Abstract
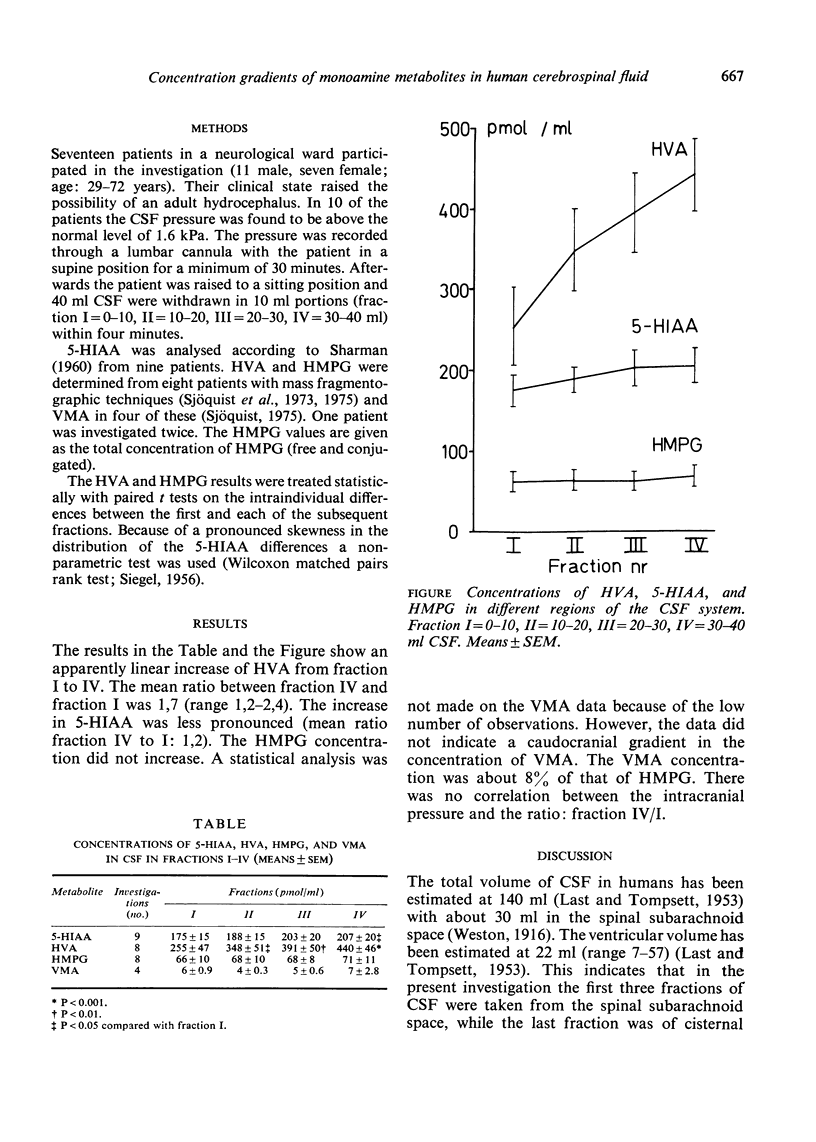
The monamine metabolites 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), homovanillic acid (HVA), vanillylmandelic acid (VMA), and 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylglycol (HMPG) were analysed in CSF from different regions of the CSF system to study the caudocranial concentration gradient of the metabolites. Four consecutive 10 ml fractions of CSF were withdrawn in 17 patients during the course of four minutes. The CSF pressure was monitored through a lumbar cannula because of suspected adult hydrocephalus. A pronounced gradient of the HVA concentration was found with a ratio between the last and the first fraction of 1,7. 5-HIAA showed a slight increase while HMPG and VMA showed no increase at higher levels of the CSF system. The results suggest that lumbar HVA reflects dopaminergic activity in the brain, whereas lumbar 5-HIAA and HMPG/VMA reflect the activity of 5-hydroxytryptamine and noradrenaline secreting neurones in both the brain and the spinal cord.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aquilonius S. M., Sjöström R. Cholinergic and dopaminergic mechanisms in Huntington's chorea. Life Sci I. 1971 Apr 1;10(7):405–414. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(71)90146-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulat M., Zivković B. Origin of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in the spinl fluid. Science. 1971 Aug 20;173(3998):738–740. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3998.738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guldberg H. C., Ashcroft G. W., Crawford T. B. Concentrations of 5-hydroxyindolylacetic acid and homovanillic acid in the cerebrospinal fluid of the dog before and during treatment with probenecid. Life Sci. 1966 Sep;5(17):1571–1575. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(66)91026-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B., Roos B. E. 5-hydroxyindoleacetic and homovanillic acid levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of healthy volunteers and patients with Parkinson's syndrome. Life Sci. 1967 Jul 1;6(13):1449–1454. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90193-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAST R. J., TOMPSETT D. H. Casts of the cerebral ventricles. Br J Surg. 1953 May;40(164):525–543. doi: 10.1002/bjs.18004016403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moir A. T., Ashcroft G. W., Crawford T. B., Eccleston D., Guldberg H. C. Cerebral metabolites in cerebrospinal fluid as a biochemical approach to the brain. Brain. 1970;93(2):357–368. doi: 10.1093/brain/93.2.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöquist B., Lindström B., Anggård E. Mass fragmentographic determination of 4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenylglycol (HMPG) in urine, cerebrospinal fluid, plasma and tissues using a deuterium-labelled internal standard. J Chromatogr. 1975 Feb 26;105(2):309–316. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)82259-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöquist B., Lindström B., Anggård E. Mass fragmentographic determination of homovanillic acid in tissues and body fluids using the deuterium labeled species as internal standard. Life Sci. 1973 Dec 16;13(12):1655–1664. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(73)90113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöquist B. Mass fragmentographic determination of 4-hydroxy-3-methoxymandelic acid in human urine, cerebrospinal fluid, brain and serum using a deuterium-labelled internal standard. J Neurochem. 1975 Jan;24(1):199–201. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb07652.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjöström R., Roos B. E. 5-Hydroxyindolacetic acid and homovanillic acid in cerebrospinal fluid in manic-depressive psychosis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1972 Jun;4(3):170–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00561141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sourkes T. L. On the origin of homovanillic acid (HVA) in the cerebrospinal fluid. J Neural Transm. 1973;34(2):153–157. doi: 10.1007/BF01244668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weir R. L., Chase T. N., Ng L. K., Kopin I. J. 5-hydroxyindoleacetic cid in spinal fluid: relative contribution from brain and spinal cord. Brain Res. 1973 Mar 30;52:409–412. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(73)90682-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



