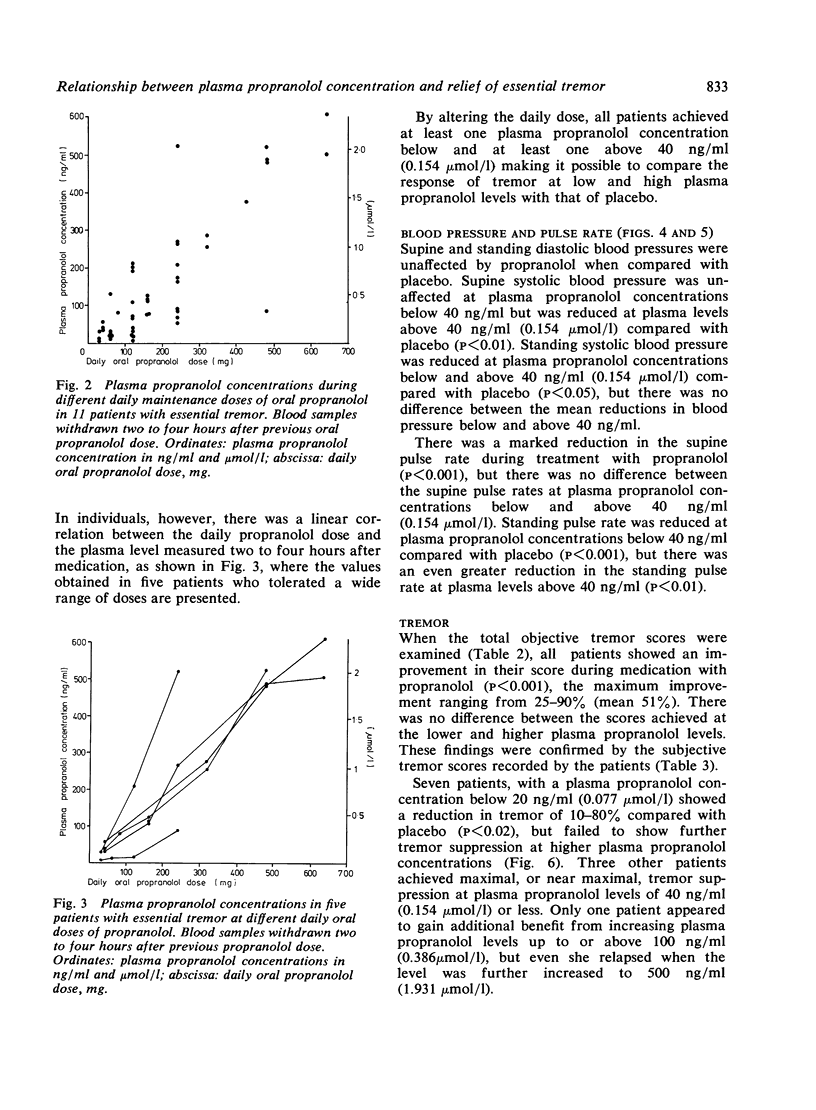
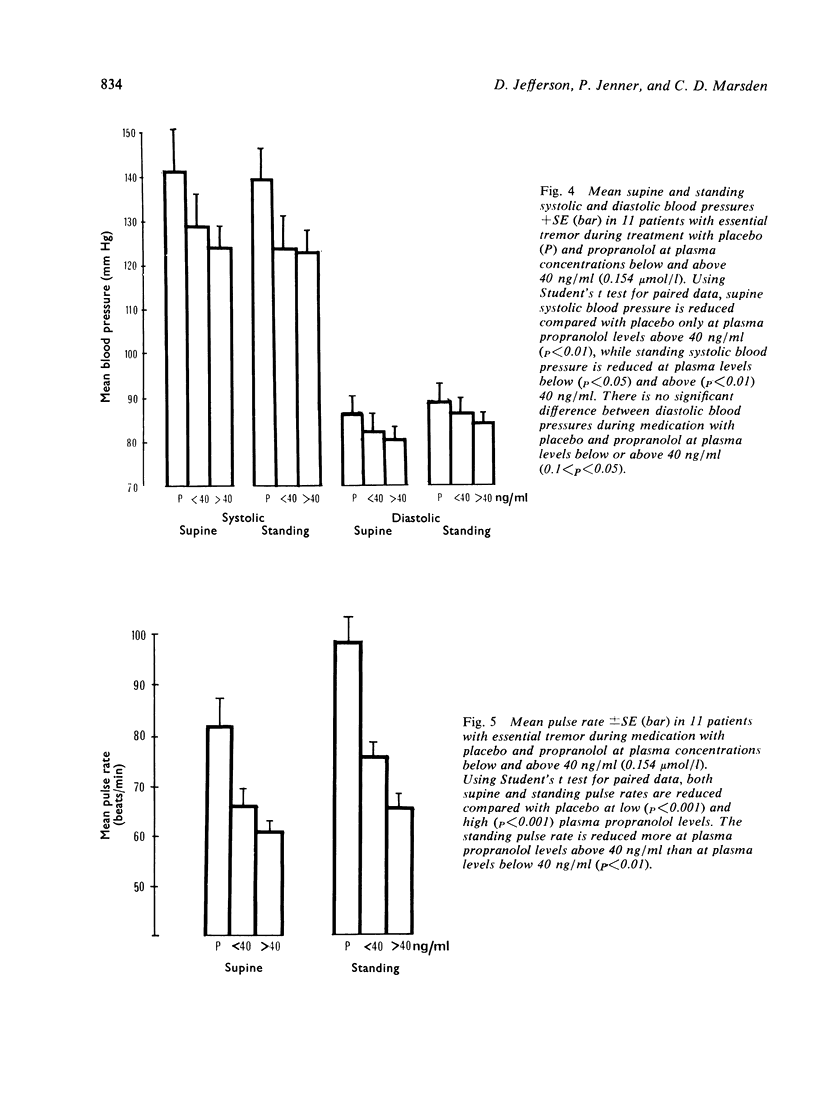
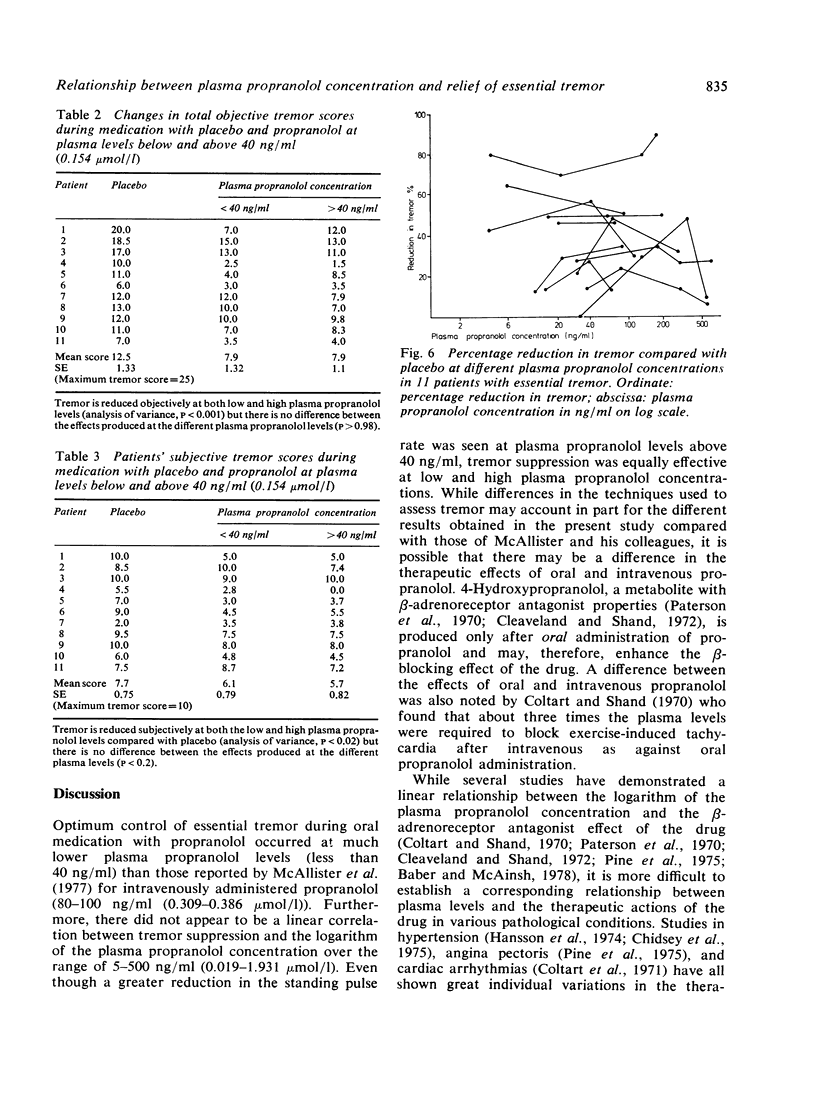
The relationship between plasma propranolol concentration and relief of essential tremor was examined in 11 patients during treatment with oral racemic propranolol in doses of 30 to 640 mg/day. Although propranolol decreased tremor in all 11 patients, the degree of improvement varied widely in individuals (mean 51%, range 25--90%), and was not related directly occurred at plasma propranolol concentrations below 20 ng/ml (0.077 mumol/l) and, in three others, below 40 ng/ml (0.154 mumol/l). It is concluded that the optimum response of essential tremor to propranolol is achieved at relatively low plasma propranolol levels, levels which are obtained by daily propranolol doses of 120--240 mg.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chidsey C. A., Morselli P., Bianchetti G., Morganti A., Leonetti G., Zanchetti A. Studies of the absorption and removal of propranolol in hypertensive patients during therapy. Circulation. 1975 Aug;52(2):313–318. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.52.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaveland C. R., Shand D. G. Effect of route of administration on the relationship between -adrenergic blockade and plasma propranolol level. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1972 Mar-Apr;13(2):181–185. doi: 10.1002/cpt1972132181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coltart D. J., Gibson D. G., Shand D. G. Plasma propranolol levels associated with suppression of ventricular ectopic beats. Br Med J. 1971 Feb 27;1(5747):490–491. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5747.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coltart D. J., Shand D. G. Plasma propranolol levels in the quaniitative assessment of beta-adrenergic blockade in man. Br Med J. 1970 Sep 26;3(5725):731–734. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5725.731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies R., Pickering T. G., Morganti A., Bianchetti G., Morselli P. L., Romankiewicz J., Laragh J. H. Beta-blockade and blood-levels after low-dose oral propranolol: The hepatic "first-pass" threshold revisited. Lancet. 1978 Feb 25;1(8061):407–410. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)91201-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupont E., Hansen H. J., Dalby M. A. Treatment of benign essential tremor with propranolol. A controlled clinical trial. Acta Neurol Scand. 1973;49(1):75–84. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1973.tb01280.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J. B., Longley BP Stewart-Wyn Propranolol in essential tremor. Lancet. 1973 Jun 23;1(7817):1455–1455. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)91795-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Growdon J. H., Shahani B. T., Young R. R. The effect of alcohol on essential tremor. Neurology. 1975 Mar;25(3):259–262. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.3.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jefferson D., Jenner P., Marsden C. D. Relationship between plasma propranolol levels and the clinical suppression of essential tremor [proceedings]. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Apr;7(4):419P–420P. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1979.tb00964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonetti G., Mayer G., Morganti A., Terzoli L., Zanchetti A., Bianchetti G., Di Salle E., Morselli P. L., Chidsey C. A. Hypotensive and renin-suppressing activities of propranolol in hypertensive patients. Clin Sci Mol Med Suppl. 1975 Jun;48(6):491–499. doi: 10.1042/cs0480491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Foley T. H., Owen D. A., McAllister R. G. Peripheral beta-adrenergic receptors concerned with tremor. Clin Sci. 1967 Aug;33(1):53–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden C. D., Meadows J. C. The effect of adrenaline on the contraction of human muscle. J Physiol. 1970 Apr;207(2):429–448. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister R. G., Jr, Markesbery W. R., Ware R. W., Howell S. M. Suppression of essential tremor by propranolol: correlation of effect with drug plasma levels and intensity of beta-adrenergic blockade. Ann Neurol. 1977 Feb;1(2):160–166. doi: 10.1002/ana.410010210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M. H., Hewer R. L., Cooper R. Effect of the beta adrenergic blocking agent propranolol on essential tremor. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973 Aug;36(4):618–624. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.36.4.618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nies A. S., Shand D. G. Clinical pharmacology of propranolol. Circulation. 1975 Jul;52(1):6–15. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.52.1.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine M., Favrot L., Smith S., McDonald K., Chidsey C. A. Correlation of plasma propranolol concentration with therapeutic response in patients with angina pectoris. Circulation. 1975 Nov;52(5):886–893. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.52.5.886. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tolosa E. S., Loewenson R. B. Essential tremor: treatment with propranolol. Neurology. 1975 Nov;25(11):1041–1044. doi: 10.1212/wnl.25.11.1041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vervloet E., Pluym B. F., Cilissen J., Köhlen K., Merkus F. W. Propranolol serum levels during twenty-four hours. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Dec;22(6):853–857. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977226853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler G. F., Young R. R. Efficacy of chronic propranolol therapy in action tremors of the familial, senile or essential varieties. N Engl J Med. 1974 May 2;290(18):984–988. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197405022901802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler G. F., Young R. R. The control of essential tremor by propranolol. Trans Am Neurol Assoc. 1971;96:66–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. R., Growdon J. H., Shahani B. T. Beta-adrenergic mechanisms in action tremor. N Engl J Med. 1975 Nov 6;293(19):950–953. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197511062931902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


