Abstract
BACKGROUND
Esophageal variceal bleeding is a severe complication associated with liver cirrhosis and typically necessitates endoscopic hemostasis. The current standard treatment is endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL), and Western guidelines recommend antibiotic prophylaxis following hemostasis. However, given the improvements in prognosis for variceal bleeding due to advancements in the management of bleeding and treatments of liver cirrhosis and the global concerns regarding the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria, there is a need to reassess the use of routine antibiotic prophylaxis after hemostasis.
AIM
To evaluate the effectiveness of antibiotic prophylaxis in patients treated for EVL.
METHODS
We conducted a 13-year observational study using the Tokushukai medical database across 46 hospitals. Patients were divided into the prophylaxis group (received antibiotics on admission or the next day) and the non-prophylaxis group (did not receive antibiotics within one day of admission). The primary outcome was composed of 6-wk mortality, 4-wk rebleeding, and 4-wk spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP). The secondary outcomes were each individual result and in-hospital mortality. A logistic regression with inverse probability of treatment weighting was used. A subgroup analysis was conducted based on the Child-Pugh classification to determine its influence on the primary outcome measures, while sensitivity analyses for antibiotic type and duration were also performed.
RESULTS
Among 980 patients, 790 were included (prophylaxis: 232, non-prophylaxis: 558). Most patients were males under the age of 65 years with a median Child-Pugh score of 8. The composite primary outcomes occurred in 11.2% of patients in the prophylaxis group and 9.5% in the non-prophylaxis group. No significant differences in outcomes were observed between the groups (adjusted odds ratio, 1.11; 95% confidence interval, 0.61-1.99; P = 0.74). Individual outcomes such as 6-wk mortality, 4-wk rebleeding, 4-wk onset of SBP, and in-hospital mortality were not significantly different between the groups. The primary outcome did not differ between the Child-Pugh subgroups. Similar results were observed in the sensitivity analyses.
CONCLUSION
No significant benefit to antibiotic prophylaxis for esophageal variceal bleeding treated with EVL was detected in this study. Global reassessment of routine antibiotic prophylaxis is imperative.
Keywords: Esophageal varices, Endoscopic hemostasis, Antibiotic prophylaxis, Liver cirrhosis, Inverse probability of treatment weighting
Core Tip: Esophageal variceal bleeding, a serious condition linked to liver cirrhosis, often requires endoscopic treatment. While western guidelines suggest using antibiotics after endoscopic treatment, data from multiple Japanese medical centers indicates that these prophylactic antibiotics are not associated with 6-wk mortality. Based on advances in cirrhosis treatment and the appropriate use of antibiotics, the necessity of routine prophylaxis must be reassessed.
INTRODUCTION
Esophageal variceal bleeding is a life-threatening complication in patients with liver cirrhosis[1], and endoscopic hemostasis is recommended as the first line of treatment[2]. However, even after hemostasis, there is a risk for infection, such as spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP)[3], and rebleeding triggered by these infections[4,5], which are believed to contribute to increased mortality. While current Japanese guidelines do not specifically address antibiotic prophylaxis[6], western guidelines advocate prophylaxis for all patients[7-10].
The rationale for this recommendation lies in several studies conducted prior to the early 2000s that reported high mortality and an infection incidence of approximately 30% after upper gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with cirrhosis[11,12]. However, since the late 2000s, both mortality and infection incidence following upper gastrointestinal bleeding have improved, to less than 10%[13,14]. This marked improvement can be attributed to the shift in the recommended hemostatic method from endoscopic injection sclerotherapy (EIS) to endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL) and advancements in the treatment of liver cirrhosis[15]. These findings have prompted a reconsideration of the current practice of universal antibiotic prophylaxis across all clinical scenarios. Recent reports suggest that such prophylaxis may not always be necessary in modern medical settings[16-19]. Yet, these assertions are primarily from single-center observational studies; no multi-center study has been conducted. Furthermore, the inappropriate use of antibiotics, which has been identified as a cause of the emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria, is a global issue[20].
Therefore, we aim to reassess the effectiveness of antibiotic prophylaxis in patients with esophageal variceal bleeding treated with EVL using data from several centers in Japan over a 13-year period. It is crucial to conduct research in regions such as Japan, where the guidelines do not recommend antibiotic prophylaxis after hemostasis.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Data source
We conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the Tokushukai medical database[21]. The Tokushukai group is a large hospital group in Japan that manages more than 70 hospitals nationwide. 50 hospitals are part of the Diagnosis Procedure Combination (DPC) system. The DPC system is a comprehensive payment system used in Japan that is specifically designed for acute care[22,23]. The Tokushukai Medical Database primarily comprises administrative claims data (specifically, DPC inpatient data) and electronic health records, including inpatient and outpatient blood test results.
The DPC inpatient data includes patient age; sex; admission and discharge dates; discharge status; main diagnosis; comorbidities at admission; post-admission complications recorded by the attending physician using the 2003 version of the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision (ICD-10) codes; types of surgery (coded with original codes and text data in Japanese); and daily records of drugs and procedures. A distinguishing feature of this database is its capacity to access individual patient medical records. If necessary, additional details can be retrieved directly from these records.
Patient selection
This study included adult patients (aged ≥ 18 years) with esophageal variceal bleeding (ICD-10 code, I850) who underwent emergency EVL on the day of admission between January 2010 and December 2022. We excluded patients with the following criteria: (1) Death occurring on the day of admission or the following day; (2) discharge on the day of admission or the following day; (3) use of a mechanical ventilator on the day of admission or the following day; (4) use of continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) on the day of admission or the following day; (5) interventional radiology (IVR) or a surgical procedure on the day of admission or the following day; and (6) the presence of symptoms of infection, defined as having a fever of ≥ 38 ℃ or obtaining a blood culture, on the day of admission or the following day.
Exposure
The patients were divided into prophylaxis and non-prophylaxis groups. The prophylaxis group included patients who received antibiotics on the day of admission or the following day. The non-prophylaxis group included patients who did not receive antibiotics on the day of admission or the following day. The types of antibiotics considered in this study are detailed in Table 1, and the duration of administration was assumed to be at least one day.
Table 1.
List of antibiotics included in the study
|
ATC code
|
Type of antibiotics
|
| J01AA | Tetracyclines |
| J01BA | Amphenicols |
| J01BB | Macrolides, lincosamides and streptogramins |
| J01CA | Penicillins with extended spectrum |
| J01CE | Beta-lactamase sensitive penicillins |
| J01CF | Beta-lactamase resistant penicillins |
| J01CR | Combinations of penicillins, including beta-lactamase inhibitors |
| J01DB | First-generation cephalosporins |
| J01DC | Second-generation cephalosporins |
| J01DD | Third-generation cephalosporins |
| J01DE | Fourth-generation cephalosporins |
| J01DF | Monobactams |
| J01DH | Carbapenems |
| J01EA | Trimethoprim and derivatives |
| J01EB | Short-acting sulfonamides |
| J01EC | Intermediate-acting sulfonamides |
| J01ED | Long-acting sulfonamides |
| J01EE | Combinations of sulfonamides |
| J01FA | Macrolides |
| J01FF | Lincosamides |
| J01FG | Streptogramins |
| J01GA | Aminoglycoside antibacterials |
| J01GB | Other aminoglycosides |
| J01MA | Fluoroquinolones |
| J01MB | Other quinolone antibacterials |
| J01XA | Glycopeptide antibacterials |
| J01XB | Polymyxins |
| J01XC | Steroid antibacterials |
| J01XD | Imidazole derivatives |
| J01XE | Nitrofuran derivatives |
| J01XX | Other antibacterials |
ATC: Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical.
Variables and outcomes
The variables included age, sex, the Barthel Index[24], the Child-Pugh Score and classification[25,26], the Charlson Comorbidity Index[27], maintenance hemodialysis, hepatic cancer, malignancy history, alcohol-related disease, and past varix rupture history. We also collected data regarding the use of antiplatelets, anticoagulants, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, and acid blockers prescribed on the day of admission or the following day or as part of the regular medications of the patient. The antiplatelet drugs used included aspirin, ticlopidine, clopidogrel, prasugrel, and ticagrelor. The anticoagulants prescribed included warfarin, dabigatran, edoxaban, rivaroxaban, apixaban, and heparin. Laboratory data collected on the day of admission included total bilirubin (mg/dL), aspartate aminotransferase (U/L), alanine aminotransferase (U/L), albumin (g/dL), white blood cells (/μL), hemoglobin (g/dL), platelets (103/μL), C-reactive protein (mg/dL), prothrombin time percentage (PT, %), activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT, sec), and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2). Additionally, the shock index[28,29] was evaluated based on the vital signs at the hospital visit. The use of vasopressors and red blood cell transfusion volume on the day of admission were also obtained. Age was classified into four categories: < 65, 65-4, 75-84, and ≥ 85 years. The Barthel Index was categorized into three groups: 0 (worst disability), 1-99, and 100 (full ability). Albumin and PT% were categorized according to the Child-Pugh score, while APTT was categorized into < 40, 40-60, and ≥ 60 sec groups. All variables, excluding the Child-Pugh classification, were used as confounders in the analysis.
The primary outcome was a composite of 6-wk mortality, 4-wk rebleeding, and 4-wk onset of SBP. We defined rebleeding as cases when patients underwent endoscopic hemostasis procedures, such as EVL, EIS, or endoscopic clip hemostasis, two or more days after admission. To ensure outcome accuracy, all hemostatic procedures were verified by an endoscopy specialist using electronic medical records. Hemostatic procedures not associated with active bleeding but instead performed for future bleeding prevention, such as EVL or EIS on other varices and argon plasma coagulation, were excluded. SBP was defined as a polymorphonuclear cell count of 250/μL or greater[7,30], resulting from an ascites puncture performed during hospitalization. The secondary outcomes were the individual assessments of 6-wk mortality, 4-wk rebleeding, and 4-wk onset of SBP each assessed individually and in-hospital mortality. Also included were the 4-wk onset of clostridium difficile infection (CDI) and the length of hospital stay. CDI was defined as a diagnosis of ICD-10 code A047 on the second day of hospitalization or later and patients who were administered metronidazole or oral vancomycin.
Statistical methods
Continuous variables are reported as median and interquartile range (IQR), and categorical variables are reported as numbers and percentage. We determined the average treatment effect on the treated-based inverse probability of treatment weighting (IPTW) for the prophylaxis and non-prophylaxis groups. This method minimizes the effects of selection bias and imbalances in patient backgrounds between groups[31,32]. We estimated the propensity scores using logistic regression with prophylaxis as the dependent variable and all covariates as independent variables. Balances in baseline variables were also examined using standardized MD (SMD), and absolute values < 10% were considered balanced[33]. We used logistic regression to evaluate odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) to assess the outcomes for categorical variables. The length of hospital stay was evaluated using negative binomial regression with rate ratios and 95%CI. The two-sided significance level for all tests was set at P < 0.05.
For the subgroup analysis, we evaluated the interaction effect between antibiotic prophylaxis and the Child-Pugh classification on the primary composite outcome. We employed logistic regression with IPTW, consistent with our primary analysis approach, using a dataset derived from multiple imputation data.
We conducted several sensitivity analyses to determine the robustness of our inferences. First, we performed both propensity score matching (PSM) to evaluate the robustness of the results. For PSM, we used the same propensity scores estimated for IPTW. A one-to-one PSM was conducted utilizing the nearest neighbor method without replacement. The caliper width was set at 20% of the standard deviation of the propensity scores on the logit scale. Second, considering the absence of a clear consensus on the duration of antibiotic prophylaxis, we narrowed the exposure period to those who received antibiotics for 2 d, 3 d, and 4 or more days. For these analyses, the exposure timing, definition of the control group, and analysis methods were identical to those used in the main analysis. Third, there is no consensus regarding the appropriate type of antibiotic for prophylaxis. Therefore, to investigate the potential differences in outcomes due to the type of antibiotic used, we conducted a similar analysis with only third-generation cephalosporins that have a relatively large amount of evidence as the exposure[8].
In this study, we handled missing data by making a missing at-random assumption and conducting multiple imputations. These multiple imputations were conducted using chained equations with 100 imputed datasets and 200 iterations (maxit = 200) for each dataset. The imputation models included all the variables of interest and relevant auxiliary variables. Pooled estimates were obtained by combining the results across the imputed datasets, according to Rubin’s rules[33,34].
All analyses were performed using R software (version 4.2.3; R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria).
Sample size calculation
Based on previous reports, we assumed the incidence of the composite outcome to be 15%[11], and the antibiotic administration rate to be > 30%[16], expecting an unexposed to exposure ratio of approximately 2:1. We set a clinically meaningful risk ratio of 0.5 that was clinically meaningful for the composite outcomes associated with antibiotic prophylaxis[11,35]. With an α error of 0.05 and a power of 80%, using Kelsey’s equation, the required sample size was calculated to be 687 cases. Our sample size became larger than the predefined sample size, as described in the Results section.
Ethics
This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. It was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Future Medical Research Centre Ethical Committee (Approval Number: No. TGE02100-02). Due to the observational nature of the study, where patient data were accessed from hospital medical records without taking biological samples from patients, informed patient consent was deemed not necessary. Instead, an opt-out method was used and provided on the website of each hospital. This study is based on the Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology guidelines.
RESULTS
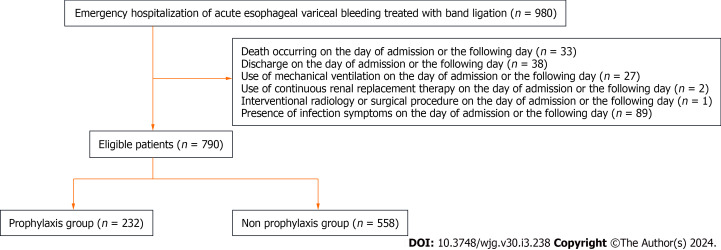
A total of 980 patients from 46 hospitals who met the inclusion criteria were considered for inclusion in this study (Table 2). After applying the exclusion criteria, 790 patients were included in the analyses (Figure 1). The patients were divided into the prophylaxis (n = 232) and non-prophylaxis (n = 558) groups. Antibiotic prophylaxis was administered in 29.4% of patients. Most patients were male, under 65 years of age, and had a moderate level of functional independence (Table 3). The prevalence of alcohol-related diseases, varix rupture history, and β-blocker usage were higher in the prophylaxis group. Other variables, including the Child-Pugh score and the Charlson Comorbidity Index, were similar between the groups. The antibiotics used in the prophylaxis group included four carbapenems, 32 first-generation cephalosporins, 51 s-generation cephalosporins, 106 third-generation cephalosporins, 14 beta-lactamase inhibitor combinations, 22 macrolides, and three lincosamides (Table 4). The mean duration of administration was 4.59 d.
Table 2.
Distribution of facilities and cases across regions in Japan
|
Region
|
Number of facilities
|
Number of cases
|
| Hokkaido | 3 | 34 |
| Tohoku | 2 | 5 |
| Kanto | 14 | 319 |
| Chubu | 5 | 32 |
| Kansai | 11 | 359 |
| Chugoku/Shikoku | 1 | 2 |
| Kyushu/Okinawa | 10 | 229 |
Figure 1.
Patient flow.
Table 3.
Patient characteristics, missing data, and comparison of standardized mean differences, n (%)
|
Before Imputation and IPTW
|
After imputation and IPTW
|
||||
|
|
Prophylactic groups
|
Non-prophylactic groups
|
Missing (%)
|
SMD
|
SMD
|
| Variables | n = 232 | n = 558 | |||
| Age, yr | 0 | 0.18 | 0.01 | ||
| < 65 | 143 (61.6) | 322 (57.7) | |||
| 65-74 | 46 (19.8) | 144 (25.8) | |||
| 75-84 | 39 (16.8) | 75 (13.4) | |||
| ≥ 85 | 4 (1.7) | 17 (3.0) | |||
| Sex, male (%) | 181 (78.0) | 417 (74.7) | 0 | 0.08 | < 0.01 |
| Barthel index (%) | 17.3 | 0.10 | < 0.01 | ||
| 100 (full activity) | 83 (40.5) | 186 (41.5) | |||
| 1-99 | 63 (30.7) | 152 (33.9) | |||
| 0 (worst disability) | 59(28.8) | 110 (24.6) | |||
| Child-Pugh score, median (IQR) | 8 (7-10) | 8 (7-10) | 12.9 | 0.05 | 0.03 |
| Child-Pugh classification (%) | 10.1 | 0.06 | 0.02 | ||
| A | 42 (19.4) | 93 (18.8) | |||
| B | 110 (50.9) | 266 (53.7) | |||
| C | 64 (29.6) | 136 (27.5) | |||
| Presence of ascites | 67 (31.0) | 171 (34.5) | |||
| Comorbidities | |||||
| Charlson Comorbidity Index, median (IQR) | 4 (4-5) | 4 (4-5) | 0 | < 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Maintenance hemodialysis | 3 (1.3) | 8 (1.4) | 0 | 0.01 | < 0.01 |
| Hepatic cancer | 38 (16.4) | 112 (20.1) | 0 | 0.10 | < 0.01 |
| Malignant tumor history | 29 (12.5) | 65 (11.6) | 0 | 0.03 | < 0.01 |
| Alcohol-related disease | 127 (54.7) | 246 (44.1) | 0 | 0.21 | < 0.01 |
| Past varix rupture history | 63 (27.2) | 127 (22.8) | 0 | 0.10 | < 0.01 |
| Medications | |||||
| Antiplatelet use | 3 (1.3) | 8 (1.4) | 0 | 0.01 | < 0.01 |
| Anticoagulant use | 5 (2.2) | 8 (1.4) | 0 | 0.05 | < 0.01 |
| NSAIDs use | 5 (2.2) | 13 (2.3) | 0 | 0.01 | < 0.01 |
| Corticosteroid use | 0 (0) | 2 (0.4) | 0 | 0.09 | < 0.01 |
| Acid blocker use | 214 (91.8) | 486 (87.1) | 0 | 0.15 | < 0.01 |
| β blocker use | 26 (11.2) | 26 (4.7) | 0 | 0.24 | < 0.01 |
| Laboratory data | |||||
| Total bilirubin, mg/dL, median (IQR) | 1.6 (1-2.9) | 1.4 (0.9-2.4) | 3.2 | 0.13 | 0.02 |
| Aspartate aminotransferase, U/L, median (IQR) | 54.5 (32.2-94.8) | 47 (31-83) | 2.2 | 0.09 | 0.01 |
| Alanine aminotransferase, U/L, median (IQR) | 30.5 (20-47) | 27 (19-42) | 2.2 | 0.08 | < 0.01 |
| Albumin | 4.6 | 0.11 | 0.02 | ||
| > 3.5 g/dL | 37 (16.5) | 72 (13.6) | |||
| 2.8–3.5 g/dL | 97 (43.3) | 256 (48.3) | |||
| < 2.8 g/dL | 90 (40) | 202 (38.1) | |||
| White blood cell, /μL, median (IQR) | 7720 (5900-10700) | 7300 (5200-10400) | 1.8 | 0.15 | 0.01 |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL, median (IQR) | 9 (7.3-10.5) | 8.5 (6.9-10.2) | 1.8 | 0.12 | < 0.01 |
| Platelet, 103/μL, median (IQR) | 99 (72-139) | 103 (75-144) | 1.8 | < 0.01 | 0.02 |
| C-reactive protein, mg/dL, median (IQR) | 0.3 (0.1-0.7) | 0.3 (0.1-0.8) | 4.7 | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| Prothrombin time | 5.9 | 0.02 | < 0.01 | ||
| > 70% | 48 (21.5) | 113 (21.7) | |||
| 40%-70% | 138 (61.9) | 324 (62.3) | |||
| < 40% | 37 (16.6) | 83 (16.0) | |||
| Activated partial thromboplastin time | 11.4 | 0.08 | 0.01 | ||
| ≤ 40 s | 185 (87.3) | 436 (89.3) | |||
| 40-60 s | 23 (10.8) | 47 (9.6) | |||
| > 60 s | 4 (1.9) | 5 (1.0) | |||
| eGFR < 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 | 19 (8.3) | 40 (7.3) | 1.9 | 0.03 | < 0.01 |
| Shock index > 1 | 94 (41.4) | 197 (36.5) | 3 | 0.10 | < 0.01 |
| Vasopressor use | 7 (3.0) | 19 (3.4) | 0 | 0.02 | < 0.01 |
| RBC transfusion, Unit, median (IQR) | 4 (0-4) | 2.5 (0-4) | 0 | 0.09 | < 0.01 |
IPTW: Inverse probability of treatment weighting; SMD: Standardized mean difference; IQR: Interquartile range; eGFR: Glomerular filtration rate; RBC: Red blood cell.
Table 4.
Antibiotic use in prophylaxis group
|
Antibiotic class
|
Number of patients
|
| Carbapenems | 4 |
| First-Generation Cephalosporins | 32 |
| Second-Generation Cephalosporins | 51 |
| Third-Generation Cephalosporins | 106 |
| Beta-Lactamase Inhibitor Combinations | 14 |
| Macrolides | 22 |
| Lincosamides | 3 |
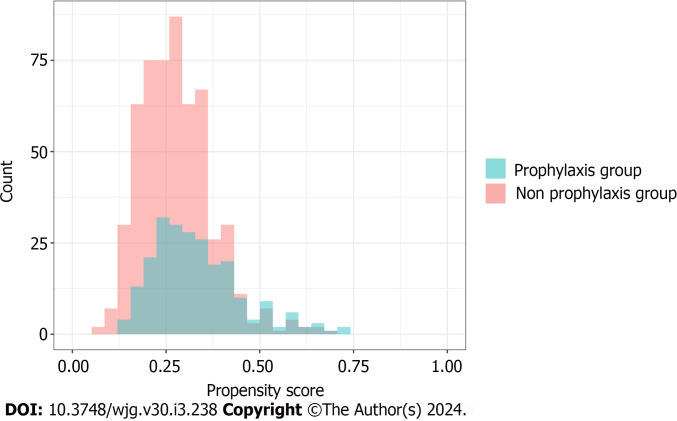
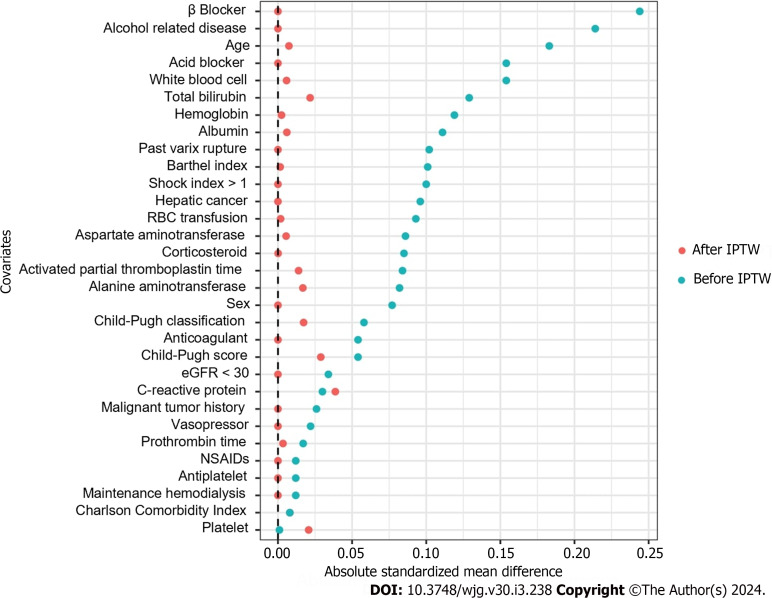
We ensured that the baseline conditions for the analysis were appropriately met. Figure 2 illustrates the overlap of the propensity scores for each group within one of the imputed datasets. The average C-statistic across the imputed datasets was 0.64. A comparison of patient characteristics before and after IPTW, as indicated by SMD, is outlined in Table 3 and Figure 3. Upon the application of IPTW, a balanced equivalence in the baseline characteristics was achieved between the groups.
Figure 2.
Overlap of the propensity score of each group.
Figure 3.
Comparison of standardized mean difference before and after inverse probability of treatment weighting. IPTW: Inverse probability of treatment weighting; RBC: Red blood cell; eGFR: Glomerular filtration rate; NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Table 5 presents the outcomes before and after adjustment using IPTW. Before the application of IPTW, the composite outcome was 11.2% in the prophylaxis group and 9.5% in the non-prophylaxis group; the 6-wk mortality was 6.9% in the prophylaxis group and 6.6% in the non-prophylaxis group; the 4-wk rebleeding was 3.9% in the prophylaxis group and 2.9% in the non-prophylaxis group; the 4-wk onset of SBP was 2.2% in the prophylaxis group and 1.8% in the non-prophylaxis group; and the in-hospital mortality was 6.0% in the prophylaxis group and 6.1% in the non-prophylaxis group. There was one case of CDI in each group (0.4% in the prophylaxis group and 0.2% in the non-prophylaxis group). The median length of hospital stay was 8 d (IQR: 5-15 d) in the prophylaxis group and 9 d (IQR: 6-15 d) in the non-prophylaxis group.
Table 5.
Crude and inverse probability of treatment weighting outcomes, n (%)
|
Before imputation and IPTW
|
After imputation and IPTW
|
||||
|
Outcomes
|
Prophylaxis group (n = 232)
|
Non-prophylaxis group (n = 558)
|
Odds ratio (95%CI)
|
Odds ratio (95%CI)
|
P value
|
| Composite outcome | 26 (11.2) | 53 (9.5) | 1.20 (0.72-1.96) | 1.11 (0.61-1.99) | 0.74 |
| 6-wk mortality | 16 (6.9) | 37 (6.6) | 1.04 (0.55-1.88) | 0.97 (0.47-1.98) | 0.93 |
| 4-wk rebleeding | 9 (3.9) | 16 (2.9) | 1.37 (0.57-3.08) | 1.21 (0.45-3.24) | 0.71 |
| 4-wk onset of SBP | 5 (2.2) | 10 (1.8) | 1.21 (0.37-3.44) | 1.20 (0.32-4.46) | 0.78 |
| In-hospital mortality | 14 (6.0) | 34 (6.1) | 0.99 (0.50-1.84) | 0.89 (0.42-1.87) | 0.75 |
| Rate ratio (95%CI) | Rate ratio (95%CI) | ||||
| Length of hospital, median (IQR) | 8 (5-15) | 9 (6-15) | 1.01 (0.90-1.14) | 1.06 (0.94-1.19) | 0.34 |
IPTW: Inverse probability of treatment weighting; CI: Confidence interval; IQR: Interquartile range.
Upon adjustment with IPTW, no significant differences regarding the composite outcome (adjusted OR, 1.11; 95%CI, 0.61-1.99; P = 0.74), 6-wk mortality (adjusted OR, 0.97; 95%CI, 0.47-1.98; P = 0.93), 4-wk rebleeding(adjusted OR, 1.21; 95%CI, 0.45-3.24; P = 0.71), 4-wk onset of SBP (adjusted OR, 1.20; 95%CI, 0.32-4.46; P = 0.78), or in-hospital mortality (adjusted OR, 0.89; 95%CI, 0.42-1.87; P = 0.75) were observed between the groups. The length of hospital stay did not significantly differ between the groups (adjusted rate ratio, 1.06; 95%CI, 0.94-1.19; P = 0.34).
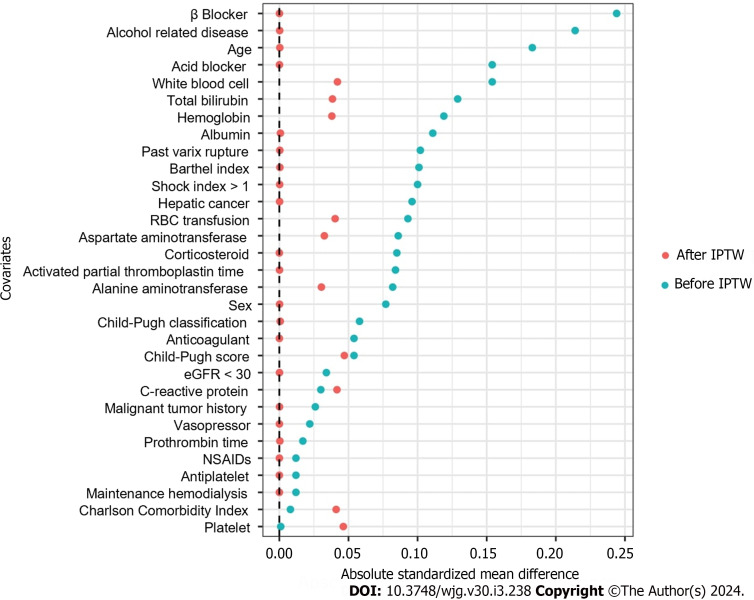
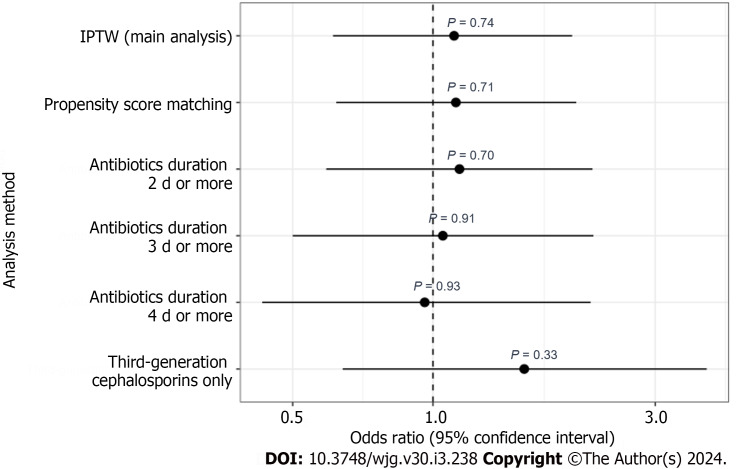
In the subgroup analysis, there was no significant interaction between antibiotic prophylaxis and the Child-Pugh classification in relation to the composite outcome (P for interaction = 0.32) (Table 6). The sensitivity analyses of the PSM results and antibiotic duration were consistent with the main analysis (Table 7, Figures 4 and 5).
Table 6.
Outcomes of subgroup analysis
| Child-Pugh classification | Odds ratio (95%CI) | P value | P for interaction |
| A | 0.87 (0.22–3.34) | 0.84 | 0.32 |
| B | 0.79 (0.46–1.38) | 0.41 | |
| C | 1.91 (1.20–3.02) | 0.01 |
Table 7.
Outcomes of sensitivity analysis
|
Analysis method
|
Odds ratio (95%CI)
|
P value
|
| IPTW | 1.11 (0.61-1.99) | 0.74 |
| Propensity score matching | 1.12 (0.62-2.03) | 0.71 |
| Duration of antibiotics | ||
| 2 d or more | 1.14 (0.59-2.20) | 0.70 |
| 3 d or more | 1.05 (0.50-2.21) | 0.91 |
| 4 d or more | 0.96 (0.43-2.18) | 0.93 |
| Third-generation cephalosporins only | 1.57 (0.64-3.87) | 0.33 |
CI: Confidence interval; IPTW: Inverse probability of treatment weighting.
Figure 4.
Comparison of standardized mean difference before and after propensity score matching. RBC: Red blood cell; eGFR: Glomerular filtration rate; NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; PTW: Inverse probability of treatment weighting.
Figure 5.
Forest plot of sensitivity analysis. IPTW: Inverse probability of treatment weighting.
DISCUSSION
This long-term observational study involving data from 46 acute care hospitals across Japan explored the effectiveness of antibiotic prophylaxis for esophageal variceal bleeding treated with EVL. No benefits of antibiotic prophylaxis in terms of composite outcomes, individual outcomes, or length of hospital stay were identified. The effectiveness of prophylactic antibiotics in terms of composite outcomes were not significantly affected by the Child-Pugh classification.
Our findings underscore the diminishing role of universal prophylactic antibiotic administration in modern medical settings, aligning more closely with post-2010 results rather than older data. In previous randomized controlled trials (RCTs) regarding variceal bleeding that were conducted until the early 2000s, early mortality ranged from 4.2%-24%, rebleeding from 12.5%-20.8%, and the incidence of infections from 15-27.5%[35-39]. In contrast, only one RCT reported after 2010 reported early mortality and rebleeding rates of 3% and 8.5%, though the infection incidence was not assessed[13]. In this study, the 6-wk mortality was 6.7%, 4-wk rebleeding was 3.2%, and 4-wk onset of SBP was 1.9%, highlighting the improving treatment outcomes. Although a 2022 systematic review advocated for the benefits of antibiotic prophylaxis[15], it included one RCT published after 2010. The majority of studies reported after 2010 are single-center observational studies, indicating a lack of strong evidence supporting the routine use of antibiotics prophylaxis in contemporary settings.
The outcomes of our study can be understood through several underlying factors. The predominant role of EVL in hemostasis may have played a significant role in our findings. EVL results in fewer complications compared to EIS and offers superior control over bleeding[7-10,40]. While several previous RCTs incorporated EIS into their hemostatic protocols[35-39], both the current investigation and the most recent RCT focused exclusively on EVL[13]. This shift in technique may have contributed to a reduced incidence of complications, such as infections, suggesting that the need for antibiotic prophylaxis may be less pronounced when EVL is conducted. Additionally, the exclusion criteria of this study provides context. Severe patients, including those requiring mechanical ventilation, CRRT, IVR, or surgery, may have an inherent increased need for antibiotics. By design, our study did not include these patients. When patients that have effectively undergone hemostasis using EVL are included and critically ill patients are excluded, prophylactic antibiotics may not be as crucial as previously reported.
In recent years, a study evaluating the effectiveness of antibiotic prophylaxis for patients with cirrhosis presenting with upper gastrointestinal bleeding was conducted in Japan using a large-scale database[41]. In this study, the rate of antibiotic prophylaxis was 11.5%. Although the target was upper gastrointestinal bleeding and not esophageal variceal bleeding, it is evident that prophylactic antibiotics are not typically administered to patients with cirrhosis in Japan. Similar to our findings, their study did not demonstrate the utility of prophylactic antibiotic administration[41]. It may be necessary to reconsider the use of antibiotic prophylaxis for patients with cirrhosis in current medical settings.
Our study’s findings, revealing no significant benefit of antibiotic prophylaxis in patients undergoing EVL for esophageal variceal bleeding, add to the critical discourse on the necessity of routine prophylactic antibiotics in an era marked by escalating antibiotic resistance. The burgeoning concern for multidrug-resistant organisms (MDROs), highlighted in recent studies, is a pressing global health issue[42-44]. While our study did not directly address the intricate challenge of MDROs' emergence, the results imply that indiscriminate antibiotic use might not offer additional advantages and may, in fact, exacerbate the threat of antibiotic resistance. Consequently, our findings support a prudent reevaluation of antibiotic prophylaxis practices, especially in clinical environments where MDRO prevalence is high, and the risk of fostering resistance is a significant worry.
Patient groups for whom prophylactic antibiotic administration is beneficial must be identified. In our study, we demonstrated only the average effect across the population, showing that antibiotic prophylaxis is not effective. Previous reports have indicated differences in effectiveness based on the severity of the Child-Pugh classification. Although we conducted a subgroup analysis evaluating the interaction effect between antibiotic prophylaxis and the Child-Pugh classification on the primary composite outcome, we did not observe any significant results. Machine learning models are currently being used to identify heterogenous effects of antibiotic prophylaxis[45-47]. Using such methods, patients who would benefit from antibiotic prophylaxis must be identified.
Our study has several strengths. First, focusing on esophageal varix bleeding, this study was conducted on an unprecedented scale and comprised a wide sample of patients from multiple hospitals throughout various regions in Japan, bolstering the generalizability of our results. Second, the Tokushukai medical database offered us unique access to detailed blood test data, vital signs, and the ability to review electronic medical records in-depth. This enabled us to conduct a study with heightened precision.
Limitations
However, this study is not without limitations. First, due to the observational nature of this study, potential unmeasured confounding factors may be present. Second, the study is based on data from Japanese individuals, which limits the ability to generalize these findings to other populations or races. Third, the study encompasses only hemostasis information resulting from EVL. Patients who received treatment solely through EIS, balloon tamponade, or pharmacological interventions, such as somatostatin and vasopressors, were excluded. Fourth, treatment approaches differ notably between Japan and other countries. In Japan, a transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt is not covered by insurance; therefore, no patients in our study received this treatment.
CONCLUSION
Our extensive multicenter observational study did not find a significant benefit to antibiotic prophylaxis for esophageal variceal bleeding treated with EVL. These results suggest that the recommendation for routine prophylactic antibiotic administration may not be universally essential. With growing concerns regarding the misuse of antibiotics and the consequential emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria combined with advances in the management of esophageal variceal bleeding and liver cirrhosis treatment, there is a compelling need for a global reassessment of the necessity of routine antibiotic prophylaxis.
ARTICLE HIGHLIGHTS
Research background
Esophageal variceal bleeding is a critical complication of liver cirrhosis, typically managed with endoscopic variceal ligation (EVL). While current Western guidelines advocate antibiotic prophylaxis post-EVL, the evolving landscape of cirrhosis management and the rise of multidrug-resistant bacteria necessitate a reevaluation of this practice.
Research motivation
This study was motivated by the need to reassess the effectiveness of routine antibiotic prophylaxis following EVL in the context of improved cirrhosis treatments and increasing concerns regarding antibiotic resistance. Understanding the real-world impact of prophylaxis on patient outcomes may result in a more effective and judicious use of antibiotics.
Research objectives
The primary objective was to evaluate the effectiveness of antibiotic prophylaxis in patients undergoing EVL for esophageal variceal bleeding using data from multiple Japanese medical centers. The study aimed to provide evidence that could influence future guideline recommendations and clinical practice.
Research methods
A 13-year observational study was conducted, using the Tokushukai medical database that includes data from 46 hospitals. Patients were categorized into prophylaxis and non-prophylaxis groups, with outcomes measured in terms of mortality, rebleeding, and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Logistic regression, inverse probability of treatment weighting, subgroup, and sensitivity analyses were conducted.
Research results
The study included 790 patients, and the primary outcomes were not significantly different between the prophylaxis and non-prophylaxis groups. These findings persisted across various subgroups and sensitivity analyses, suggesting that routine antibiotic prophylaxis post-EVL may not be beneficial.
Research conclusions
These findings challenge the current standard of prescribing antibiotics following EVL for esophageal variceal bleeding. They highlight the need for a global reassessment of this practice, considering the minimal impact on patient outcomes and the broader context of antibiotic resistance.
Research perspectives
Future research should focus on personalized approaches to antibiotic use in cirrhosis-related procedures, considering patient-specific factors and broader public health concerns. Further studies should also explore alternative strategies for managing complications in patients with liver cirrhosis.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We would like to express our gratitude to the gastroenterologists at the Tokushukai Hospitals throughout Japan who supported the treatment of esophageal variceal bleeding by providing emergency care without exception. We also express our gratitude to the staff at the Tokushukai Information Systems for their cooperation in extracting data and tracing back the electronic medical records.
Footnotes
Institutional review board statement: The study was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Future Medical Research Centre Ethical Committee (Approval No. TGE02100-02).
Informed consent statement: Owing to the observational nature of the study, where patient data were accessed from hospital medical records without taking biological samples from patients, informed patient consent was not deemed to be necessary. Instead, an opt-out method directed at patients was employed on the website of each hospital.
Conflict-of-interest statement: All other authors have nothing to disclose.
STROBE statement: The authors have read the STROBE Statement-checklist of items, and the manuscript was prepared and revised according to the STROBE Statement-checklist of items.
Provenance and peer review: Unsolicited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Peer-review started: October 4, 2023
First decision: December 6, 2023
Article in press: January 3, 2024
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: Japan
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): A
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C, C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Abraham P, India; Haj Ali S, Jordan; Sukocheva OA, Australia S-Editor: Qu XL L-Editor: A P-Editor: Cai YX
Contributor Information
Chikamasa Ichita, Gastroenterology Medicine Center, Shonan Kamakura General Hospital, Kamakura 247-8533, Kanagawa, Japan; Department of Health Data Science, Yokohama City University, Yokohama 236-0027, Kanagawa, Japan. ichikamasa@yahoo.co.jp.
Sayuri Shimizu, Department of Health Data Science, Yokohama City University, Yokohama 236-0027, Kanagawa, Japan.
Tadahiro Goto, Department of Health Data Science, Yokohama City University, Yokohama 236-0027, Kanagawa, Japan; TXP Research, TXP Medical Co., Ltd., Chiyoda-ku 101-0042, Tokyo, Japan; Department of Clinical Epidemiology and Health Economics, School of Public Health, The University of Tokyo, Bunkyo-ku 113-0033, Tokyo, Japan.
Uojima Haruki, Gastroenterology Medicine Center, Shonan Kamakura General Hospital, Kamakura 247-8533, Kanagawa, Japan; Department of Genome Medical Sciences Project, Research Institute, National Center for Global Health and Medicine, Ichikawa 272-8516, Chiba, Japan.
Naoya Itoh, Division of Infectious Diseases, Aichi Cancer Center, Nagoya 464-8681, Aichi, Japan.
Masao Iwagami, Department of Health Services Research, Institute of Medicine, University of Tsukuba, Tsukuba 305-8575, Ibaraki, Japan.
Akiko Sasaki, Gastroenterology Medicine Center, Shonan Kamakura General Hospital, Kamakura 247-8533, Kanagawa, Japan.
Data sharing statement
Due to privacy and ethical considerations, the data supporting the findings of this study is not publicly available. However, the study protocol and analysis code can be made available upon contacting the corresponding author. As for the participant data, ethical approval is required for access. The corresponding author can facilitate this process upon receipt of an appropriate request. After ethical approval, data sharing will be possible. The process of accessing the data will be carried out in accordance with ethical guidelines, ensuring respect for participant privacy and confidentiality.
References
- 1.Garcia-Tsao G, Bosch J. Management of varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:823–832. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra0901512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.de Franchis R. Updating consensus in portal hypertension: report of the Baveno III Consensus Workshop on definitions, methodology and therapeutic strategies in portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2000;33:846–852. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(00)80320-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lee YY, Tee HP, Mahadeva S. Role of prophylactic antibiotics in cirrhotic patients with variceal bleeding. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:1790–1796. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i7.1790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Wong F, Bernardi M, Balk R, Christman B, Moreau R, Garcia-Tsao G, Patch D, Soriano G, Hoefs J, Navasa M International Ascites Club. Sepsis in cirrhosis: report on the 7th meeting of the International Ascites Club. Gut. 2005;54:718–725. doi: 10.1136/gut.2004.038679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Goulis J, Patch D, Burroughs AK. Bacterial infection in the pathogenesis of variceal bleeding. Lancet. 1999;353:139–142. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(98)06020-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yoshiji H, Nagoshi S, Akahane T, Asaoka Y, Ueno Y, Ogawa K, Kawaguchi T, Kurosaki M, Sakaida I, Shimizu M, Taniai M, Terai S, Nishikawa H, Hiasa Y, Hidaka H, Miwa H, Chayama K, Enomoto N, Shimosegawa T, Takehara T, Koike K. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for Liver Cirrhosis 2020. J Gastroenterol. 2021;56:593–619. doi: 10.1007/s00535-021-01788-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.European Association for the Study of the Liver. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of patients with decompensated cirrhosis. J Hepatol. 2018;69:406–460. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tripathi D, Stanley AJ, Hayes PC, Patch D, Millson C, Mehrzad H, Austin A, Ferguson JW, Olliff SP, Hudson M, Christie JM Clinical Services and Standards Committee of the British Society of Gastroenterology. U.K. guidelines on the management of variceal haemorrhage in cirrhotic patients. Gut. 2015;64:1680–1704. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Garcia-Tsao G, Abraldes JG, Berzigotti A, Bosch J. Portal hypertensive bleeding in cirrhosis: Risk stratification, diagnosis, and management: 2016 practice guidance by the American Association for the study of liver diseases. Hepatology. 2017;65:310–335. doi: 10.1002/hep.28906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.de Franchis R, Bosch J, Garcia-Tsao G, Reiberger T, Ripoll C Baveno VII Faculty. Baveno VII - Renewing consensus in portal hypertension. J Hepatol. 2022;76:959–974. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2021.12.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chavez-Tapia NC, Barrientos-Gutierrez T, Tellez-Avila F, Soares-Weiser K, Mendez-Sanchez N, Gluud C, Uribe M. Meta-analysis: antibiotic prophylaxis for cirrhotic patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding - an updated Cochrane review. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011;34:509–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04746.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chavez-Tapia NC, Barrientos-Gutierrez T, Tellez-Avila FI, Soares-Weiser K, Uribe M. Antibiotic prophylaxis for cirrhotic patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;2010:CD002907. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002907.pub2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lee TH, Huang CT, Lin CC, Chung CS, Lin CK, Tsai KC. Similar rebleeding rate in 3-day and 7-day intravenous ceftriaxone prophylaxis for patients with acute variceal bleeding. J Formos Med Assoc. 2016;115:547–552. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2016.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Zullo A, Soncini M, Bucci C, Marmo R Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio dell'Emorragia Digestiva (GISED) (Appendix) Clinical outcomes in cirrhotics with variceal or nonvariceal gastrointestinal bleeding: A prospective, multicenter cohort study. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;36:3219–3223. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Wong YJ, Tan CK, Yii YL, Wong Y, Tam YC, Chan E, Abraldes JG. Antibiotic prophylaxis in cirrhosis patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. PH and C. 2022;1:167–177. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ueno M, Kayahara T, Sunami T, Takayama H, Takabatake H, Morimoto Y, Yamamoto H, Mizuno M. Universal antibiotic prophylaxis may no longer be necessary for patients with acute variceal bleeding: A retrospective observational study. Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e19981. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Ueno M, Mano T, Kayahara T, Mizuno M. Antibiotic prophylaxis for cirrhotic patients with upper gastrointestinal bleeding: Is evidence adequate? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;36:3249–3250. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chang TS, Tsai YH, Lin YH, Chen CH, Lu CK, Huang WS, Yang YH, Chen WM, Hsieh YY, Wu YC, Tung SY, Huang YH. Limited effects of antibiotic prophylaxis in patients with Child-Pugh class A/B cirrhosis and upper gastrointestinal bleeding. PLoS One. 2020;15:e0229101. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0229101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Tandon P, Abraldes JG, Keough A, Bastiampillai R, Jayakumar S, Carbonneau M, Wong E, Kao D, Bain VG, Ma M. Risk of Bacterial Infection in Patients With Cirrhosis and Acute Variceal Hemorrhage, Based on Child-Pugh Class, and Effects of Antibiotics. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:1189–96.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2014.11.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fernández J, Piano S, Bartoletti M, Wey EQ. Management of bacterial and fungal infections in cirrhosis: The MDRO challenge. J Hepatol. 2021;75 Suppl 1:S101–S117. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2020.11.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Iwagami M, Moriya H, Doi K, Yasunaga H, Isshiki R, Sato I, Mochida Y, Ishioka K, Ohtake T, Hidaka S, Noiri E, Kobayashi S. Seasonality of acute kidney injury incidence and mortality among hospitalized patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2018;33:1354–1362. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfy011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hayashida K, Murakami G, Matsuda S, Fushimi K. History and Profile of Diagnosis Procedure Combination (DPC): Development of a Real Data Collection System for Acute Inpatient Care in Japan. J Epidemiol. 2021;31:1–11. doi: 10.2188/jea.JE20200288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wang K, Li P, Chen L, Kato K, Kobayashi M, Yamauchi K. Impact of the Japanese diagnosis procedure combination-based payment system in Japan. J Med Syst. 2010;34:95–100. doi: 10.1007/s10916-008-9220-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shah S, Vanclay F, Cooper B. Improving the sensitivity of the Barthel Index for stroke rehabilitation. J Clin Epidemiol. 1989;42:703–709. doi: 10.1016/0895-4356(89)90065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Child CG, Turcotte JG. Surgery and portal hypertension. Major Probl Clin Surg. 1964;1:1–85. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pugh RN, Murray-Lyon IM, Dawson JL, Pietroni MC, Williams R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973;60:646–649. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Quan H, Sundararajan V, Halfon P, Fong A, Burnand B, Luthi JC, Saunders LD, Beck CA, Feasby TE, Ghali WA. Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data. Med Care. 2005;43:1130–1139. doi: 10.1097/01.mlr.0000182534.19832.83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Allgöwer M, Burri C. ["Shock index"] Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1967;92:1947–1950. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1106070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Koch E, Lovett S, Nghiem T, Riggs RA, Rech MA. Shock index in the emergency department: utility and limitations. Open Access Emerg Med. 2019;11:179–199. doi: 10.2147/OAEM.S178358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Runyon BA AASLD Practice Guidelines Committee. Management of adult patients with ascites due to cirrhosis: an update. Hepatology. 2009;49:2087–2107. doi: 10.1002/hep.22853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Austin PC. An Introduction to Propensity Score Methods for Reducing the Effects of Confounding in Observational Studies. Multivariate Behav Res. 2011;46:399–424. doi: 10.1080/00273171.2011.568786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Robins JM, Hernán MA, Brumback B. Marginal structural models and causal inference in epidemiology. Epidemiology. 2000;11:550–560. doi: 10.1097/00001648-200009000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rubin DB. Multiple Imputation for Nonresponse in Surveys. Wiley Series in Probability and Statistics. 1987. [Google Scholar]
- 34.White IR, Royston P, Wood AM. Multiple imputation using chained equations: Issues and guidance for practice. Stat Med. 2011;30:377–399. doi: 10.1002/sim.4067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jun CH, Park CH, Lee WS, Joo YE, Kim HS, Choi SK, Rew JS, Kim SJ, Kim YD. Antibiotic prophylaxis using third generation cephalosporins can reduce the risk of early rebleeding in the first acute gastroesophageal variceal hemorrhage: a prospective randomized study. J Korean Med Sci. 2006;21:883–890. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2006.21.5.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rolando N, Gimson A, Philpott-Howard J, Sahathevan M, Casewell M, Fagan E, Westaby D, Williams R. Infectious sequelae after endoscopic sclerotherapy of oesophageal varices: role of antibiotic prophylaxis. J Hepatol. 1993;18:290–294. doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80272-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Selby WS, Norton ID, Pokorny CS, Benn RA. Bacteremia and bacterascites after endoscopic sclerotherapy for bleeding esophageal varices and prevention by intravenous cefotaxime: a randomized trial. Gastrointest Endosc. 1994;40:680–684. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Hong SN, Kim BJ, Lee SY, Lee CY, Ryu MK, Choi MS, Lee JH, Rhee PL, Koh KC, Kim JJ, Paik SW, Rhee JC, Choi KW. [Prospective randomized trial of intravenous ciprofloxacin for prevention of bacterial infection in cirrhotic patients with esophageal variceal bleeding] Taehan Kan Hakhoe Chi. 2002;8:288–296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Hou MC, Lin HC, Liu TT, Kuo BI, Lee FY, Chang FY, Lee SD. Antibiotic prophylaxis after endoscopic therapy prevents rebleeding in acute variceal hemorrhage: a randomized trial. Hepatology. 2004;39:746–753. doi: 10.1002/hep.20126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Lo GH, Lai KH, Cheng JS, Chen MH, Chiang HT. A prospective, randomized trial of butyl cyanoacrylate injection versus band ligation in the management of bleeding gastric varices. Hepatology. 2001;33:1060–1064. doi: 10.1053/jhep.2001.24116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ueno M, Fujiwara T, Tokumasu H, Mano T, Kayahara T, Takabatake H, Morimoto Y, Matsueda K, Fukuoka T, Mizuno M. Real-world efficacy of antibiotic prophylaxis for upper gastrointestinal bleeding in cirrhotic patients in Japan. J Gastroenterol. 2023;58:766–777. doi: 10.1007/s00535-023-02000-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Caron WP, Mousa SA. Prevention strategies for antimicrobial resistance: a systematic review of the literature. Infect Drug Resist. 2010;3:25–33. doi: 10.2147/idr.s10018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Morris S, Cerceo E. Trends, Epidemiology, and Management of Multi-Drug Resistant Gram-Negative Bacterial Infections in the Hospitalized Setting. Antibiotics (Basel) 2020;9 doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9040196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mücke VT, Peiffer KH, Kessel J, Schwarzkopf KM, Bojunga J, Zeuzem S, Finkelmeier F, Mücke MM. Impact of colonization with multidrug-resistant organisms on antibiotic prophylaxis in patients with cirrhosis and variceal bleeding. PLoS One. 2022;17:e0268638. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0268638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Inoue K, Seeman TE, Horwich T, Budoff MJ, Watson KE. Heterogeneity in the Association Between the Presence of Coronary Artery Calcium and Cardiovascular Events: A Machine-Learning Approach in the MESA Study. Circulation. 2023;147:132–141. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.122.062626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Inoue K, Athey S, Tsugawa Y. Machine-learning-based high-benefit approach versus conventional high-risk approach in blood pressure management. Int J Epidemiol. 2023;52:1243–1256. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyad037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Shiba K, Daoud A, Hikichi H, Yazawa A, Aida J, Kondo K, Kawachi I. Uncovering Heterogeneous Associations Between Disaster-Related Trauma and Subsequent Functional Limitations: A Machine-Learning Approach. Am J Epidemiol. 2023;192:217–229. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwac187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Due to privacy and ethical considerations, the data supporting the findings of this study is not publicly available. However, the study protocol and analysis code can be made available upon contacting the corresponding author. As for the participant data, ethical approval is required for access. The corresponding author can facilitate this process upon receipt of an appropriate request. After ethical approval, data sharing will be possible. The process of accessing the data will be carried out in accordance with ethical guidelines, ensuring respect for participant privacy and confidentiality.