Figure 2. HIF1A stabilization restores NOS1 and reverses diabetic gastroparesis.
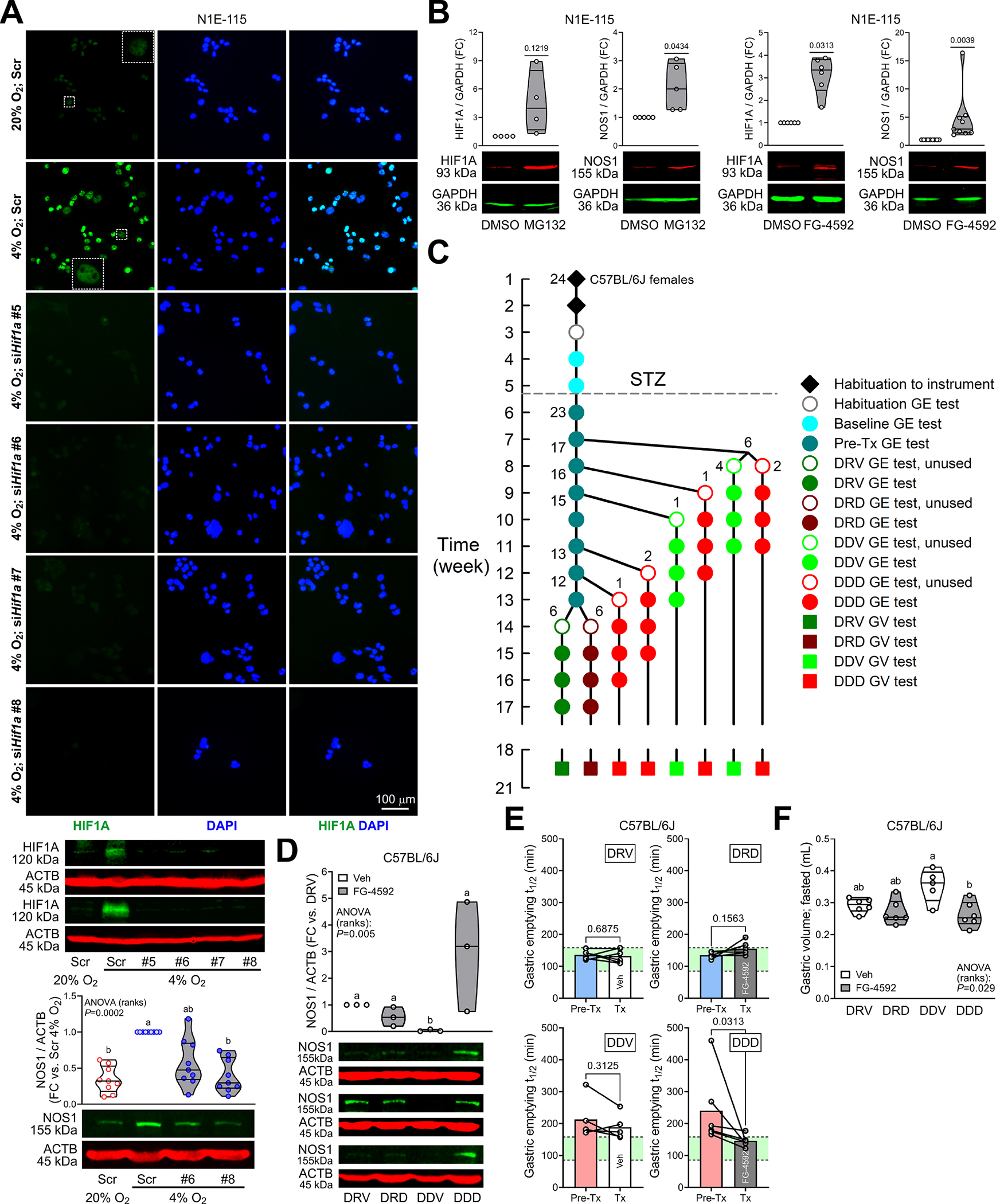
(A) Top and middle: Validation of Hif1a knockdown in N1E-115 cells by HIF1A immunofluorescence and immunoblotting (HIF1A antibody: Cell Signaling Technology #36169). Top: Wide-field images from 2 experiments. Scr, scrambled. Insets are enlargements of the outlined areas. Bottom: Effects of Hif1a knockdown on 4% O2-induced upregulation of NOS1 protein (n=9). P, Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA on ranks. Groups not sharing the same superscript are different by Dunn’s test. (B) Upregulation of HIF1A (Novus Biologicals NB100–134) and NOS1 protein by HIF1A stabilization with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 (10μM, 4h) or the PHD inhibitor FG-4592 (20μM, 2 days) (HIF1A: nMG132/Veh=4, nFG-4592/Veh=6; NOS1: nMG132/Veh=5; nFG-4592/Veh=9). P, one sample t or Wilcoxon signed rank tests. NOS1 was upregulated even relative to the HIF1A target GAPDH. (C) Design of longitudinal GE study. One mouse did not develop diabetes. DRV, diabetic, resistant to GP, Veh-treated (n=6); DRD, diabetic, resistant to GP, FG-4592-treated (n=6); DDV, diabetic, delayed GE, Veh-treated (n=5); DDD, diabetic, delayed GE, FG-4592-treated (n=6). (D) Upregulation of NOS1 in GP mouse gastric corpus+antrum tunica muscularis by FG-4592 (n=3). P, Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA on ranks. Groups not sharing the same superscript are different by Tukey’s test. (E) Significant reduction of GE t1/2 from pretreatment values in GP mice treated with FG-4592 (DDD) but not in Veh-treated animals (DDV). GE t1/2 did not change significantly in the non-GP mice (DRV, DRD). Green area: strain- and sex-specific normal range. P, Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank tests. (F) Normalization of fasting GVs by FG-4592. P, Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA on ranks. Groups not sharing the same superscript are different by Dunn’s test.
