Abstract
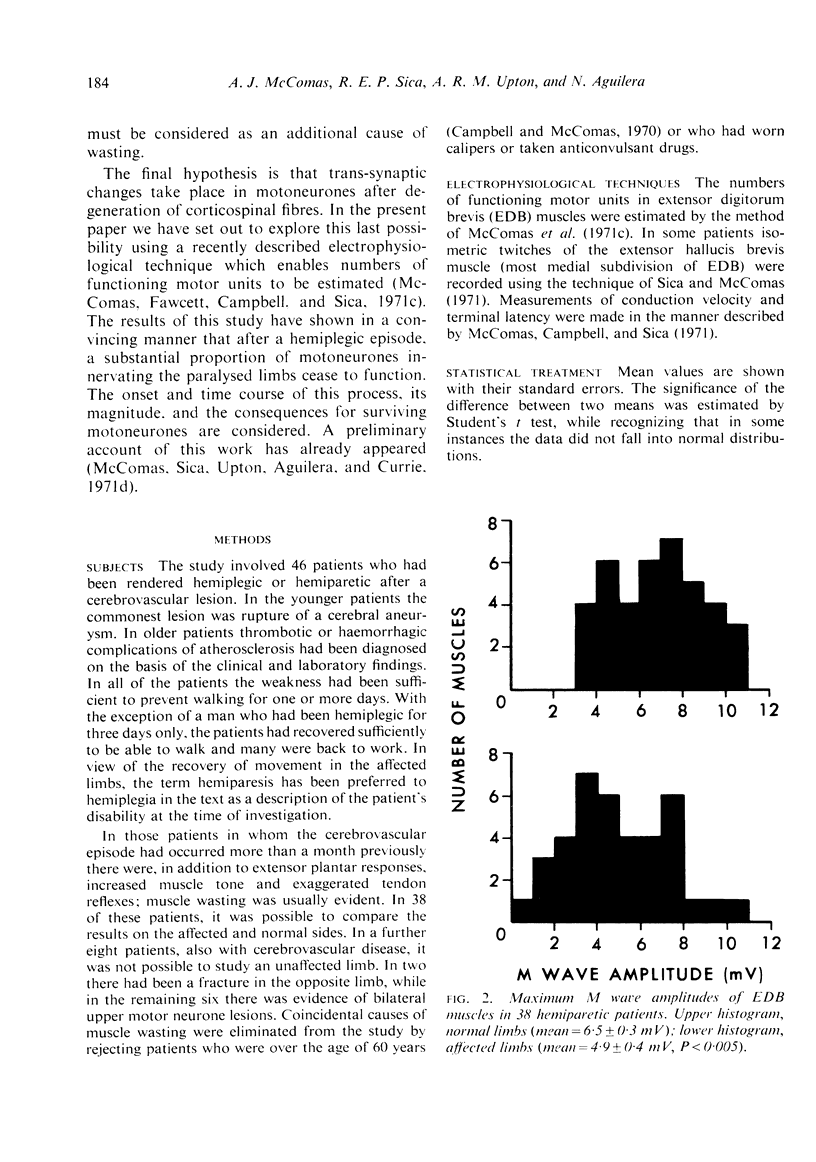
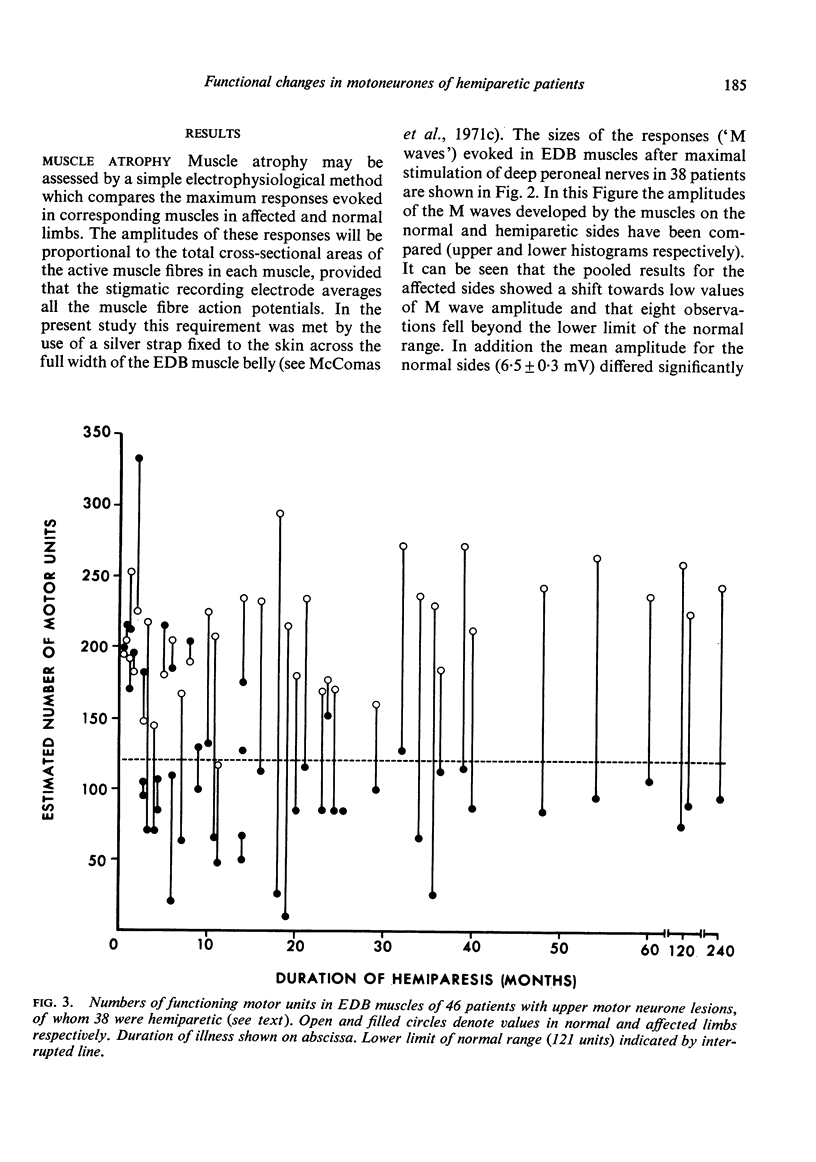
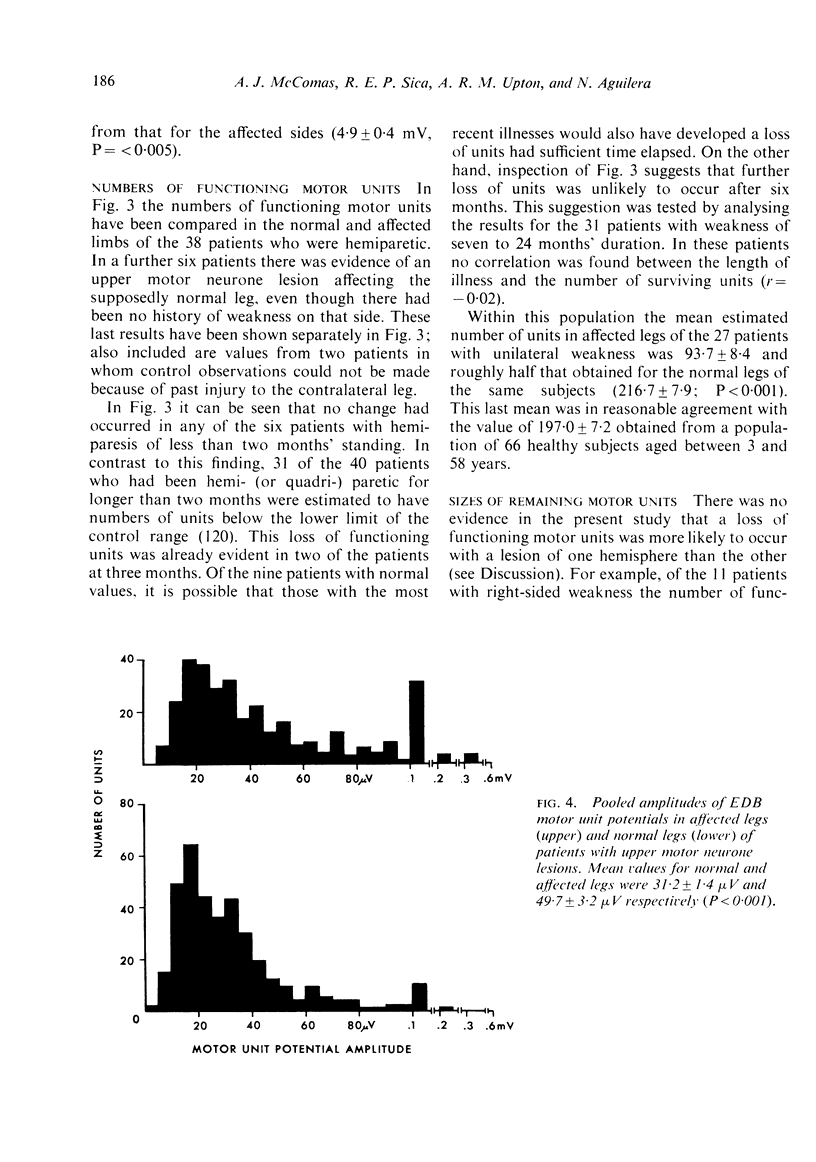
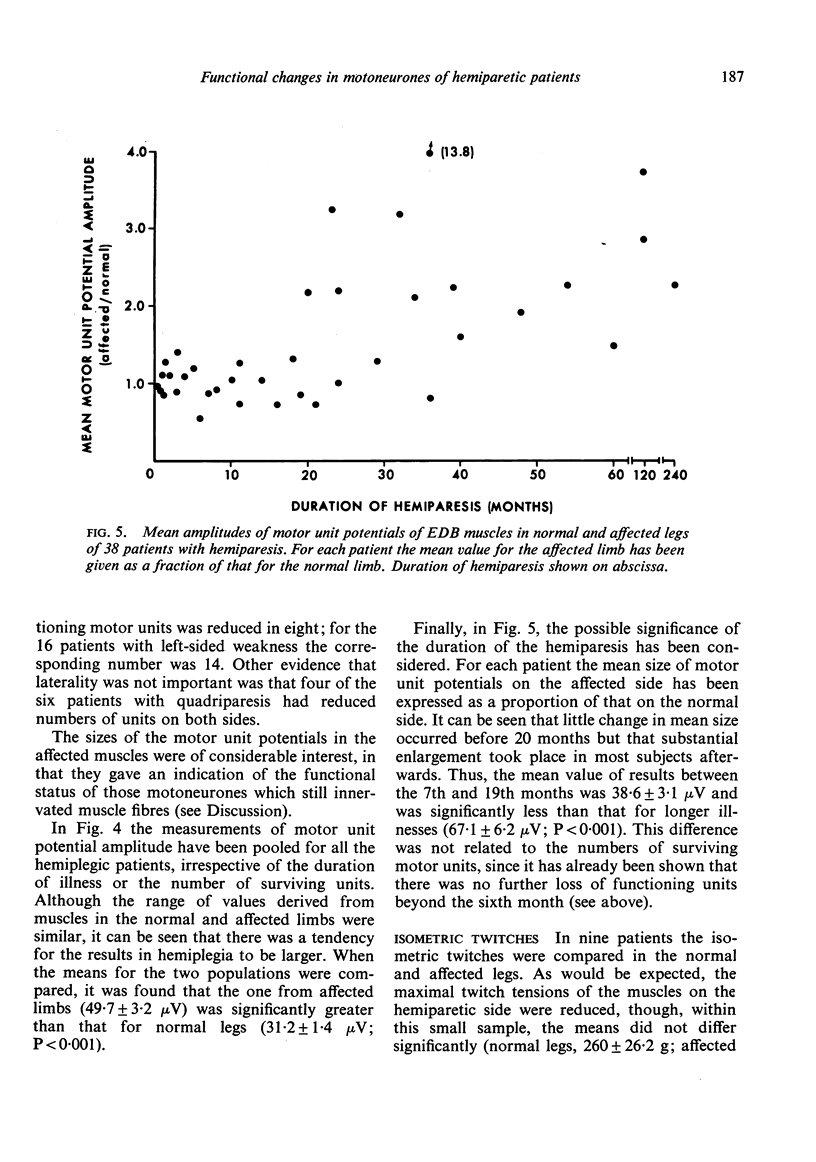
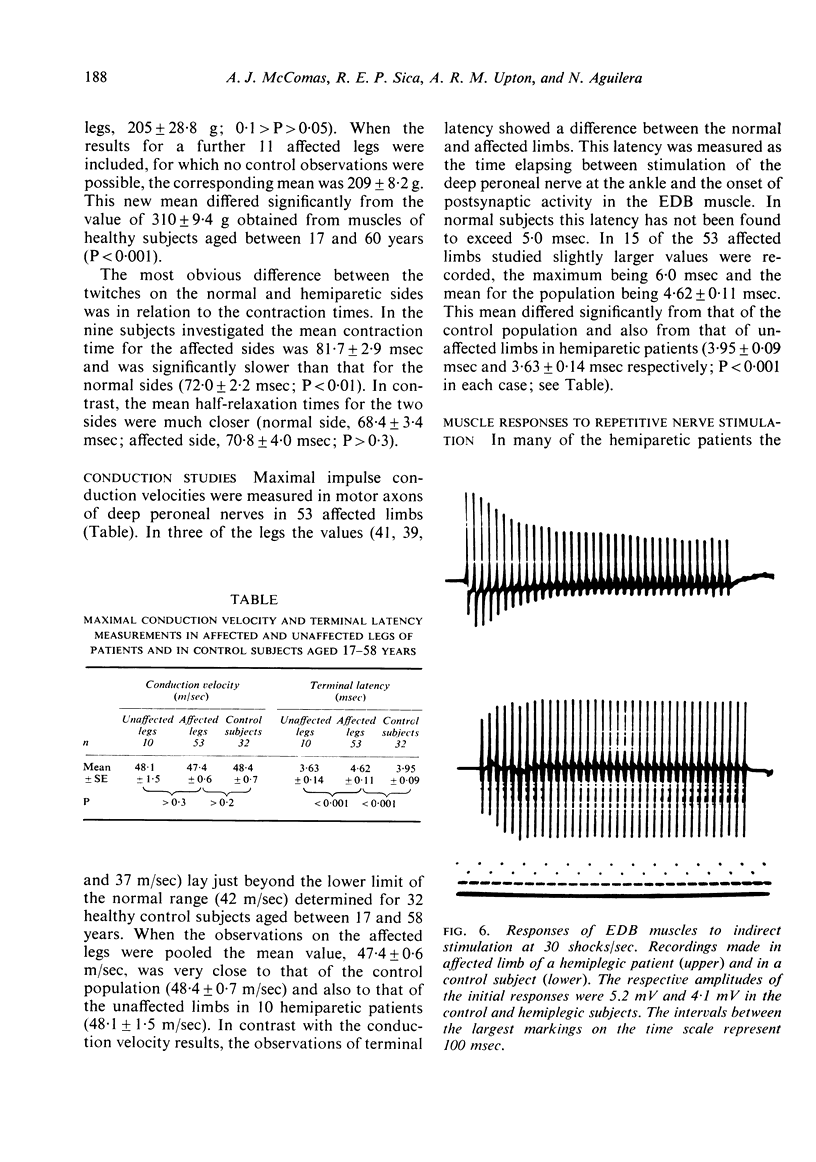
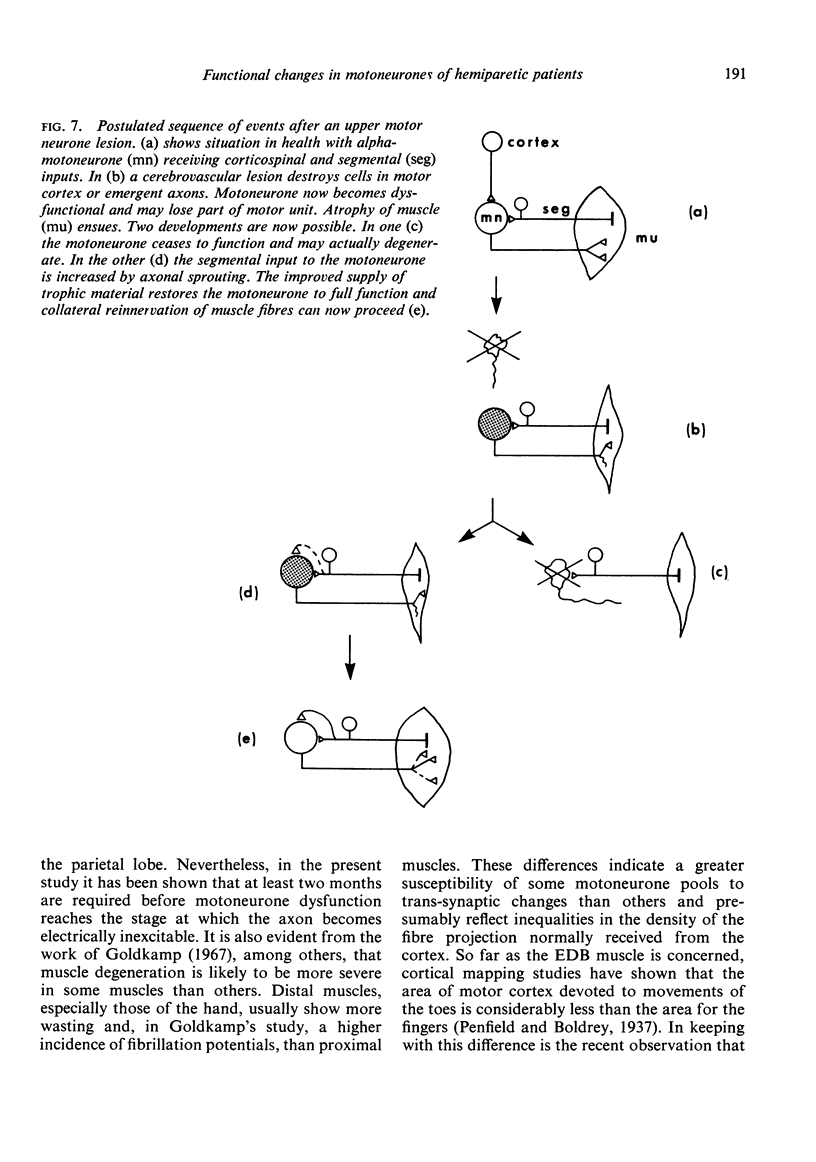
Forty-six patients have been studied after upper motor neurone lesions of cerebrovascular origin. The numbers of functioning motor units in extensor digitorum brevis muscles were reduced to approximately half between the second and sixth months after a hemiplegic episode. The surviving motor units tended to have slow twitches and appeared to increase their sizes after the lesions had been present for about 20 months. The findings are explained on the basis of transsynaptic changes in alpha-motoneurones after degeneration of corticospinal fibres.
Full text
PDF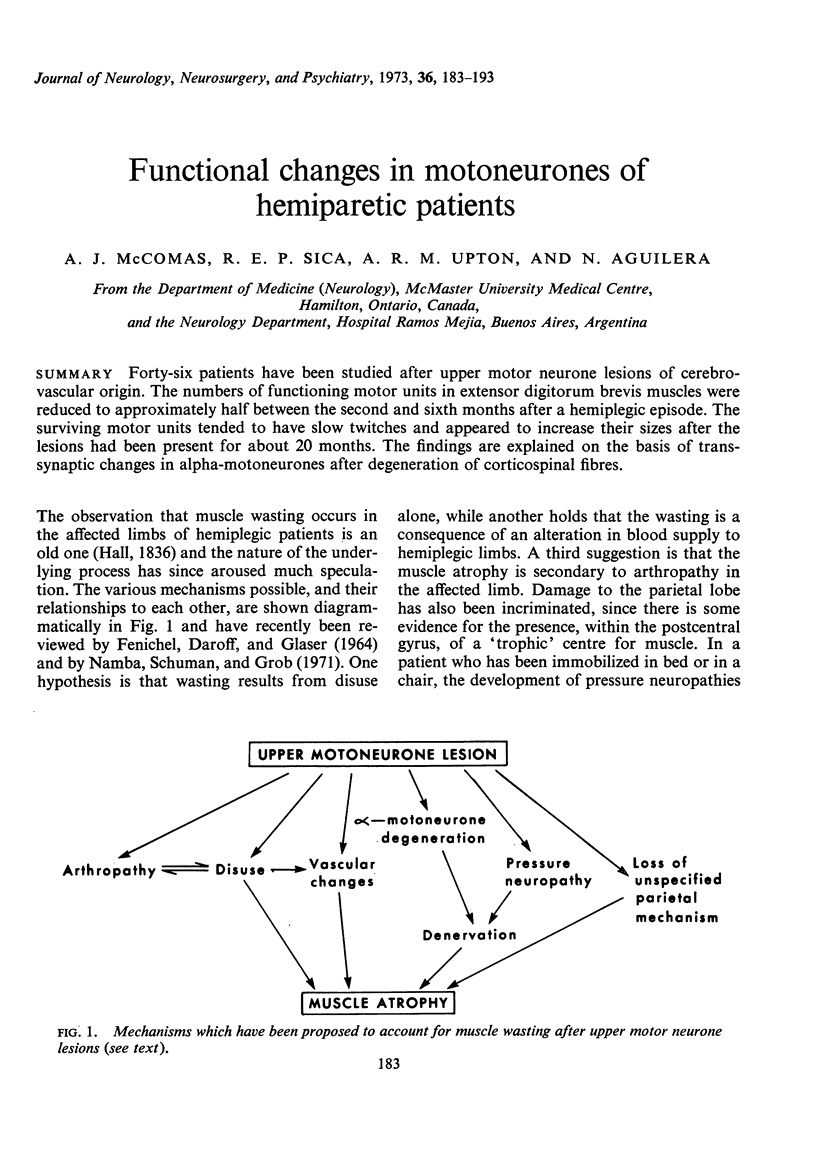




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CAVANAGH J. B. PERIPHERAL NERVE CHANGES IN ORTHO-CRESYL PHOSPHATE POISONING IN THE CAT. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1964 Apr;87:365–383. doi: 10.1002/path.1700870217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOK W. H., WALKER J. H., BARR M. L. A cytological study of transneuronal atrophy in the cat and rabbit. J Comp Neurol. 1951 Apr;94(2):267–291. doi: 10.1002/cne.900940207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENICHEL G. M., DAROFF R. B., GLASER G. H. HEMIPLEGIC ATROPHY: HISTOLOGICAL AND ETIOLOGIC CONSIDERATIONS. Neurology. 1964 Oct;14:883–890. doi: 10.1212/wnl.14.10.883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOLDBY F. A note on transneuronal atrophy in the human lateral geniculate body. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1957 Aug;20(3):202–207. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.20.3.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glees P., le Gros Clark W. E. The termination of optic fibres in the lateral geniculate body of the monkey. J Anat. 1941 Apr;75(Pt 3):295–308.3. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldkamp O. Electromyography and nerve conduction studies in 116 patients with hemiplegia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1967 Feb;48(2):59–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthews M. R., Cowan W. M., Powell T. P. Transneuronal cell degeneration in the lateral geniculate nucleus of the macaque monkey. J Anat. 1960 Apr;94(Pt 2):145–169. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCOUCH G. P., AUSTIN G. M., LIU C. N., LIU C. Y. Sprouting as a cause of spasticity. J Neurophysiol. 1958 May;21(3):205–216. doi: 10.1152/jn.1958.21.3.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McComas A. J., Campbell M. J., Sica R. E. Electrophysiological study of dystrophia myotonica. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Apr;34(2):132–139. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McComas A. J., Sica R. E., Campbell M. J. "Sick" motoneurones. A unifying concept of muscle disease. Lancet. 1971 Feb 13;1(7694):321–326. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(71)91045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McComas A. J., Sica R. E., Upton A. R., Aguilera N., Currie S. Motoneurone dysfunction in patients with hemiplegic atrophy. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 1;233(35):21–23. doi: 10.1038/newbio233021a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Slater C. R. On the degeneration of rat neuromuscular junctions after nerve section. J Physiol. 1970 Apr;207(2):507–528. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba T., Schuman M. H., Grob D. Conduction velocity in the ulnar nerve in hemiplegic patients. J Neurol Sci. 1971 Feb;12(2):177–186. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(71)90048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERSTEIN A. Diagnostic localizing value of muscle atrophy in parietal lobe lesions. Neurology. 1955 Jan;5(1):30–55. doi: 10.1212/wnl.5.1.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sica R. E., McComas A. J. Fast and slow twitch units in a human muscle. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Apr;34(2):113–120. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.2.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton A. R., McComas A. J., Sica R. E. Potentiation of "late" responses evoked in muscles during effort. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1971 Dec;34(6):699–711. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.34.6.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young I. J. Morphological and histochemical studies of partially and totally deafferented spinal cord segments. Exp Neurol. 1966 Feb;14(2):238–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(66)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



