Abstract
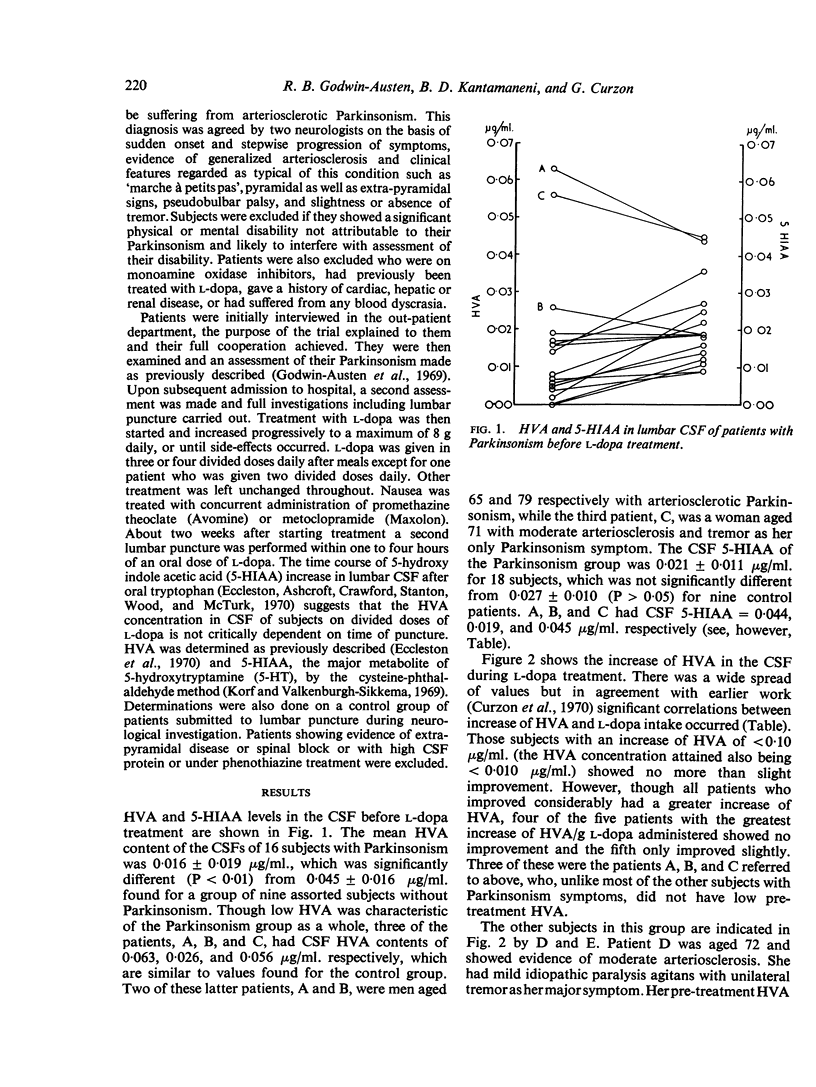
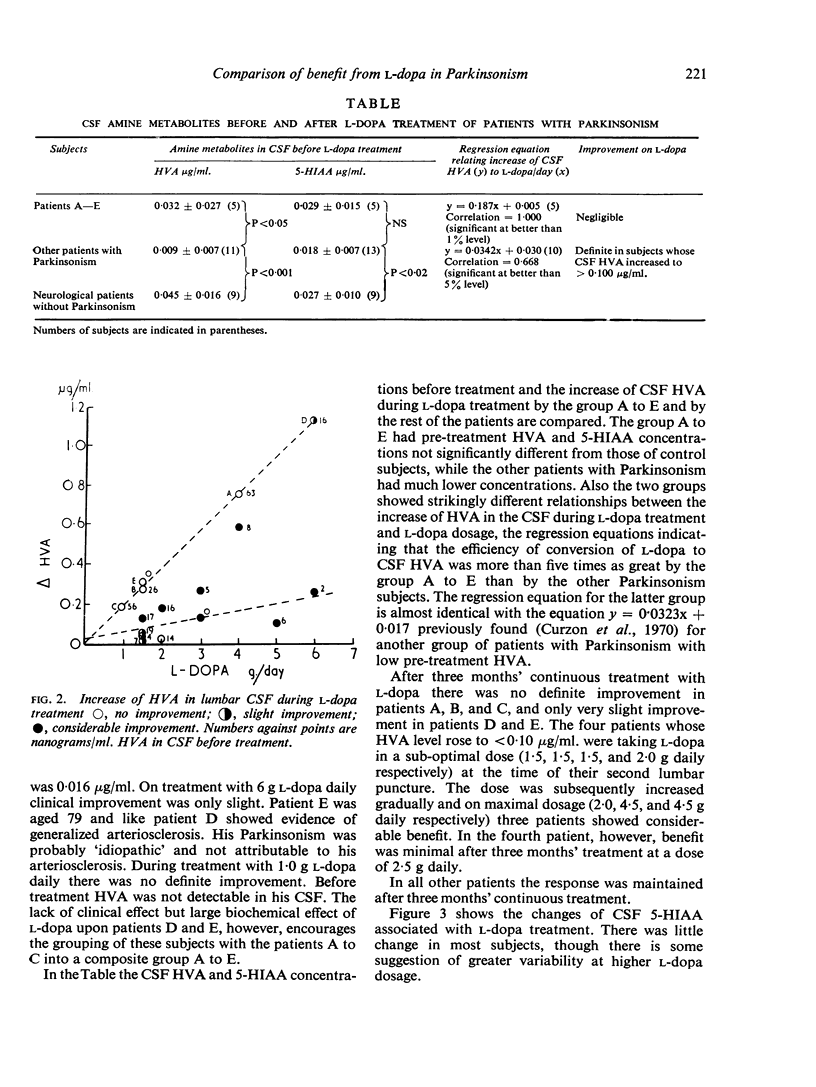
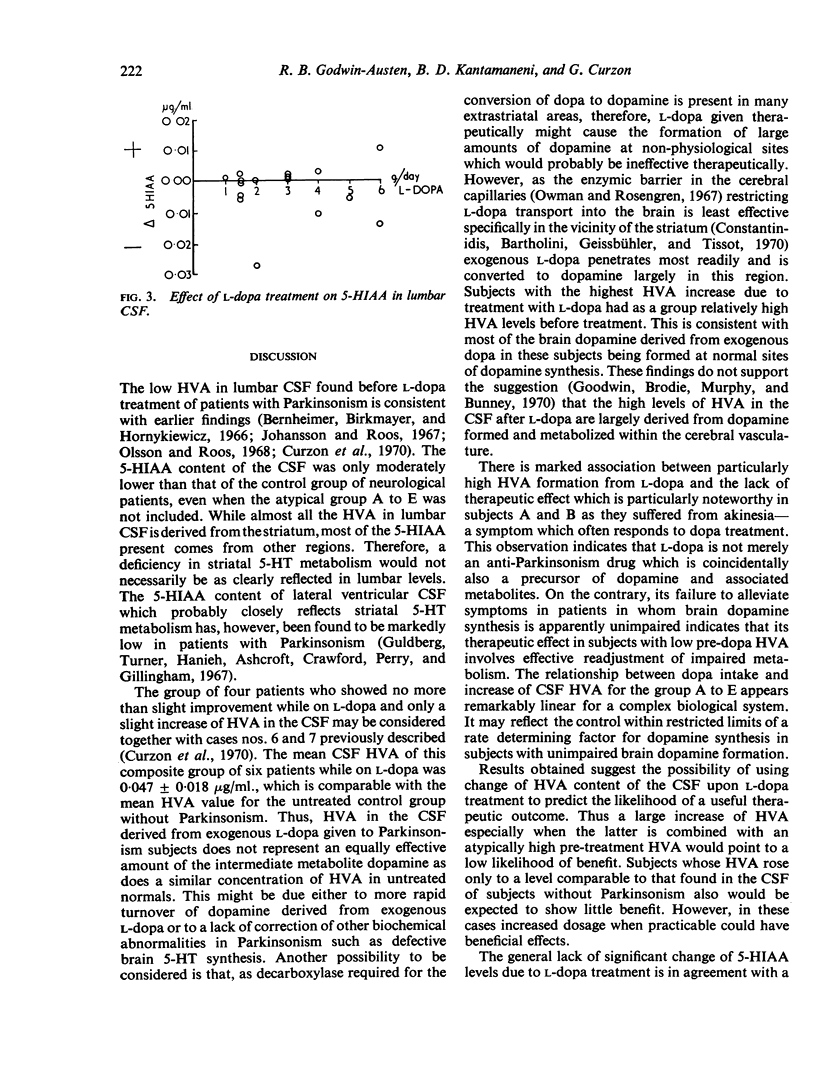
Homovanillic acid (HVA) and 5-hydroxy indole acetic acid (5-HIAA) concentrations have been estimated in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of 16 and 18 patients respectively with Parkinsonism both before and during treatment with l-dopa. The rise of HVA correlated with dose of l-dopa. An increase of HVA concentration to less than 0·10 μg/ml. was associated with little or no clinical improvement. The five patients with the greatest increase of HVA concentration/g l-dopa showed little or no improvement from treatment and four of these patients had normal pre-treatment HVA and 5-HIAA. In those patients who responded well to l-dopa the CSF HVA/g l-dopa was intermediate between that of these two groups. It is suggested that change in HVA content of CSF during l-dopa treatment might be of value in the prediction of response to l-dopa.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernheimer H., Birkmayer W., Hornykiewicz O. Homovanillinsäure im Liquor cerebrospinalis: Untersuchungen beim Parkinson-Syndrom und anderen Erkrankungen des ZNS. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1966 Jun 10;78(23):417–419. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calne D. B., Stern G. M., Spiers A. S., Laurence D. R. L-dopa in idiopathic parkinsonism. Lancet. 1969 Nov 8;2(7628):973–976. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)90536-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constantinidis J., Bartholini G., Geissbühler F., Tissot R. La barrière capillaire enzymatique pour la DOPA au niveau de quelques noyaux du tronc cérébral du rat. Experientia. 1970 Apr 15;26(4):381–383. doi: 10.1007/BF01896900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotzias G. C., Papavasiliou P. S., Gellene R. Modification of Parkinsonism--chronic treatment with L-dopa. N Engl J Med. 1969 Feb 13;280(7):337–345. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196902132800701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon G., Godwin-Austen R. B., Tomlinson E. B., Kantamaneni B. D. The cerebrospinal fluid homovanillic acid concentration in patients with Parkinsonism treated with L-dopa. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Feb;33(1):1–6. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccleston D., Ashcroft G. W., Crawford T. B. Effect of tryptophan administration on 5HIAA in cerebrospinal fluid in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1970 Apr;33(2):269–272. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.33.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godwin-Austen R. B., Tomlinson E. B., Frears C. C., Kok H. W. Effects of L-dopa in Parkinson's disease. Lancet. 1969 Jul 26;2(7613):165–168. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(69)91417-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin F. K., Brodie H. K., Murphy D. L., Bunney W. E., Jr Administration of a peripheral decarboxylase inhibitor with L-dopa to depressed patients. Lancet. 1970 May 2;1(7653):908–911. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)91044-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guldberg H. C., Turner J. W., Hanieh A., Ashcroft G. W., Crawford T. B., Perry W. L., Gillingham F. J. On the occurrence of homovanillic acid and 5-hydroxyindol-3-ylacetic acid in the ventricular C.S.F. of patients suffering from parkinsonism. Confin Neurol. 1967;29(2):73–77. doi: 10.1159/000103680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guldberg H. C., Yates C. M. Some studies of the effects of chlorpromazine, reserpine and dihydroxyphenylalanine on the concentrations of homovanillic acid, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid and 5-hydroxyindol-3-ylacetic acid in ventricular cerebrospinal fluid of the dog using the technique of serial sampling of the cerebrospinal fluid. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jul;33(3):457–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00494.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johansson B., Roos B. E. 5-hydroxyindoleacetic and homovanillic acid levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of healthy volunteers and patients with Parkinson's syndrome. Life Sci. 1967 Jul 1;6(13):1449–1454. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(67)90193-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korf J., Valkenburgh-Sikkema T. Fluorimetric determination of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in human urine and cerebrospinal fluid. Clin Chim Acta. 1969 Nov;26(2):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(69)90383-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mawdsley C. Treatment of Parkinsonism with Laevo-dopa. Br Med J. 1970 Feb 7;1(5692):331–337. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5692.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson R., Roos B. E. Concentrations of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid and homovanillic acid in the cerebrospinal fluid after treatment with probenecid in patients with Parkinson's disease. Nature. 1968 Aug 3;219(5153):502–503. doi: 10.1038/219502a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owman C., Rosengren E. Dopamine formation in brain capillaries--an enzymic blood-brain barrier mechanism. J Neurochem. 1967 May;14(5):547–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1967.tb09553.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peaston M. J., Bianchine J. R. Metabolic studies and clinical observations during L-dopa treatment of Parkinson's disease. Br Med J. 1970 Feb 14;1(5693):400–403. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5693.400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson T., Roos B. E. Clinical and pharmacological effects of monoamine precursors or haloperidol in chronic schizophrenia. Nature. 1968 Mar 2;217(5131):854–854. doi: 10.1038/217854a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner W., Harrison W., Klawans H. L-dopa and cerebrospinal fluid homovanillic acid in Parkinsonism. Life Sci. 1969 Sep 1;8(17):971–976. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(69)90428-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yahr M. D., Duvoisin R. C., Schear M. J., Barrett R. E., Hoehn M. M. Treatment of parkinsonism with levodopa. Arch Neurol. 1969 Oct;21(4):343–354. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480160015001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Woert M. H., Bowers M. B., Jr The effect of L-dopa on monoamine metabolites in Parkinson's disease. Experientia. 1970;26(2):161–163. doi: 10.1007/BF01895555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


