Abstract
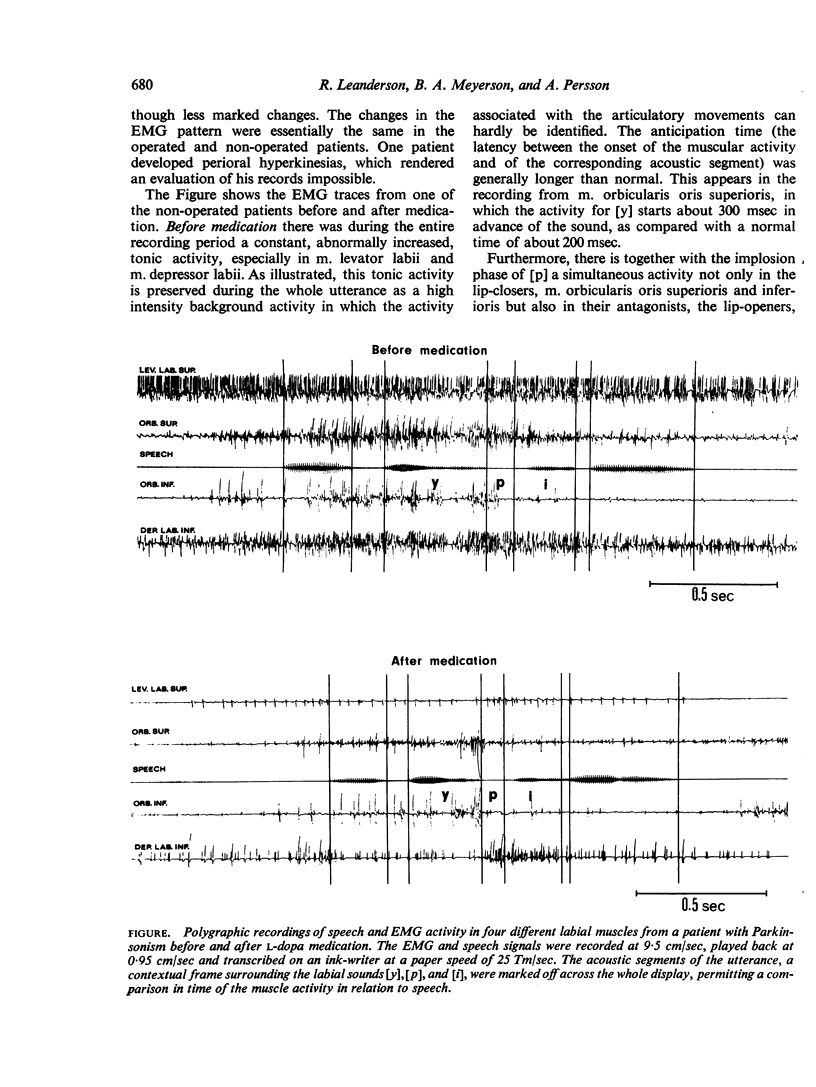
The articulatory function of the labial musculature has been investigated electromyographically before and after treatment with l-dopa in patients with Parkinsonism who had dysarthria. Before medication the EMG traces generally showed a constant, abnormally increased, tonic activity, together with disturbed reciprocal innervation, which impaired the articulatory activity. After medication the tonic hyperactivity was reduced and the reciprocal innervation re-established. This normalization of the EMG articulatory pattern was paralleled by an improvement of the dysarthria.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andén N. E., Carlsson A., Kerstell J., Magnusson T., Olsson R., Roos B. E., Steen B., Steg G., Svanborg A., Thieme G. Oral L-dopa treatment of parkinsonism. Acta Med Scand. 1970 Apr;187(4):247–255. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1970.tb02939.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIRKMAYER W., HORNYKIEWICZ O. [The L-3,4-dioxyphenylalanine (DOPA)-effect in Parkinson-akinesia]. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1961 Nov 10;73:787–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotzias G. C., Papavasiliou P. S., Gellene R. Modification of Parkinsonism--chronic treatment with L-dopa. N Engl J Med. 1969 Feb 13;280(7):337–345. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196902132800701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREWEL F. Dysarthria in post-encephalitic parkinsonism. Acta Psychiatr Neurol Scand. 1957;32(4):440–449. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1957.tb07555.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leanderson R., Persson A., Ohman S. Electromyographic studies of the function of the facial muscles in dysarthria. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl. 1969;263:89–94. doi: 10.3109/00016487009131528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mawdsley C. Treatment of Parkinsonism with Laevo-dopa. Br Med J. 1970 Feb 7;1(5692):331–337. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5692.331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson A., Leanderson R., Ohman S. Electromyographic studies of facial muscle activity in speech. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1969 Sep;27(7):725–725. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(69)91412-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider P. Quantitative Analyse und Mechanismen der Bradykinesie bei Parkinsonpatienten. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd. 1968;194(2):89–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


