Full text
PDF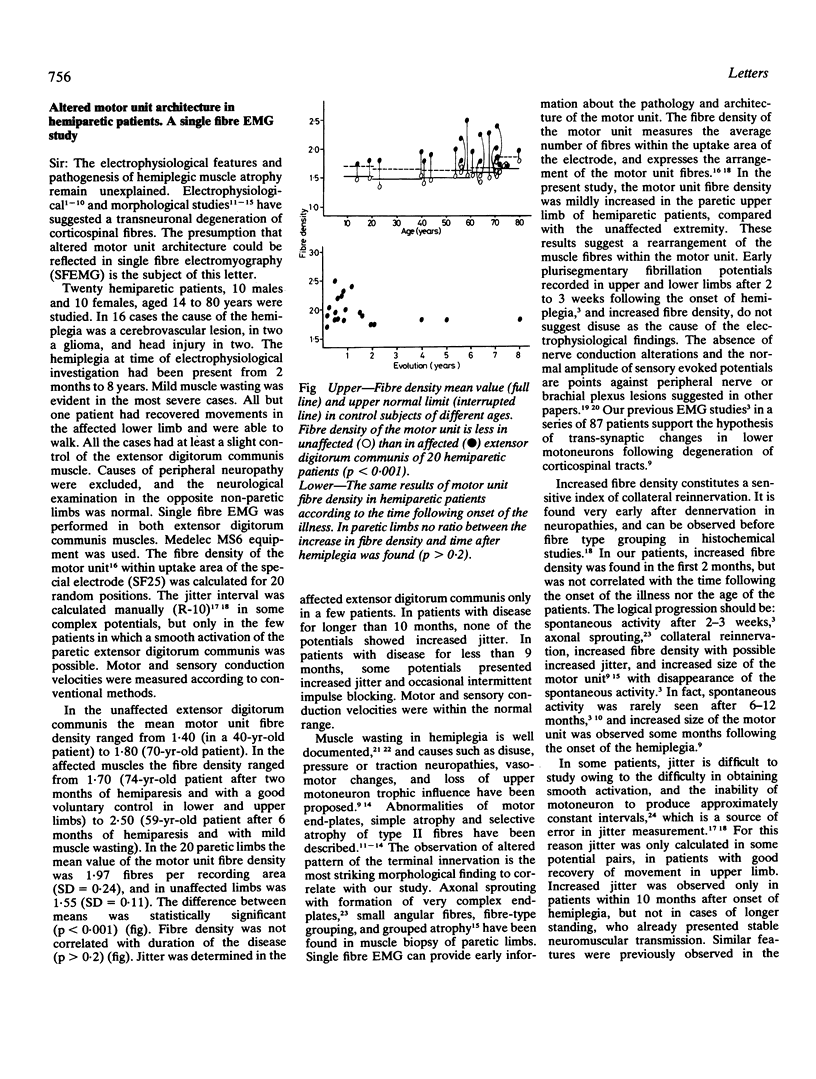

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chokroverty S., Medina J. Electrophysiological study of hemiplegia. Motor nerve conduction velocity, brachial plexus latency, and electromyography. Arch Neurol. 1978 Jun;35(6):360–363. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1978.00500300034005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chokroverty S., Reyes M. G., Rubino F. A., Barron K. D. Hemiplegic amyotrophy. Muscle and motor point biopsy study. Arch Neurol. 1976 Feb;33(2):104–110. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1976.00500020032006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowley L. H., Cress R. H., Fleming W. C. Motor nerve conduction velocity studies on lower extremities of hemiplegics. South Med J. 1967 Dec;60(12):1324–1327. doi: 10.1097/00007611-196712000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström L. Selective changes in the sizes of red and white muscle fibres in upper motor lesions and Parkinsonism. J Neurol Sci. 1970 Dec;11(6):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(70)90104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekstedt J., Nilsson G., Stalberg E. Calculation of the electromyographic jitter. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1974 May;37(5):526–539. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.37.5.526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENICHEL G. M., DAROFF R. B., GLASER G. H. HEMIPLEGIC ATROPHY: HISTOLOGICAL AND ETIOLOGIC CONSIDERATIONS. Neurology. 1964 Oct;14:883–890. doi: 10.1212/wnl.14.10.883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSKOWITZ E., PORTER J. I. PERIPHERAL NERVE LESIONS IN THE UPPER EXTREMITY IN HEMIPLEGIC PATIENTS. N Engl J Med. 1963 Oct 10;269:776–778. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196310102691503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McComas A. J., Sica R. E., Upton A. R., Aguilera N. Functional changes in motoneurones of hemiparetic patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1973 Apr;36(2):183–193. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.36.2.183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba T., Schuman M. H., Grob D. Conduction velocity in the ulnar nerve in hemiplegic patients. J Neurol Sci. 1971 Feb;12(2):177–186. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(71)90048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PANIN N., PAUL B. J., POLICOFF L. D. NERVE CONDUCTION VELOCITIES IN HEMIPLEGIA: PRELIMINARY REPORT. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1965 Jul;46:467–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERSTEIN A. Diagnostic localizing value of muscle atrophy in parietal lobe lesions. Neurology. 1955 Jan;5(1):30–55. doi: 10.1212/wnl.5.1.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segura R. P., Sahgal V. Hemiplegic atrophy: electrophysiological and morphological studies. Muscle Nerve. 1981 May-Jun;4(3):246–248. doi: 10.1002/mus.880040312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålberg E., Schwartz M. S., Trontelj J. V. Single fibre electromyography in various processes affecting the anterior horn cell. J Neurol Sci. 1975 Apr;24(4):403–415. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(75)90166-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stålberg E., Thiele B. Motor unit fibre density in the extensor digitorum communis muscle. Single fibre electromyographic study in normal subjects at different ages. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1975 Sep;38(9):874–880. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.38.9.874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widener T., Cochran T., Fleming W. C., Cress R. H. Studies on velocity of nerve conduction in hemiplegics. South Med J. 1967 Nov;60(11):1194–1196. doi: 10.1097/00007611-196711000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


