Abstract
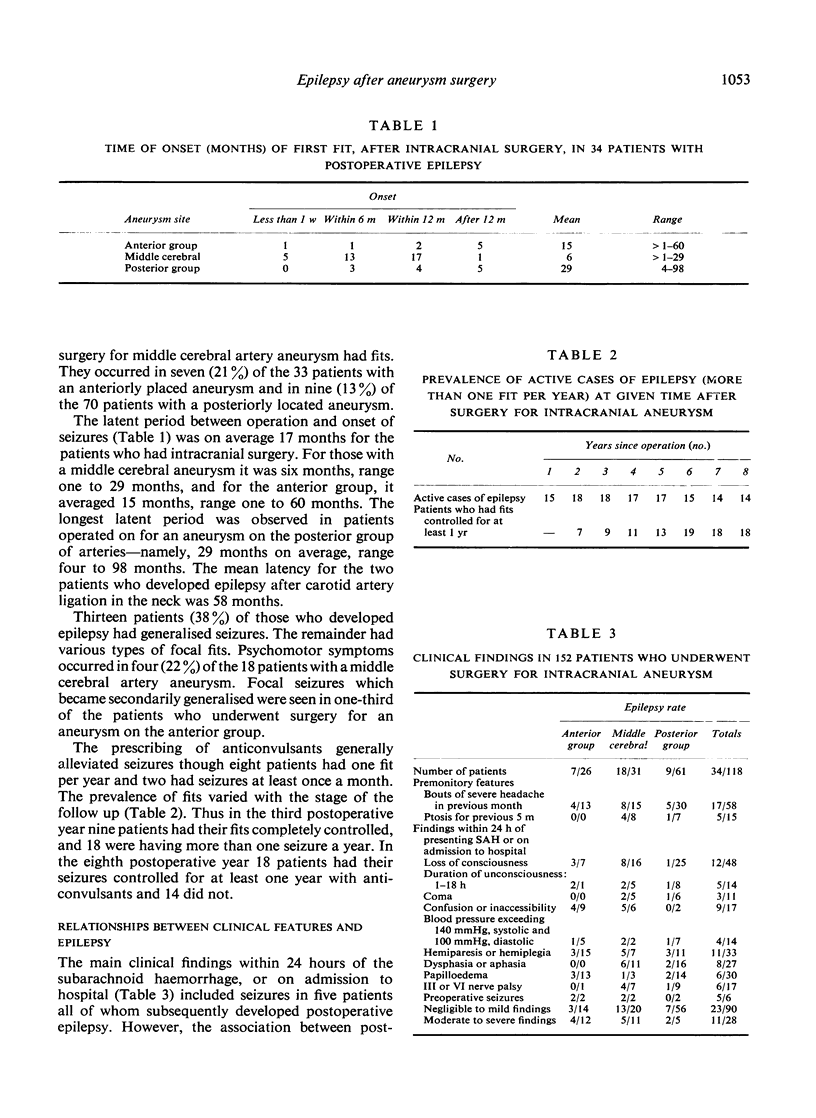
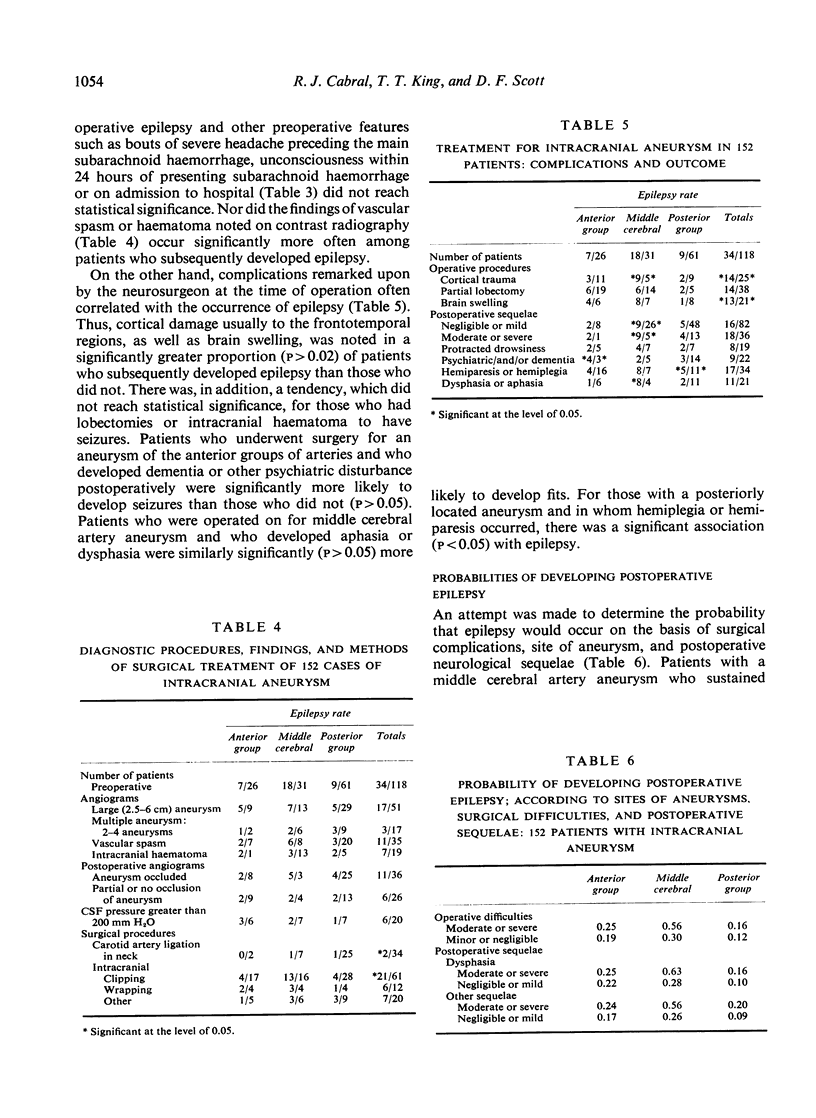
One-hundred-and-fifty-two patients who underwent surgery for intracranial aneurysm were studied to determine the incidence of postoperative epilepsy in relation to the site of the aneurysm and the type of surgical approach. The overall incidence of epilepsy was 22%. Of the 116 patients treated by the intracranial approach 27.5% developed epilepsy, in contrast with only 5% of the 36 patients who had carotid artery ligation in the neck. Epilepsy occurred most frequently (35%) with middle cerebral artery aneurysms, especially if moderate or severe operative trauma was sustained and there was postoperative dysphasia.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cabral R., King T. T., Scott D. F. Incidence of postoperative epilepsy after a transtentorial approach to acoustic nerve tumours. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1976 Jul;39(7):663–665. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.39.7.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN W. Lobotomy and epilepsy; a study of 1000 patients. Neurology. 1953 Jul;3(7):479–494. doi: 10.1212/wnl.3.7.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt W. E., Hess R. M. Surgical risk as related to time of intervention in the repair of intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 1968 Jan;28(1):14–20. doi: 10.3171/jns.1968.28.1.0014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legg N. J., Gupta P. C., Scott D. F. Epilepsy following cerebral abscess. A clinical and EEG study of 70 patients. Brain. 1973 Jun;96(2):259–268. doi: 10.1093/brain/96.2.259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSE F. C., SARNER M. EPILEPSY AFTER RUPTURED INTRACRANIAL ANEURYSM. Br Med J. 1965 Jan 2;1(5426):18–21. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL W. R., WHITTY C. W. Studies in traumatic epilepsy. I. Factors influencing the incidence of epilepsy after brain wounds. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1952 May;15(2):93–98. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.15.2.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storey P. B. Psychiatric sequelae of subarachnoid haemorrhage. Br Med J. 1967 Jul 29;3(5560):261–266. doi: 10.1136/bmj.3.5560.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


